- Esenciales
- Empezando
- Datadog
- Sitio web de Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless para Lambda AWS
- Agent
- Integraciones
- Contenedores
- Dashboards
- Monitores
- Logs
- Rastreo de APM
- Generador de perfiles
- Etiquetas (tags)
- API
- Catálogo de servicios
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Monitorización Synthetic
- Gestión de incidencias
- Monitorización de bases de datos
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Análisis de código
- Centro de aprendizaje
- Compatibilidad
- Glosario
- Atributos estándar
- Guías
- Agent
- Uso básico del Agent
- Arquitectura
- IoT
- Plataformas compatibles
- Recopilación de logs
- Configuración
- Configuración remota
- Automatización de flotas
- Actualizar el Agent
- Solucionar problemas
- Detección de nombres de host en contenedores
- Modo de depuración
- Flare del Agent
- Estado del check del Agent
- Problemas de NTP
- Problemas de permisos
- Problemas de integraciones
- Problemas del sitio
- Problemas de Autodiscovery
- Problemas de contenedores de Windows
- Configuración del tiempo de ejecución del Agent
- Consumo elevado de memoria o CPU
- Guías
- Seguridad de datos
- Integraciones
- OpenTelemetry
- Desarrolladores
- Autorización
- DogStatsD
- Checks personalizados
- Integraciones
- Crear una integración basada en el Agent
- Crear una integración API
- Crear un pipeline de logs
- Referencia de activos de integración
- Crear una oferta de mercado
- Crear un cuadro
- Crear un dashboard de integración
- Crear un monitor recomendado
- Crear una regla de detección Cloud SIEM
- OAuth para integraciones
- Instalar la herramienta de desarrollo de integraciones del Agente
- Checks de servicio
- Complementos de IDE
- Comunidad
- Guías
- API
- Aplicación móvil de Datadog
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- En la aplicación
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- Editor DDSQL
- Hojas
- Monitores y alertas
- Infraestructura
- Métricas
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Catálogo de servicios
- Catálogo de APIs
- Error Tracking
- Gestión de servicios
- Objetivos de nivel de servicio (SLOs)
- Gestión de incidentes
- De guardia
- Gestión de eventos
- Gestión de casos
- Workflow Automation
- App Builder
- Infraestructura
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Contenedores
- Serverless
- Monitorización de red
- Coste de la nube
- Rendimiento de las aplicaciones
- APM
- Términos y conceptos de APM
- Instrumentación de aplicación
- Recopilación de métricas de APM
- Configuración de pipelines de trazas
- Correlacionar trazas (traces) y otros datos de telemetría
- Trace Explorer
- Observabilidad del servicio
- Instrumentación dinámica
- Error Tracking
- Seguridad de los datos
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Gastos generales de integración del Agent
- Arquitecturas de configuración
- Configuración de Postgres
- Configuración de MySQL
- Configuración de SQL Server
- Configuración de Oracle
- Configuración de MongoDB
- Conexión de DBM y trazas
- Datos recopilados
- Explorar hosts de bases de datos
- Explorar métricas de consultas
- Explorar ejemplos de consulta
- Solucionar problemas
- Guías
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Experiencia digital
- Real User Monitoring
- Monitorización del navegador
- Configuración
- Configuración avanzada
- Datos recopilados
- Monitorización del rendimiento de páginas
- Monitorización de signos vitales de rendimiento
- Monitorización del rendimiento de recursos
- Recopilación de errores del navegador
- Rastrear las acciones de los usuarios
- Señales de frustración
- Error Tracking
- Solucionar problemas
- Monitorización de móviles y TV
- Plataforma
- Session Replay
- Exploración de datos de RUM
- Feature Flag Tracking
- Error Tracking
- Guías
- Seguridad de los datos
- Monitorización del navegador
- Análisis de productos
- Pruebas y monitorización de Synthetics
- Continuous Testing
- Entrega de software
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Configuración
- Tests en contenedores
- Búsqueda y gestión
- Explorador
- Monitores
- Flujos de trabajo de desarrolladores
- Cobertura de código
- Instrumentar tests de navegador con RUM
- Instrumentar tests de Swift con RUM
- Detección temprana de defectos
- Reintentos automáticos de tests
- Correlacionar logs y tests
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- Métricas de DORA
- Seguridad
- Información general de seguridad
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Observabilidad de la IA
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Gestión de logs
- Administración
- Gestión de cuentas
- Seguridad de los datos
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Ayuda
Tests DNS
Información general
Los tests DNS te permiten monitorizar proactivamente la resolubilidad y los tiempos de búsqueda de tus registros DNS utilizando cualquier servidor de nombres. Si la resolución es inesperadamente lenta o un servidor DNS responde con entradas A, AAAA, CNAME, TXT o MX inesperadas, Datadog te envía una alerta con detalles sobre el fallo, lo cual te permite localizar rápidamente la causa del problema y solucionarlo.
Los tests DNS pueden ejecutarse tanto desde localizaciones gestionadas como desde localizaciones privadas dependiendo de si prefieres ejecutar el test desde fuera o desde dentro de tu red. Los tests DNS pueden ejecutarse de forma programada, bajo demanda o directamente dentro de tus pipelines CI/CD.
Configuración
Cuando decidas crear un test DNS, define la solicitud de tu test.
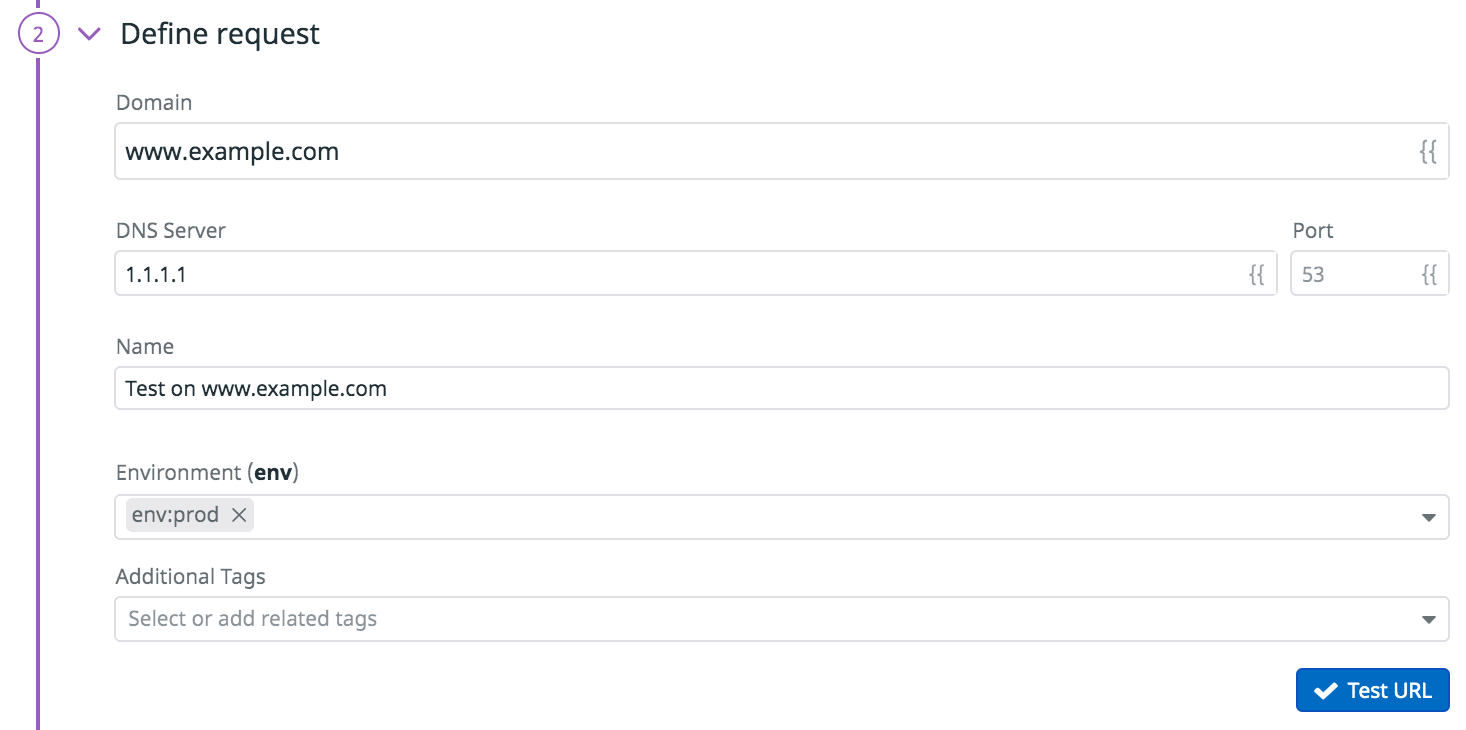
Definición de la solicitud
- Especifica el Dominio que quieres que consulte tu test. Por ejemplo,
www.example.com. - Especifica el Servidor DNS a utilizar (opcional). Puede ser un nombre de dominio o una dirección IP. Si no se especifica, el test DNS realiza la resolución utilizando
8.8.8.8, con una restauración en1.1.1.1y un servidor DNS interno de AWS. - Especifica el Puerto de tu servidor DNS (opcional). Si no se especifica, el puerto predeterminado del servidor DNS es 53.
- Especifica la cantidad de tiempo en segundos antes de que se inicie un tiempo de espera en el test (opcional).
- Dale un nombre a tu test DNS.
- Añade Etiquetas (tags)
envasí como cualquier otra etiqueta a tu test DNS. Luego, puedes utilizar estas etiquetas para filtrar tus tests Synthetic en la página de monitorización y tests continuos Synthetic.
Haz clic en Test de URL para probar la configuración de la solicitud. Aparecerá una vista previa de la respuesta en la parte derecha de la pantalla.
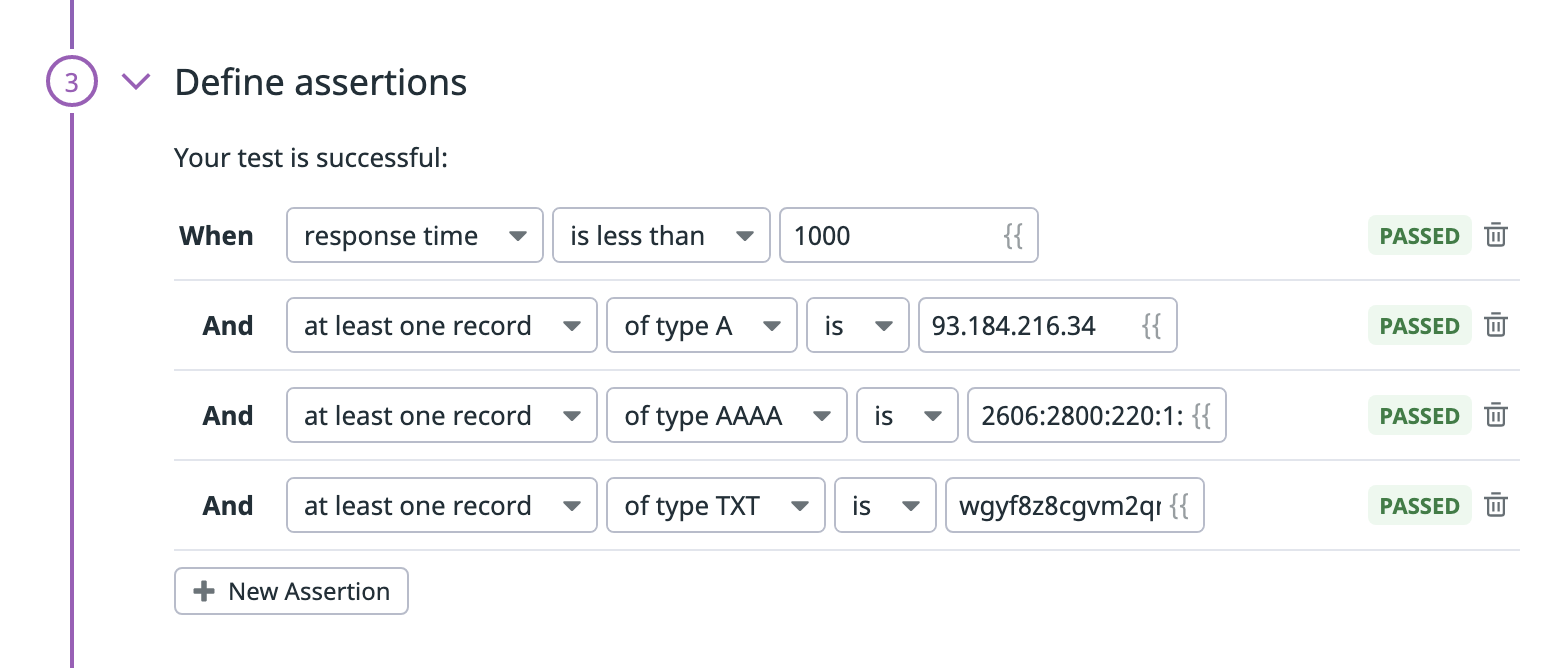
Definición de aserciones
Las aserciones definen cuál es un resultado de test esperado. Al hacer clic en Test de URL, se añaden aserciones básicas sobre el response time y los registros disponibles. Debes definir al menos una aserción para que sea monitorizada por tu test.
| Tipo | Tipo de registro | Operador | Tipo de valor |
|---|---|---|---|
| tiempo de respuesta | is less than | Integer (ms) | |
| todos los registros disponibles | de tipo A, de tipo AAAA, de tipo CNAME, de tipo MX, de tipo NS, de tipo TXT | is, contains,matches, does not match | String Regex |
| al menos un registro | de tipo A, de tipo AAAA, de tipo CNAME, de tipo MX, de tipo NS, de tipo TXT | is, contains,matches, does not match | String Regex |
Nota: Los registros SOA no están disponibles para realizar tests con Synthetic.
Puedes crear hasta 20 aserciones por test de API haciendo clic en Nueva aserción o haciendo clic directamente en la vista previa de la respuesta:
Para realizar la lógica OR en una aserción, utiliza el comparador matches regex para definir una expresión regular con varios valores esperados para el mismo tipo de aserción, como (0|100). El resultado del test es correcto si todos los registros disponibles o al menos el valor de una aserción del registro es 0 o 100.
Si un test no contiene una aserción en el cuerpo de la respuesta, la carga útil del cuerpo cae y devuelve un tiempo de respuesta asociado para la solicitud, dentro del límite de tiempo de espera establecido por el worker de Synthetics.
Si un test contiene una aserción en el cuerpo de la respuesta y se alcanza el límite de tiempo de espera, aparecerá un error Assertions on the body/response cannot be run beyond this limit.
Seleccionar localizaciones
Selecciona las Localizaciones desde donde ejecutar tu test DNS. Los tests DNS pueden ejecutarse tanto desde localizaciones gestionadas como privadas, en función de si prefieres monitorizar un dominio privado o público.
Datadog’s out-of-the-box managed locations allow you to test public-facing websites and endpoints from regions where your customers are located.
| Americas | APAC | EMEA |
|---|---|---|
| Canada Central (AWS) | Hong Kong (AWS) | Cape Town (AWS) |
| Northern California (AWS) | Mumbai (AWS) | Frankfurt (AWS) |
| Northern Virginia (AWS) | Seoul (AWS) | Ireland (AWS) |
| Ohio (AWS) | Singapore (AWS) | London (AWS) |
| Oregon (AWS) | Sydney (AWS) | Paris (AWS) |
| São Paulo (AWS) | Tokyo (AWS) | Stockholm (AWS) |
| Virginia (Azure) | Osaka (AWS) | Milan (AWS) |
| Jakarta (AWS) | Bahrain (AWS) |
The Datadog for Government site (US1-FED) uses the following managed location:
| Americas |
|---|
| US-West |
Indicar la frecuencia del test
Los test DNS se pueden ejecutar:
- De forma programada, para garantizar que los servicios más importantes siempre resulten accesibles para tus usuarios. Selecciona la frecuencia con la que quieres que Datadog ejecute tu test DNS.
- Dentro de tus pipelines CI/CD.
- Bajo demanda para ejecutar tus tests cuando sea más conveniente para tu equipo.
Define alert conditions
Set alert conditions to determine the circumstances under which you want a test to fail and trigger an alert.
Alerting rule
When you set the alert conditions to: An alert is triggered if any assertion fails for X minutes from any n of N locations, an alert is triggered only if these two conditions are true:
- At least one location was in failure (at least one assertion failed) during the last X minutes;
- At one moment during the last X minutes, at least n locations were in failure.
Fast retry
Your test can trigger retries X times after Y ms in case of a failed test result. Customize the retry interval to suit your alerting sensibility.
Location uptime is computed on a per-evaluation basis (whether the last test result before evaluation was up or down). The total uptime is computed based on the configured alert conditions. Notifications sent are based on the total uptime.
Configure the test monitor
A notification is sent by your test based on the alerting conditions previously defined. Use this section to define how and what to message your team.
Similar to how you configure monitors, select users and/or services that should receive notifications either by adding an
@notificationto the message or by searching for team members and connected integrations with the dropdown menu.Enter the notification message for your test. This field allows standard Markdown formatting and supports the following conditional variables:
Conditional Variable Description {{ #is_alert }} Show when the test alerts. {{ ^is_alert }} Show unless the test alerts. {{ #is_recovery }} Show when the test recovers from alert. {{ ^is_recovery }} Show unless the test recovers from alert. {{ #is_renotify }} Show when the monitor renotifies. {{ ^is_renotify }} Show unless the monitor renotifies. {{ #is_priority }} Show when the monitor matches priority (P1 to P5). {{ ^is_priority }} Show unless the monitor matches priority (P1 to P5). Specify how often you want your test to re-send the notification message in case of test failure. To prevent renotification on failing tests, leave the option as
Never renotify if the monitor has not been resolved.Click Create to save your test configuration and monitor.
For more information, see Using Synthetic Test Monitors.
Variables
Create local variables
To create a local variable, click Create a Local Variable. You can select one of the following available builtins to add to your variable string:
- {{ numeric(n) }}
- Generates a numeric string with
ndigits. - {{ alphabetic(n) }}
- Generates an alphabetic string with
nletters. - {{ alphanumeric(n) }}
- Generates an alphanumeric string with
ncharacters. - {{ date(n unit, format) }}
- Generates a date in one of Datadog’s accepted formats with a value corresponding to the UTC date the test is initiated at + or -
nunits. - {{ timestamp(n, unit) }}
- Generates a timestamp in one of Datadog’s accepted units with a value corresponding to the UTC timestamp the test is initiated at +/-
nunits. - {{ uuid }}
- Generates a version 4 universally unique identifier (UUID).
- {{ public-id }}
- Injects the Public ID of your test.
- {{ result-id }}
- Injects the Result ID of your test run.
To obfuscate local variable values in test results, select Hide and obfuscate variable value. Once you have defined the variable string, click Add Variable.
Uso de variables
Puedes utilizar las variables globales definidas en la página Parámetros en la URL, las opciones avanzadas y las aserciones de tus tests DNS.
Para visualizar tu lista de variables, escribe {{ en el campo de tu elección.
Fallo del test
Un test se considera FAILED si no satisface una o más aserciones o si la solicitud ha fallado prematuramente. En algunos casos, el test puede fallar sin comprobar las aserciones respecto al endpoint.
Entre las razones figuran las siguientes:
CONNRESET- El servidor remoto ha cerrado bruscamente la conexión. Entre las posibles causas se incluyen que el servidor web haya encontrado un error o falla al responder, o que se haya perdido la conectividad del servidor web.
DNS:
No se ha encontrado la entrada DNS para la URL del test. Entre las posibles causas se incluyen una URL de test mal configurada o una configuración incorrecta de las entradas DNS.
INVALID_REQUEST- La configuración del test no es válida (por ejemplo, un error tipográfico en la URL).
TIMEOUT- La solicitud no se ha podido completar en un plazo razonable. Pueden ocurrir dos tipos de
TIMEOUT:TIMEOUT: The request couldn't be completed in a reasonable time.indica que la duración de la solicitud ha alcanzado el tiempo de espera definido en el test (por defecto se establece en 60 segundos). Para cada solicitud, en la cascada de la red sólo se muestran las etapas completadas de la solicitud. Por ejemplo, en el caso de que sólo se muestreTotal response time, el tiempo de espera se produjo durante la resolución DNS.TIMEOUT: Overall test execution couldn't be completed in a reasonable time.indica que la duración del test (solicitud + aserciones) alcanza la duración máxima (60,5 segundos).
Permisos
De manera predeterminada, sólo los usuarios con los roles de administrador de Datadog y estándar de Datadog pueden crear, editar y eliminar tests DNS Synthetic. Para crear, editar y eliminar tests DNS Synthetic, actualiza tu usuario a uno de esos dos roles predeterminados.
Si estás utilizando la función de rol personalizado, añade tu usuario a cualquier rol que incluya permisos synthetics_read y synthetics_write.
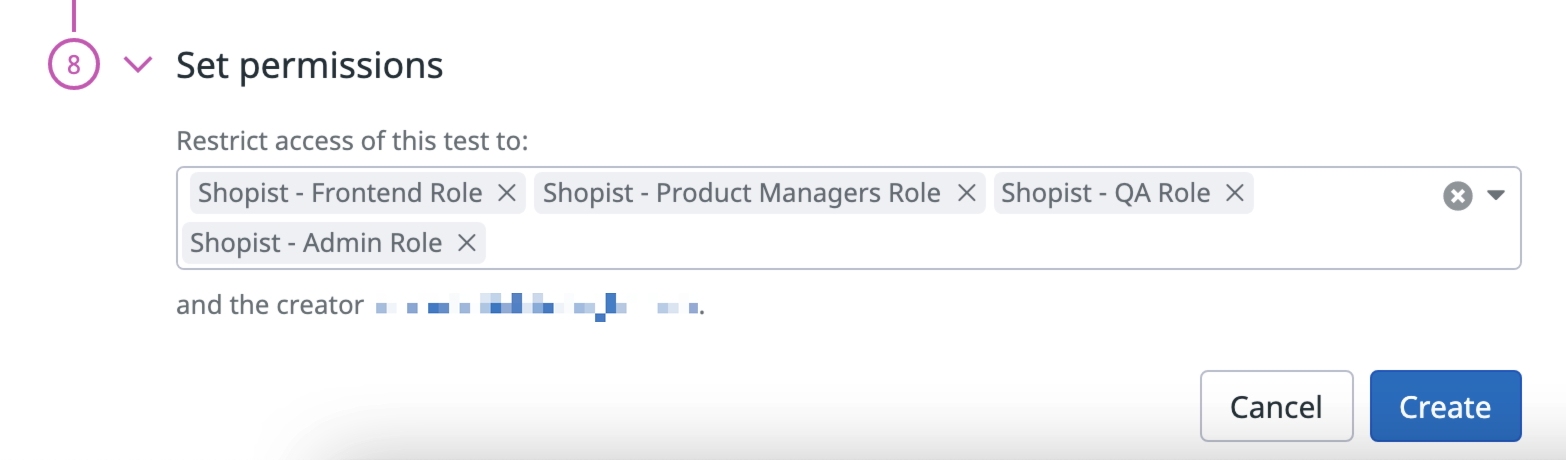
Restringir el acceso
La restricción del acceso está disponible para clientes que utilizan roles personalizados en sus cuentas.
Puedes restringir el acceso a un test DNS en función de los roles de tu organización. Al crear un test DNS, elige qué roles (además de tu usuario) pueden leer y redactar tu test.
Referencias adicionales
Más enlaces, artículos y documentación útiles: