- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Integrations
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- APM Tracing
- Profiler
- Tags
- API
- Software Catalog
- Session Replay
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- Software Delivery
- Code Security
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Datadog Mobile App
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Software Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Product Analytics
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Code Security
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Connect to Datadog over Google Cloud Private Service Connect
This feature is not supported for the selected Datadog site.
Google Cloud Private Service Connect (PSC) allows you to send telemetry to Datadog without using the public internet.
Datadog exposes some of its data intake services in Google Cloud as Private Service Connect published services, as seen in the table of published services.
You can configure a PSC endpoint to expose a private IP address for each Datadog intake service. This IP address routes traffic to the Datadog backend. You can then configure a Google Cloud Private DNS Zone to override the DNS names corresponding to the products for each endpoint that is consumed.
Setup
Connect an endpoint
In your Google Cloud console, navigate to Network services > Private Service Connect.
Go to the Endpoints section. Click on Connect endpoint.
- Under Target, select Published service.
- For Target service, enter the PSC target name that corresponds to the Datadog intake service that you want to use. You can find your PSC target name in the table of published services.
- For Endpoint name, enter a unique identifier to use for this endpoint. You can use
datadog-<SERVICE>. For example:datadog-api. - For Network and Subnetwork, choose the network and subnetwork where you want to publish your endpoint.
- For IP address, click the dropdown and select Create IP address to create an internal IP from your subnet dedicated to the endpoint. Select this IP.
- Check Enable global access if you intend to connect the endpoint to virtual machines outside of the
us-central1region.
Note: Datadog exposes PSC producer endpoints from the
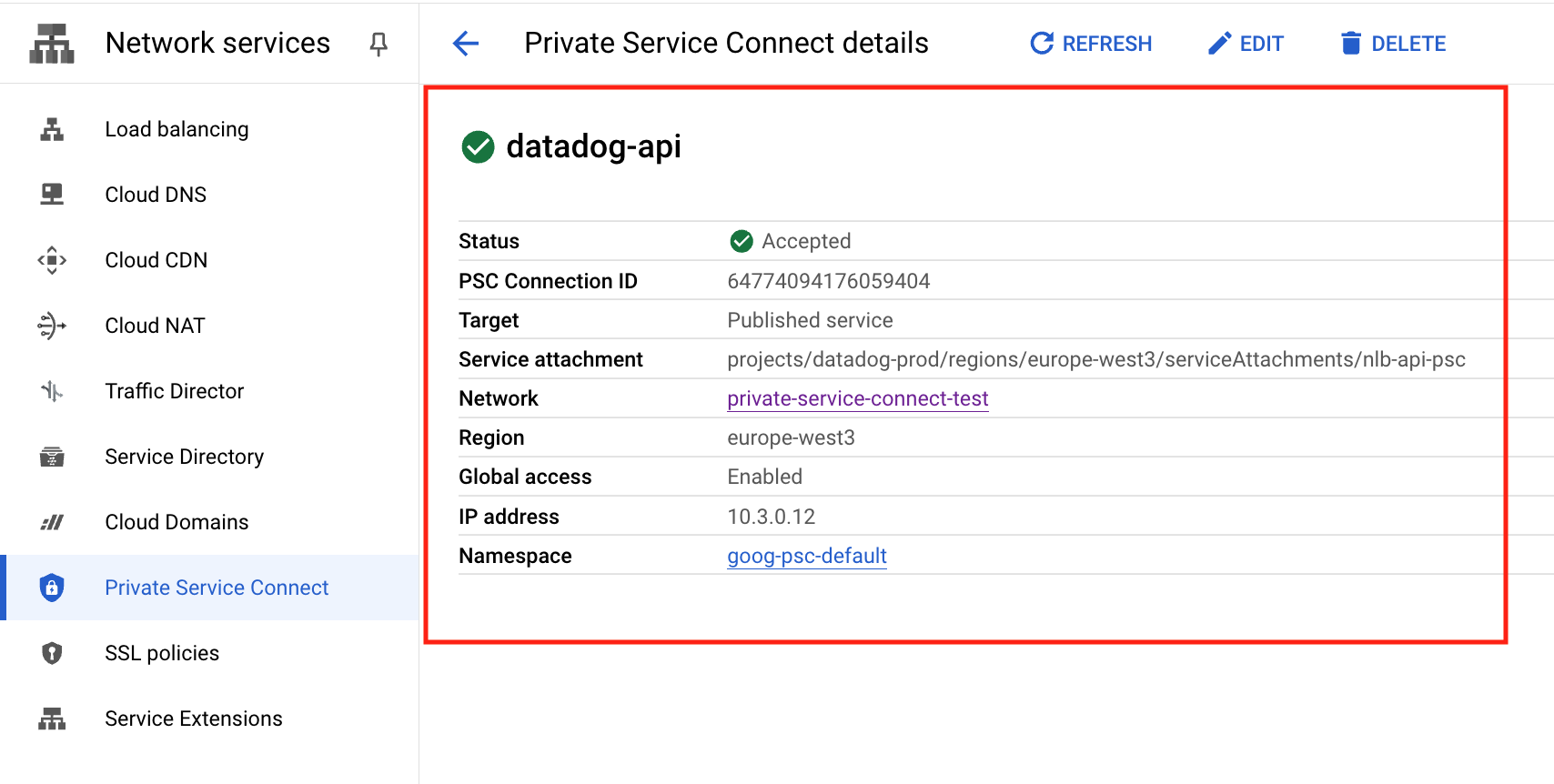
us-central1region. These endpoints support global access, allowing services to connect from any region. However, the forwarding rule must be created in theus-central1region.Click Add endpoint. Verify that your status is Accepted. Take note of the IP address, as this is used in the next section.
Create a DNS zone
In your Google Cloud console, navigate to Network services > Cloud DNS.
Click on Create zone.
- Under Zone type, select Private.
- For Zone name, enter a descriptive name for your zone.
- For DNS name, enter the private DNS name that corresponds to the Datadog intake service that you want to use. You can find your DNS name in the table of published services.
Next, create an
Arecord that points to the endpoint IP. On the Zone details page of the zone you created, click on Add record set.- For DNS name, leave the field unmodified.
- For Resource record type, select
A. - Under IPv4 Address, enter the IP address that was displayed at the end of the previous section.
Additional required steps for metrics and traces
There are two Datadog Intake Services that are subdomains of the (agent.) domain. Because of this, the Private Hosted Zone is slightly different from other intakes.
Create a Private Zone for (agent.), as outlined in the Create a DNS Zone section. Then add the three records below.
| DNS name | Resource record type | IPv4 address |
|---|---|---|
(apex) | A | IP address for your metrics endpoint |
* | A | IP address for your metrics endpoint |
trace | A | IP address for your traces endpoint |
Note: this zone requires a wildcard (*) record that points to the IP address for your metrics endpoint. This is because Datadog Agents submit telemetry using a versioned endpoint in the form (<version>-app.agent.).
Validation
To verify your configuration, SSH into one of your local nodes and run a dig command similar to the following:
Verify that that the wildcard is routing to the metrics endpoint
> dig +noall +answer 7-49-0-app.agent.us5.datadoghq.com
The response resembles:
7-49-0-app.agent.us5.datadoghq.com. 300 IN A 10.1.0.4
Verify that the trace subdomain is routing to the traces endpoint
> dig +noall +answer trace.agent.us5.datadoghq.com
The response resembles:
trace.agent.us5.datadoghq.com. 300 IN A 10.1.0.9
Ensure that the IP address in the response matches the one associated with your PSC target.
Published services
| Datadog intake service | PSC target name | Private DNS name |
|---|---|---|
| Logs (Agent) | projects/datadog-prod-us5/regions/us-central1/serviceAttachments/nlb-logs-agent-intake-psc | agent-http-intake.logs.us5.datadoghq.com |
| Logs (User HTTP Intake) | projects/datadog-prod-us5/regions/us-central1/serviceAttachments/nlb-logs-intake-psc | http-intake.logs.us5.datadoghq.com |
| API | projects/datadog-prod-us5/regions/us-central1/serviceAttachments/nlb-api-psc | api.us5.datadoghq.com |
| Metrics | projects/datadog-prod-us5/regions/us-central1/serviceAttachments/nlb-metrics-agent-psc | agent.us5.datadoghq.com |
| Containers | projects/datadog-prod-us5/regions/us-central1/serviceAttachments/nlb-orchestrator-psc | orchestrator.us5.datadoghq.com |
| Process | projects/datadog-prod-us5/regions/us-central1/serviceAttachments/nlb-process-psc | process.us5.datadoghq.com |
| Profiling | projects/datadog-prod-us5/regions/us-central1/serviceAttachments/nlb-logs-http-profile-psc | intake.profile.us5.datadoghq.com |
| Traces | projects/datadog-prod-us5/regions/us-central1/serviceAttachments/nlb-trace-edge-psc | agent.us5.datadoghq.com |
| Database Monitoring | projects/datadog-prod-us5/regions/us-central1/serviceAttachments/nlb-dbm-metrics-psc | dbm-metrics-intake.us5.datadoghq.com |
| Remote Configuration | projects/datadog-prod-us5/regions/us-central1/serviceAttachments/nlb-fleet-psc | config.us5.datadoghq.com |
Private Service Connect (PSC) allows you to send telemetry to Datadog without using the public internet.
Datadog exposes some of its data intake services in Google Cloud Platform as PSC published services, as seen in the table of published services.
You can configure a PSC endpoint to expose a private IP address for each Datadog intake service. This IP address routes traffic to the Datadog backend. You can then configure a Google Cloud Private DNS Zone to override the DNS names corresponding to the products for each endpoint that is consumed.
Setup
Connect an endpoint
In your GCP console, navigate to Network services > Private Service Connect.
Go to the Endpoints section. Click on Connect endpoint.
- Under Target, select Published service.
- For Target service, enter the PSC target name that corresponds to the Datadog intake service that you want to use. You can find your PSC target name in the table of published services.
- For Endpoint name, enter a unique identifier to use for this endpoint. You can use
datadog-<SERVICE>. For example:datadog-metrics. - For Network and Subnetwork, choose the network and subnetwork where you want to publish your endpoint.
- For IP address, click the dropdown and select Create IP address to create an internal IP from your subnet dedicated to the endpoint. Select this IP.
- Check Enable global access if you intend to connect the endpoint to virtual machines outside of the
europe-west3region.
Note: Datadog exposes PSC producer endpoints from the
europe-west3region. These endpoints support global access, allowing services to connect from any region. However, the forwarding rule must be created in theeurope-west3region.Click Add endpoint. Verify that your status is Accepted. Take note of the IP address, as this is used in the next section.
Create a DNS zone
In your Google Cloud console, navigate to Network services > Cloud DNS.
Click on Create zone.
- Under Zone type, select Private.
- For Zone name, enter a descriptive name for your zone.
- For DNS name, enter the private DNS name that corresponds to the Datadog intake service that you want to use. You can find your DNS name in the table of published services.
Next, create an
Arecord that points to the endpoint IP. On the Zone details page of the zone you created, click on Add record set.- For DNS name, leave the field unmodified.
- For Resource record type, select
A. - Under IPv4 Address, enter the IP address that was displayed at the end of the previous section.
Additional required steps for metrics and traces
There are two Datadog Intake Services that are subdomains of the (agent.) domain. Because of this, the Private Hosted Zone is slightly different from other intakes.
Create a Private Zone for (agent.), as outlined in the Create a DNS Zone section. Then add the three records below.
| DNS name | Resource record type | IPv4 address |
|---|---|---|
(apex) | A | IP address for your metrics endpoint |
* | A | IP address for your metrics endpoint |
trace | A | IP address for your traces endpoint |
Note: this zone requires a wildcard (*) record that points to the IP address for your metrics endpoint. This is because Datadog Agents submit telemetry using a versioned endpoint in the form (<version>-app.agent.).
Validation
To verify your configuration, SSH into one of your local nodes and run a dig command similar to the following:
Verify that that the wildcard is routing to the metrics endpoint
> dig +noall +answer 7-49-0-app.agent.datadoghq.eu
The response resembles:
7-49-0-app.agent.datadoghq.eu. 300 IN A 10.1.0.4
Verify that the trace subdomain is routing to the traces endpoint
> dig +noall +answer trace.agent.datadoghq.eu
The response resembles:
trace.agent.datadoghq.eu. 300 IN A 10.1.0.9
Ensure that the IP address in the response matches the one associated with your PSC target.
Published services
| Datadog intake service | PSC target name | Private DNS name |
|---|---|---|
| Logs (Agent) | projects/datadog-prod/regions/europe-west3/serviceAttachments/nlb-logs-agent-intake-psc | agent-http-intake.logs.datadoghq.eu |
| Logs (User HTTP Intake) | projects/datadog-prod/regions/europe-west3/serviceAttachments/nlb-logs-intake-psc | http-intake.logs.datadoghq.eu |
| API | projects/datadog-prod/regions/europe-west3/serviceAttachments/nlb-api-psc | api.datadoghq.eu |
| Metrics | projects/datadog-prod/regions/europe-west3/serviceAttachments/nlb-metrics-agent-psc | agent.datadoghq.eu |
| Containers | projects/datadog-prod/regions/europe-west3/serviceAttachments/nlb-orchestrator-psc | orchestrator.datadoghq.eu |
| Process | projects/datadog-prod/regions/europe-west3/serviceAttachments/nlb-process-psc | process.datadoghq.eu |
| Profiling | projects/datadog-prod/regions/europe-west3/serviceAttachments/nlb-logs-http-profile-psc | intake.profile.datadoghq.eu |
| Traces | projects/datadog-prod/regions/europe-west3/serviceAttachments/nlb-trace-edge-psc | agent.datadoghq.eu |
| Database Monitoring | projects/datadog-prod/regions/europe-west3/serviceAttachments/nlb-dbm-metrics-psc | dbm-metrics-intake.datadoghq.eu |
| Remote Configuration | projects/datadog-prod/regions/europe-west3/serviceAttachments/nlb-fleet-psc | config.datadoghq.eu |
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: