- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- Tracing
- Profileur
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Développeurs
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Checks custom
- Intégrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Checks de service
- IDE Plugins
- Communauté
- Guides
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Application mobile
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Alertes
- Infrastructure
- Métriques
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Conteneurs
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Product Analytics
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Exécuteur de tests intelligent
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- Administration
Install Serverless Monitoring for AWS Step Functions
Cette page n'est pas encore disponible en français, sa traduction est en cours.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Requirements
- The full Step Function execution length must be less than 6 hours for full traces.
How it works
AWS Step Functions is a fully managed service, and the Datadog Agent cannot be directly installed on Step Functions. However, Datadog can monitor Step Functions through Cloudwatch metrics and logs.
Datadog collects Step Functions metrics from Cloudwatch through the AWS Step Functions integration. Datadog collects Step Functions logs from Cloudwatch through one of the following:
- Datadog Forwarder. For instructions, see the Setup section on this page.
- Amazon Data Firehose. For instructions, see Send AWS service logs to the Datadog Amazon Data Firehose destination.
Datadog uses these ingested logs to generate enhanced metrics and traces for your Step Function executions.
Setup
Ensure that the AWS Step Functions integration is installed.
Then, to send your Step Functions logs to Datadog:
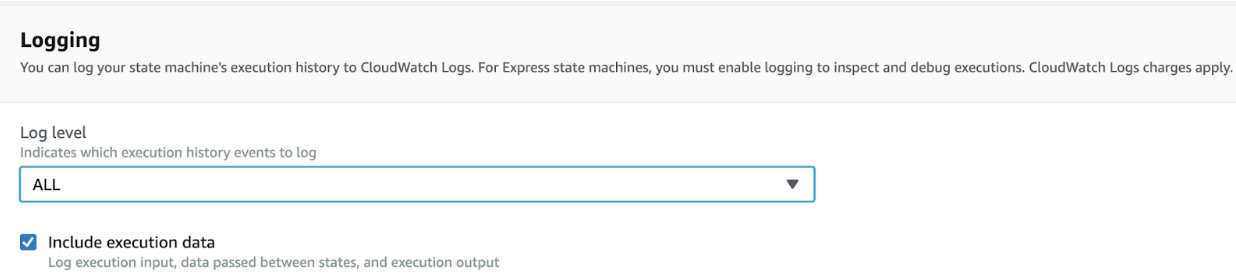
Enable all logging for your Step Function. In your AWS console, open your state machine. Click Edit and find the Logging section. There, set Log level to
ALLand enable the Include execution data checkbox.Ensure you have deployed the Datadog Lambda Forwarder, and that you are using v3.130.0+. You might need to update your Forwarder. As an alternative, you may also use Amazon Data Firehose, which can subscribe to Amazon CloudWatch log groups across multiple AWS regions. However, it requires that the Step Functions log group name begins with “/aws/vendedlogs/states/”.
Subscribe CloudWatch logs to the Datadog Lambda Forwarder. If the log group name for your Step Functions begins with “/aws/vendedlogs/states/”, you can also use the Serverless Framework or the Datadog CLI to configure the subscription.
Automatic custom installation
- Ensure that you have set up the Datadog-AWS integration.
- In Datadog, open the AWS integration tile, and view the Configuration tab.
- On the left, select the AWS account where your Step Function is running. Open the Log Collection tab.
- In the Log Autosubscription section, under Autosubscribe Forwarder Lambda Functions, enter the ARN of your Datadog Lambda Forwarder, as noted previously. Click Add.
- Toggle on Step Functions CloudWatch Logs. Changes take 15 minutes to take effect.
Note: Log Autosubscription requires your Lambda Forwarder and Step Function to be in the same region.
Manual custom installation
- Open your AWS console and go to your Datadog Lambda Forwarder. In the Function overview section, click on Add trigger.
- Under Add trigger, in the Trigger configuration section, use the Select a source dropdown to select
CloudWatch Logs. - Under Log group, select the log group for your state machine. For example,
/aws/vendedlogs/states/my-state-machine. - Enter a filter name. You can choose to name it “empty filter” and leave the Filter pattern box blank.
Set up tags. Open your AWS console and go to your Step Functions state machine. Open the Tags section and add
env:<ENV_NAME>,service:<SERVICE_NAME>, andversion:<VERSION>tags. Theenvtag is required to see traces in Datadog, and it defaults todev. Theservicetag defaults to the state machine’s name. Theversiontag defaults to1.0.To enable tracing, you have two options:
- Per Step Function: Add the
DD_TRACE_ENABLEDtag to each Step Function and set the value totrue. - At the Forwarder level: To enable tracing for all Step Functions connected to the Forwarder, you have two options:
- When creating the CloudFormation stack for the forwarder, set the
DdStepFunctionsTraceEnabledparameter totrue. - After the forwarder is created, set the environment variable
DD_STEP_FUNCTIONS_TRACE_ENABLEDtotrue.
- When creating the CloudFormation stack for the forwarder, set the
- Per Step Function: Add the
If you haven’t already, install the Datadog CLI v2.18.0+.
npm install -g @datadog/datadog-ciEnsure you have deployed the Datadog Lambda Forwarder, and that you are using v3.130.0+. You might need to update your Forwarder. As an alternative, you can also use Amazon Data Firehose, which can subscribe to Amazon CloudWatch log groups across multiple AWS regions. Your Step Functions log group name should use this format:
/aws/vendedlogs/states/<STEP_FUNCTION_NAME>-LogsOptionally, you can add your environment to this log group name:
/aws/vendedlogs/states/<STEP_FUNCTION_NAME>-Logs-<ENV>Take note of your Forwarder’s ARN.
Run:
datadog-ci stepfunctions instrument \ --step-function <STEP_FUNCTION_ARN> \ --forwarder <FORWARDER_ARN> \ --env <ENVIRONMENT> \ --propagate-upstream-trace \ --merge-step-function-and-lambda-traces- Replace
<STEP_FUNCTION_ARN>with the ARN of your Step Function. Repeat the--step-functionflag for each Step Function you wish to instrument. - Replace
<FORWARDER_ARN>with the ARN of your Datadog Lambda Forwarder. This step configures the log stream subscription for the Forwarder. - Replace
<ENVIRONMENT>with the environment tag you would like to apply to your Step Functions.
For more information about the
datadog-ci stepfunctionscommand, see the Datadog CLI documentation.- Replace
Note: The datadog-ci stepfunctions instrument command automatically enables tracing.
If you haven’t already, install the Datadog Serverless Framework Plugin v5.40.0+:
serverless plugin install --name serverless-plugin-datadogEnsure you have deployed the Datadog Lambda Forwarder, and that you are using v3.130.0+. You might need to update your Forwarder. As an alternative, you can also use Amazon Data Firehose, which can subscribe to Amazon CloudWatch log groups across multiple AWS regions. Your Step Functions log group name should use this format:
/aws/vendedlogs/states/<STEP_FUNCTION_NAME>-Logs-<STAGE>Add the following to your
serverless.yml:custom: datadog: site: <DATADOG_SITE> apiKeySecretArn: <DATADOG_API_KEY_SECRET_ARN> forwarderArn: <FORWARDER_ARN> enableStepFunctionsTracing: true propagateUpstreamTrace: true mergeStepFunctionAndLambdaTraces: true- Replace
<DATADOG_SITE>with(ensure the correct DATADOG SITE is selected on the right of this docs page). - Replace
<DATADOG_API_KEY_SECRET_ARN>with the ARN of the AWS secret where your Datadog API key is securely stored. The key needs to be stored as a plaintext string (not a JSON blob). Thesecretsmanager:GetSecretValuepermission is required. For quick testing, you can instead useapiKeyand set the Datadog API key in plaintext. - Replace
<FORWARDER_ARN>with the ARN of your Datadog Lambda Forwarder. This step configures the log stream subscription for the Forwarder.
For additional settings, see Datadog Serverless Framework Plugin - Configuration parameters.
Note: The
enableStepFunctionsTracing: trueline automatically enables tracing.- Replace
Ensure you have deployed the Datadog Lambda Forwarder, and that you are using v3.130.0+. You might need to update your Forwarder.
Install Datadog’s CDK Construct Library, which automatically sets up logging and subscribes the Forwarder to the log group.
Example
from aws_cdk import (
aws_stepfunctions as sfn,
aws_stepfunctions_tasks as tasks,
)
from datadog_cdk_constructs_v2 import DatadogStepFunctions, DatadogLambda
state_machine = sfn.StateMachine(...)
datadog_sfn = DatadogStepFunctions(
self,
"DatadogSfn",
env="<ENV>", # e.g. "dev"
service="<SERVICE>", # e.g. "my-cdk-service"
version="<VERSION>", # e.g. "1.0.0"
forwarderArn="<FORWARDER_ARN>", # e.g. "arn:test:forwarder:sa-east-1:12345678:1"
tags=<TAGS>, # optional, e.g. "custom-tag-1:tag-value-1,custom-tag-2:tag-value-2"
)
datadog_sfn.add_state_machines([child_state_machine, parent_state_machine])
For sample stacks and additional code examples, see CDK Examples for Instrumenting AWS Step Functions.
Note: The Datadog Step Functions CDK construct automatically enables tracing.
Enhanced metrics are automatically enabled if you enable tracing. Therefore, if tracing is enabled, you are billed for both Serverless Workload Monitoring and Serverless APM. See Pricing.
Additional options for instrumentation
Merge Step Functions with AWS Lambda traces
See Merge Step Functions traces with Lambda traces. Ensure that you have also set up Serverless Monitoring for AWS Lambda.
Sample traces
To manage the APM traced invocation sampling rate for serverless functions, set the DD_TRACE_SAMPLE_RATE environment variable on the function to a value between 0.00 (no tracing of Step Function invocations) and 1.00 (trace all Step Function invocations).
The dropped traces are not ingested into Datadog.
Enable enhanced metrics (without tracing)
Datadog generates enhanced metrics from collected Cloudwatch logs. Enhanced metrics are automatically enabled if you enable traces.
To enable enhanced metrics without enabling tracing, add a DD_ENHANCED_METRICS tag to each of your Step Functions and set the value to true.
If you enable enhanced metrics without enabling traces, you are only billed for Serverless Workload Monitoring. If you enable tracing (which automatically includes enhanced metrics), you are billed for both Serverless Workload Monitoring and Serverless APM. See Pricing.
See your Step Function metrics, logs, and traces in Datadog
After you have invoked your state machine, go to the Serverless app in Datadog. Search for service:<YOUR_STATE_MACHINE_NAME> to see the relevant metrics, logs, and traces associated with that state machine. If you set the service tag on your state machine to a custom value, search for service:<CUSTOM_VALUE>.
If you cannot see your traces, see Troubleshooting.