- Esenciales
- Empezando
- Datadog
- Sitio web de Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless para Lambda AWS
- Agent
- Integraciones
- Contenedores
- Dashboards
- Monitores
- Logs
- Rastreo de APM
- Generador de perfiles
- Etiquetas (tags)
- API
- Catálogo de servicios
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Monitorización Synthetic
- Gestión de incidencias
- Monitorización de bases de datos
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Análisis de código
- Centro de aprendizaje
- Compatibilidad
- Glosario
- Atributos estándar
- Guías
- Agent
- Uso básico del Agent
- Arquitectura
- IoT
- Plataformas compatibles
- Recopilación de logs
- Configuración
- Configuración remota
- Automatización de flotas
- Actualizar el Agent
- Solucionar problemas
- Detección de nombres de host en contenedores
- Modo de depuración
- Flare del Agent
- Estado del check del Agent
- Problemas de NTP
- Problemas de permisos
- Problemas de integraciones
- Problemas del sitio
- Problemas de Autodiscovery
- Problemas de contenedores de Windows
- Configuración del tiempo de ejecución del Agent
- Consumo elevado de memoria o CPU
- Guías
- Seguridad de datos
- Integraciones
- OpenTelemetry
- Desarrolladores
- Autorización
- DogStatsD
- Checks personalizados
- Integraciones
- Crear una integración basada en el Agent
- Crear una integración API
- Crear un pipeline de logs
- Referencia de activos de integración
- Crear una oferta de mercado
- Crear un cuadro
- Crear un dashboard de integración
- Crear un monitor recomendado
- Crear una regla de detección Cloud SIEM
- OAuth para integraciones
- Instalar la herramienta de desarrollo de integraciones del Agente
- Checks de servicio
- Complementos de IDE
- Comunidad
- Guías
- API
- Aplicación móvil de Datadog
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- En la aplicación
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- Editor DDSQL
- Hojas
- Monitores y alertas
- Infraestructura
- Métricas
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Catálogo de servicios
- Catálogo de APIs
- Error Tracking
- Gestión de servicios
- Objetivos de nivel de servicio (SLOs)
- Gestión de incidentes
- De guardia
- Gestión de eventos
- Gestión de casos
- Workflow Automation
- App Builder
- Infraestructura
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Contenedores
- Serverless
- Monitorización de red
- Coste de la nube
- Rendimiento de las aplicaciones
- APM
- Términos y conceptos de APM
- Instrumentación de aplicación
- Recopilación de métricas de APM
- Configuración de pipelines de trazas
- Correlacionar trazas (traces) y otros datos de telemetría
- Trace Explorer
- Observabilidad del servicio
- Instrumentación dinámica
- Error Tracking
- Seguridad de los datos
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Gastos generales de integración del Agent
- Arquitecturas de configuración
- Configuración de Postgres
- Configuración de MySQL
- Configuración de SQL Server
- Configuración de Oracle
- Configuración de MongoDB
- Conexión de DBM y trazas
- Datos recopilados
- Explorar hosts de bases de datos
- Explorar métricas de consultas
- Explorar ejemplos de consulta
- Solucionar problemas
- Guías
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Experiencia digital
- Real User Monitoring
- Monitorización del navegador
- Configuración
- Configuración avanzada
- Datos recopilados
- Monitorización del rendimiento de páginas
- Monitorización de signos vitales de rendimiento
- Monitorización del rendimiento de recursos
- Recopilación de errores del navegador
- Rastrear las acciones de los usuarios
- Señales de frustración
- Error Tracking
- Solucionar problemas
- Monitorización de móviles y TV
- Plataforma
- Session Replay
- Exploración de datos de RUM
- Feature Flag Tracking
- Error Tracking
- Guías
- Seguridad de los datos
- Monitorización del navegador
- Análisis de productos
- Pruebas y monitorización de Synthetics
- Continuous Testing
- Entrega de software
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Configuración
- Tests en contenedores
- Búsqueda y gestión
- Explorador
- Monitores
- Flujos de trabajo de desarrolladores
- Cobertura de código
- Instrumentar tests de navegador con RUM
- Instrumentar tests de Swift con RUM
- Detección temprana de defectos
- Reintentos automáticos de tests
- Correlacionar logs y tests
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- Métricas de DORA
- Seguridad
- Información general de seguridad
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Observabilidad de la IA
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Gestión de logs
- Administración
- Gestión de cuentas
- Seguridad de los datos
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Ayuda
Monitoring Resource Performance
This page is not yet available in Spanish. We are working on its translation.
If you have any questions or feedback about our current translation project, feel free to reach out to us!
If you have any questions or feedback about our current translation project, feel free to reach out to us!
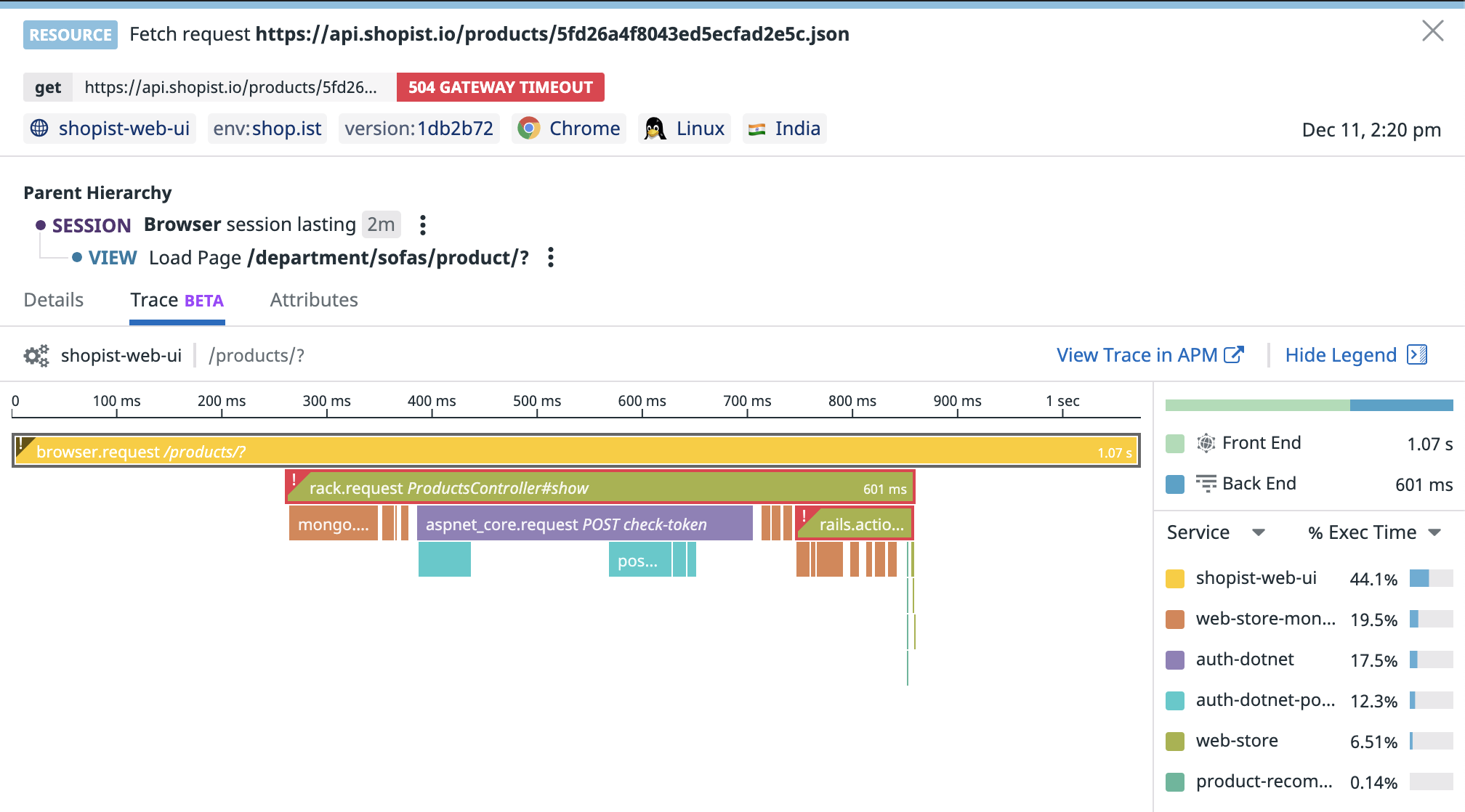
The RUM Browser SDK collects resources and assets for every RUM view (page load): XMLHttpRequest (XHRs) and Fetch requests, but also images, CSS files, JavaScript assets, and font files. A RUM Resource event is generated for each one of them, with detailed timings and metadata.
RUM Resources inherit from all the context related to the active RUM View at the time of collection.
Link RUM Resources to APM traces
To get even more complete, end-to-end visibility into requests as they move across layers of your stack, connect your RUM data with corresponding backend traces. This enables you to:
- Locate backend problems that resulted in a user-facing error.
- Identify the extent to which users are affected by an issue within your stack.
- See complete end-to-end requests on the flame graphs, allowing you to seamlessly navigate between RUM and APM and back with precise context.
See Connect RUM and Traces for information about setting up this feature.
Resource timing and metrics
Detailed network timing data for resources is collected from the Fetch and XHR native browser methods and from the Performance Resource Timing API.
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
duration | number | Entire time spent loading the resource. |
resource.size | number (bytes) | Resource size. |
resource.connect.duration | number (ns) | Time spent establishing a connection to the server (connectEnd - connectStart). |
resource.ssl.duration | number (ns) | Time spent for the TLS handshake. If the last request is not over HTTPS, this metric does not appear (connectEnd - secureConnectionStart). |
resource.dns.duration | number (ns) | Time spent resolving the DNS name of the last request (domainLookupEnd - domainLookupStart). |
resource.redirect.duration | number (ns) | Time spent on subsequent HTTP requests (redirectEnd - redirectStart). |
resource.first_byte.duration | number (ns) | Time spent waiting for the first byte of response to be received (responseStart - RequestStart). |
resource.download.duration | number (ns) | Time spent downloading the response (responseEnd - responseStart). |
Note: If you are having trouble collecting detailed timing for some resources, see Resource timing and CORS.
Resource attributes
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
resource.type | string | The type of resource being collected (for example, css, javascript, media, XHR, image). |
resource.method | string | The HTTP method (for example POST, GET). |
resource.status_code | number | The response status code. |
resource.url | string | The resource URL. |
resource.url_host | string | The host part of the URL. |
resource.url_path | string | The path part of the URL. |
resource.url_query | object | The query string parts of the URL decomposed as query params key/value attributes. |
resource.url_scheme | string | The protocol name of the URL (HTTP or HTTPS). |
resource.provider.name | string | The resource provider name. Default is unknown. |
resource.provider.domain | string | The resource provider domain. |
resource.provider.type | string | The resource provider type (for example first-party, cdn, ad, analytics). |
Identify third-party resources
RUM infers the name and category of the resource provider from the resource URL host part. If the resource URL host matches the current page URL host, the category is set to first party. Otherwise, the category will be cdn, analytics, or social for example.
Resource timing and CORS
The Resource Timing API is used to collect RUM resource timing. It is subject to the cross-origin security limitations that browsers enforce on scripts. For example, if your web application is hosted on www.example.com and it loads your images via images.example.com, you will only get timing for resources loaded hosted on www.example.com by default.
To resolve this, enable extended data collection for resources subject to CORS by adding the Timing-Allow-Origin HTTP response header to your cross-origin resources. For example, to grant access to the resource timing to any origin, use Timing-Allow-Origin: *. Find more about CORS on the MDN Web Docs
Further Reading
Más enlaces, artículos y documentación útiles: