- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- Tracing
- Profileur
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Développeurs
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Checks custom
- Intégrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Checks de service
- IDE Plugins
- Communauté
- Guides
- API
- Application mobile
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Alertes
- Infrastructure
- Métriques
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Conteneurs
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Product Analytics
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Exécuteur de tests intelligent
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- Administration
OpenStack (ancienne version)
Supported OS
Intégration1.13.0
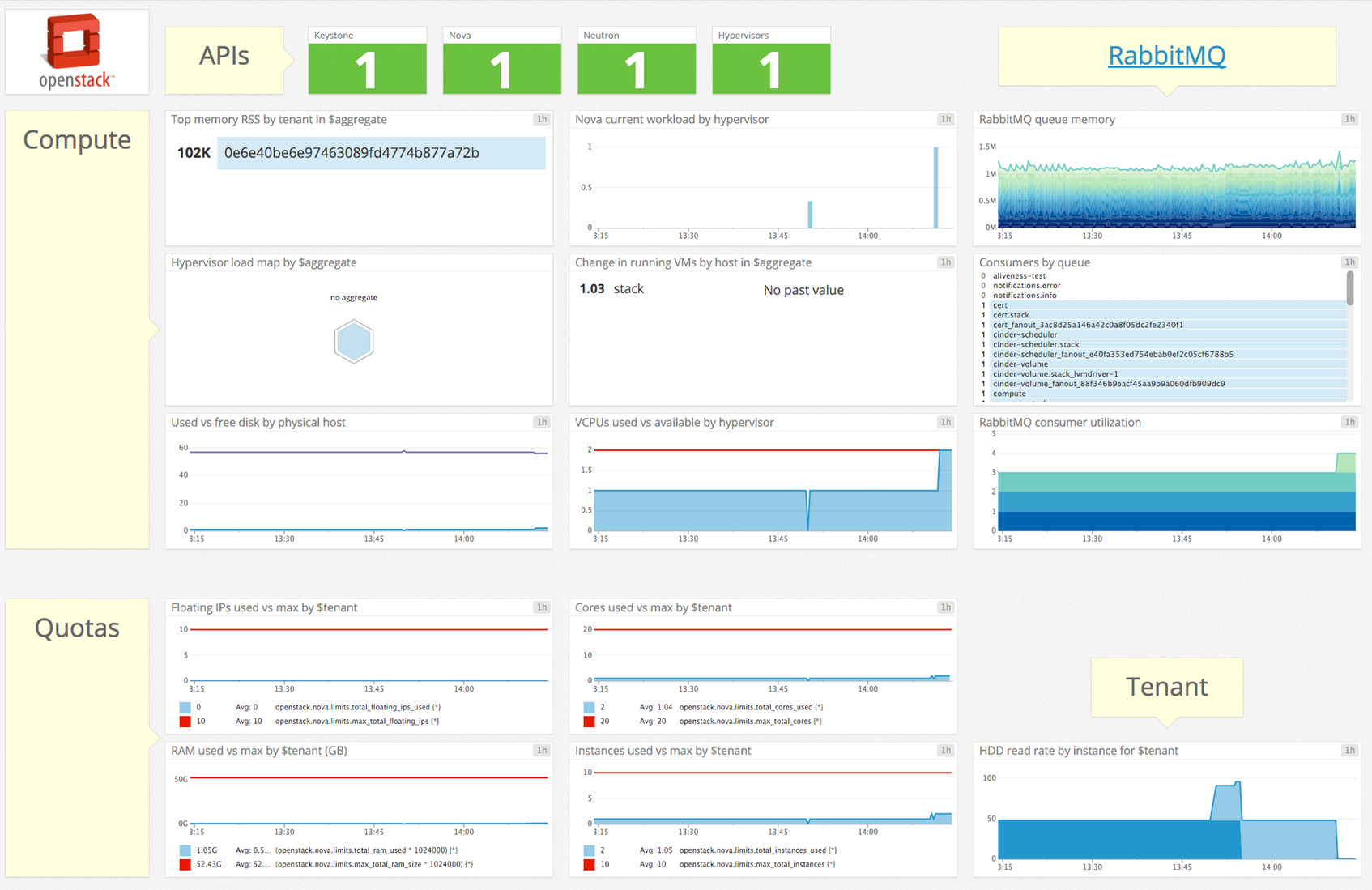
Présentation
Remarque : cette intégration s’applique uniquement à la version 12 et aux versions antérieures d’OpenStack (non conteneurisées). Pour recueillir des métriques pour les versions 13 et ultérieures (conteneurisées), utilisez l’intégration OpenStack Controller.
Recueillez des métriques du service OpenStack en temps réel pour :
- Visualiser et surveiller les états OpenStack
- Être informé des failovers et des événements OpenStack
Configuration
Installation
Pour recueillir vos métriques OpenStack, vous devez installer l’Agent sur vos hosts exécutant des hyperviseurs.
Configuration
Préparer OpenStack
Configurez un rôle et un utilisateur Datadog avec votre serveur d’identité :
openstack role create datadog_monitoring
openstack user create datadog \
--password my_password \
--project my_project_name
openstack role add datadog_monitoring \
--project my_project_name \
--user datadog
Mettez ensuite à jour vos fichiers policy.json afin d’accorder les autorisations nécessaires. role:datadog_monitoring doit pouvoir accéder aux opérations suivantes :
Nova
{
"compute_extension": "aggregates",
"compute_extension": "hypervisors",
"compute_extension": "server_diagnostics",
"compute_extension": "v3:os-hypervisors",
"compute_extension": "v3:os-server-diagnostics",
"compute_extension": "availability_zone:detail",
"compute_extension": "v3:availability_zone:detail",
"compute_extension": "used_limits_for_admin",
"os_compute_api:os-aggregates:index": "rule:admin_api or role:datadog_monitoring",
"os_compute_api:os-aggregates:show": "rule:admin_api or role:datadog_monitoring",
"os_compute_api:os-hypervisors": "rule:admin_api or role:datadog_monitoring",
"os_compute_api:os-server-diagnostics": "rule:admin_api or role:datadog_monitoring",
"os_compute_api:os-used-limits": "rule:admin_api or role:datadog_monitoring"
}
Neutron
{
"get_network": "rule:admin_or_owner or rule:shared or rule:external or rule:context_is_advsvc or role:datadog_monitoring"
}
Keystone
{
"identity:get_project": "rule:admin_required or project_id:%(target.project.id)s or role:datadog_monitoring",
"identity:list_projects": "rule:admin_required or role:datadog_monitoring"
}
Vous devrez peut-être redémarrer vos services d’API Keystone, Neutron et Nova pour que les modifications apportées au fichier policy.json prennent effet.
Remarque : l’installation de l’intégration OpenStack est susceptible d’augmenter le nombre de machines virtuelles surveillées par Datadog, ce qui peut avoir une incidence sur votre facturation. Pour en savoir plus, consultez la FAQ sur la facturation.
Configuration de l’Agent
Configurez l’Agent Datadog de façon à le connecter à votre serveur Keystone, puis spécifiez les projets à surveiller. Modifiez le fichier
openstack.d/conf.yamldans le dossierconf.d/à la racine du répertoire de configuration de votre Agent en ajoutant la configuration ci-dessous. Consultez le fichier d’exemple openstack.d/conf.yaml pour découvrir toutes les options de configuration disponibles :init_config: ## @param keystone_server_url - string - required ## Where your identity server lives. ## Note that the server must support Identity API v3 # keystone_server_url: "https://<KEYSTONE_SERVER_ENDPOINT>:<PORT>/" instances: ## @param name - string - required ## Unique identifier for this instance. # - name: "<INSTANCE_NAME>" ## @param user - object - required ## User credentials ## Password authentication is the only auth method supported. ## `user` object expects the parameter `username`, `password`, ## and `user.domain.id`. ## ## `user` should resolve to a structure like: ## ## {'password': '<PASSWORD>', 'name': '<USERNAME>', 'domain': {'id': '<DOMAINE_ID>'}} # user: password: "<PASSWORD>" name: datadog domain: id: "<DOMAINE_ID>"
Collecte de logs
La collecte de logs est désactivée par défaut dans l’Agent Datadog. Vous pouvez l’activer dans
datadog.yaml:logs_enabled: trueAjoutez ce bloc de configuration à votre fichier
openstack.d/conf.yamlpour commencer à recueillir vos logs Openstack :logs: - type: file path: "<LOG_FILE_PATH>" source: openstackModifiez la valeur du paramètre
pathet configurez-le pour votre environnement. Consultez le fichier d’exemple openstack.d/conf.yaml pour découvrir toutes les options de configuration disponibles.
Validation
Lancez la sous-commande status de l’Agent et cherchez openstack dans la section Checks.
Données collectées
Métriques
| openstack.nova.current_workload (gauge) | Current workload on the Nova hypervisor |
| openstack.nova.disk_available_least (gauge) | Disk available for the Nova hypervisor Shown as gibibyte |
| openstack.nova.free_disk_gb (gauge) | Free disk on the Nova hypervisor Shown as gibibyte |
| openstack.nova.free_ram_mb (gauge) | Free RAM on the Nova hypervisor Shown as mebibyte |
| openstack.nova.hypervisor_load.1 (gauge) | The average hypervisor load over one minute. |
| openstack.nova.hypervisor_load.15 (gauge) | The average hypervisor load over fifteen minutes. |
| openstack.nova.hypervisor_load.5 (gauge) | The average hypervisor load over five minutes. |
| openstack.nova.limits.max_image_meta (gauge) | The maximum allowed image metadata definitions for this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.max_personality (gauge) | The maximum allowed personalities for this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.max_personality_size (gauge) | The maximum size of a single personality allowed for this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.max_security_group_rules (gauge) | The maximum number of security group rules allowed for this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.max_security_groups (gauge) | The maximum number of security groups allowed for this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.max_server_meta (gauge) | The maximum allowed service metadata definitions for this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.max_total_cores (gauge) | The maximum allowed cores for this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.max_total_floating_ips (gauge) | The maximum allowed floating IPs for this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.max_total_instances (gauge) | The maximum number of instances allowed for this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.max_total_keypairs (gauge) | The maximum allowed key pairs allowed for this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.max_total_ram_size (gauge) | The max allowed RAM size for this tenant in megabytes (MB) Shown as mebibyte |
| openstack.nova.limits.total_cores_used (gauge) | The total cores used by this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.total_floating_ips_used (gauge) | The total floating IPs used by this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.total_instances_used (gauge) | The total instances used by this tenant |
| openstack.nova.limits.total_ram_used (gauge) | The current RAM used by this tenant in megabytes (MB) Shown as mebibyte |
| openstack.nova.limits.total_security_groups_used (gauge) | The total number of security groups used by this tenant |
| openstack.nova.local_gb (gauge) | The size in GB of the ephemeral disk present on this hypervisor host Shown as gibibyte |
| openstack.nova.local_gb_used (gauge) | The size in GB of disk used on this hypervisor host Shown as gibibyte |
| openstack.nova.memory_mb (gauge) | The size in MB of RAM present on this hypervisor host Shown as mebibyte |
| openstack.nova.memory_mb_used (gauge) | The size in MB of RAM used on this hypervisor host Shown as mebibyte |
| openstack.nova.running_vms (gauge) | Number of running VMs on this hypervisor host |
| openstack.nova.server.cpu0_time (gauge) | CPU time in nanoseconds of this virtual CPU Shown as nanosecond |
| openstack.nova.server.hdd_errors (gauge) | The number of errors seen by the server when accessing an HDD device |
| openstack.nova.server.hdd_read (gauge) | Number of bytes read from an HDD device by this server Shown as byte |
| openstack.nova.server.hdd_read_req (gauge) | The number of read requests made to an HDD device by this server |
| openstack.nova.server.hdd_write (gauge) | Number of bytes written to an HDD device by this server Shown as byte |
| openstack.nova.server.hdd_write_req (gauge) | The number of write requests made to an HDD device by this server |
| openstack.nova.server.memory (gauge) | The amount of memory in MB provisioned for this server Shown as mebibyte |
| openstack.nova.server.memory_actual (gauge) | The amount of memory in MB provisioned for this server Shown as mebibyte |
| openstack.nova.server.memory_rss (gauge) | The amount of memory used by the processes of this server that is not associated with disk pages - such as stack and heap memory Shown as mebibyte |
| openstack.nova.server.vda_errors (gauge) | The number of errors seen by the server when accessing a VDA device |
| openstack.nova.server.vda_read (gauge) | Number of bytes read from a VDA device by this server Shown as byte |
| openstack.nova.server.vda_read_req (gauge) | The number of read requests made to a VDA device by this server |
| openstack.nova.server.vda_write (gauge) | Number of bytes written to a VDA device by this server Shown as byte |
| openstack.nova.server.vda_write_req (gauge) | The number of write requests made to a VDA device by this server |
| openstack.nova.vcpus (gauge) | Number of vCPUs available on this hypervisor host |
| openstack.nova.vcpus_used (gauge) | Number of vCPUS used on this hypervisor host |
Événements
Le check OpenStack n’inclut aucun événement.
Checks de service
openstack.neutron.api.up
Renvoie CRITICAL si l’Agent n’est pas capable d’interroger l’API Neutron, renvoie UNKNOWN en cas de problème avec l’API Keystone ou renvoie OK pour les autres cas.
Statuses: ok, critical, unknown
openstack.nova.api.up
Renvoie CRITICAL si l’Agent n’est pas capable d’interroger l’API Nova, renvoie UNKNOWN en cas de problème avec l’API Keystone ou renvoie OK pour les autres cas.
Statuses: ok, critical, unknown
openstack.keystone.api.up
Renvoie CRITICAL si l’Agent n’est pas capable d’interroger l’API Keystone. Si ce n’est pas le cas, renvoie OK.
Statuses: ok, critical
openstack.nova.hypervisor.up
Renvoie UNKNOWN si l’Agent n’est pas capable d’obtenir l’état de l’hyperviseur, renvoie CRITICAL si l’hyperviseur est indisponible ou renvoie OK pour les autres cas.
Statuses: ok, critical, unknown
openstack.neutron.network.up
Renvoie UNKNOWN si l’Agent n’est pas capable d’obtenir l’état du réseau, renvoie CRITICAL si le réseau est indisponible ou renvoie OK pour les autres cas.
Statuses: ok, critical, unknown
Dépannage
Besoin d’aide ? Contactez l’assistance Datadog.
Pour aller plus loin
Documentation, liens et articles supplémentaires utiles :
