- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- Tracing
- Profileur
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Développeurs
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Checks custom
- Intégrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Checks de service
- IDE Plugins
- Communauté
- Guides
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Application mobile
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Alertes
- Infrastructure
- Métriques
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Conteneurs
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Product Analytics
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Exécuteur de tests intelligent
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- Administration
Trace An LLM Application
Cette page n'est pas encore disponible en français, sa traduction est en cours.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
LLM Observability is not available in the selected site () at this time.
Overview
This guide uses the LLM Observability SDKs for Python and Node.js. If your application is written in another language, you can create traces by calling the API instead.
Setup
Jupyter notebooks
To better understand LLM Observability terms and concepts, you can explore the examples in the LLM Observability Jupyter Notebooks repository. These notebooks provide a hands-on experience, and allow you to apply these concepts in real time.
Trace an LLM application
To generate an LLM Observability trace, you can run a Python or Node.js script.
Prerequisites
- LLM Observability requires a Datadog API key. For more information, see the instructions for creating an API key.
- The following example script uses OpenAI, but you can modify it to use a different provider. To run the script as written, you need:
- An OpenAI API key stored in your environment as
OPENAI_API_KEY. To create one, see Account Setup and Set up your API key in the official OpenAI documentation. - The OpenAI Python library installed. See Setting up Python in the official OpenAI documentation for instructions.
- An OpenAI API key stored in your environment as
Install the SDK and OpenAI packages:
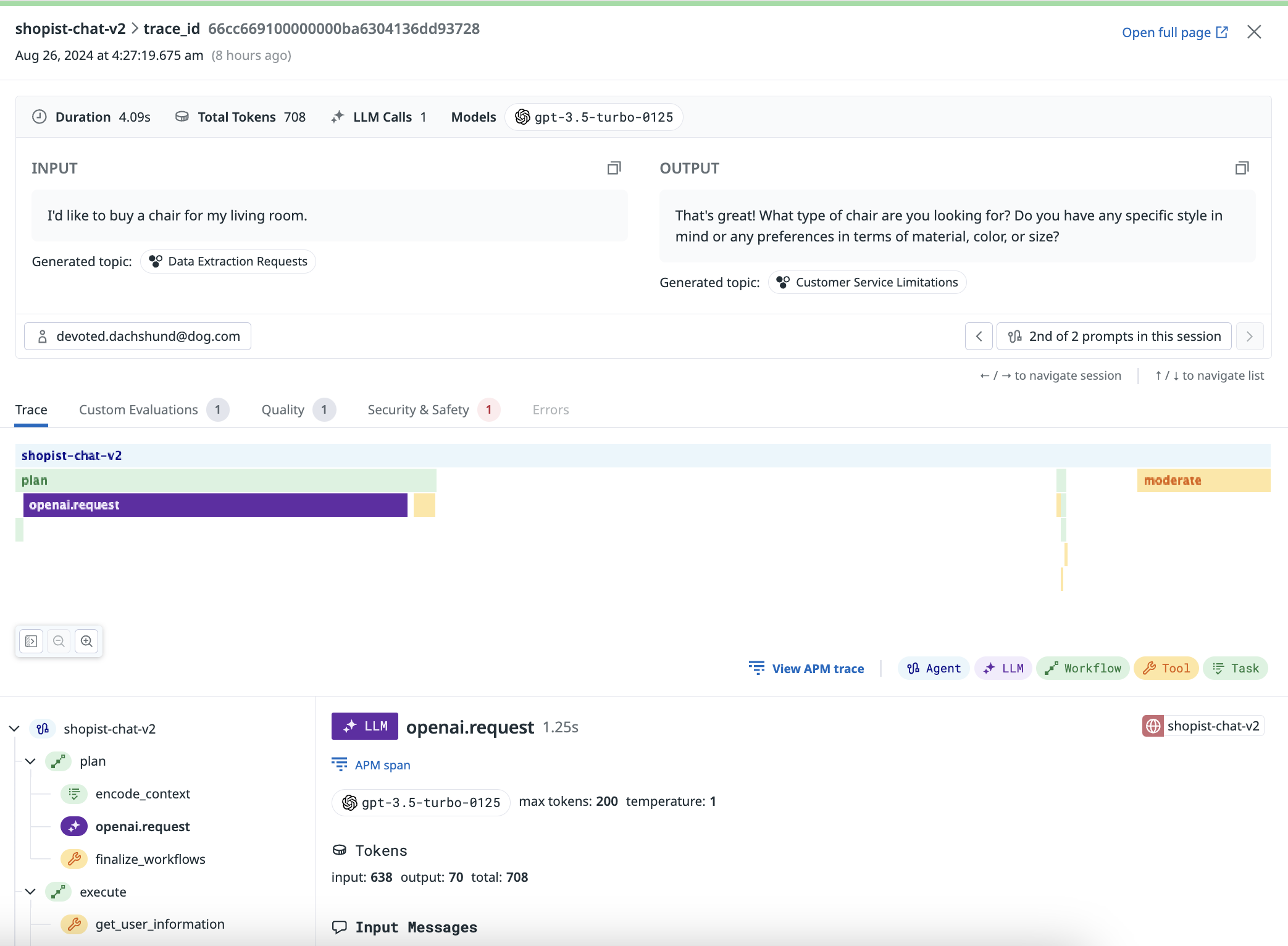
pip install ddtrace pip install openaiCreate a script, which makes a single OpenAI call.
import os from openai import OpenAI oai_client = OpenAI(api_key=os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY")) completion = oai_client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=[ {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful customer assistant for a furniture store."}, {"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to buy a chair for my living room."}, ], )Run the script with the following shell command. This sends a trace of the OpenAI call to Datadog.
DD_LLMOBS_ENABLED=1 DD_LLMOBS_ML_APP=onboarding-quickstart \ DD_API_KEY=<YOUR_DATADOG_API_KEY> DD_SITE=<YOUR_DD_SITE> \ DD_LLMOBS_AGENTLESS_ENABLED=1 ddtrace-run python quickstart.pyReplace
<YOUR_DATADOG_API_KEY>with your Datadog API key, and replace<YOUR_DD_SITE>with your Datadog site.For more information about required environment variables, see the SDK documentation.
Install the SDK and OpenAI packages:
npm install dd-trace npm install openaiCreate a script, which makes a single OpenAI call.
const { OpenAI } = require('openai'); const oaiClient = new OpenAI(process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY); function main () { const completion = await oaiClient.chat.completions.create({ model: 'gpt-3.5-turbo', messages: [ { role: 'system', content: 'You are a helpful customer assistant for a furniture store.' }, { role: 'user', content: 'I\'d like to buy a chair for my living room.' }, ] }); } main();Run the script with the following shell command. This sends a trace of the OpenAI call to Datadog.
DD_LLMOBS_ENABLED=1 DD_LLMOBS_ML_APP=onboarding-quickstart \ DD_API_KEY=<YOUR_DATADOG_API_KEY> DD_SITE=<YOUR_DD_SITE> \ DD_LLMOBS_AGENTLESS_ENABLED=1 NODE_OPTIONS="--import dd-trace/initialize.mjs" node quickstart.jsReplace
<YOUR_DATADOG_API_KEY>with your Datadog API key, and replace<YOUR_DD_SITE>with your Datadog site.For more information about required environment variables, see the SDK documentation.
Note: DD_LLMOBS_AGENTLESS_ENABLED is only required if you do not have the Datadog Agent running. If the Agent is running in your production environment, make sure this environment variable is unset.
View the trace of your LLM call on the Traces tab of the LLM Observability page in Datadog.
The trace you see is composed of a single LLM span. The ddtrace-run or NODE_OPTIONS="--import dd-trace/initialize.mjs" command automatically traces your LLM calls from Datadog’s list of supported integrations.
If your application consists of more elaborate prompting or complex chains or workflows involving LLMs, you can trace it using the Setup documentation and the SDK documentation.
Trace an LLM application in AWS Lambda
The following steps generate an LLM Observability trace in an AWS Lambda environment and create an Amazon Bedrock based chatbot running with LLM Observability in AWS Lambda.
- Create a Lambda function chatbot using Amazon Bedrock.
- Instrument your Lambda function:
- Open a Cloudshell
- Install the Datadog CLI client
npm install -g @datadog/datadog-ci- Set the Datadog API key and site
If you already have or prefer to use a secret in Secrets Manager, you can set the API key by using the secret ARN:export DD_SITE=<YOUR_DD_SITE> export DD_API_KEY=<YOUR_DATADOG_API_KEY>export DATADOG_API_KEY_SECRET_ARN=<DATADOG_API_KEY_SECRET_ARN>- Instrument your Lambda function with LLM Observability (this requires at least version 77 of the Datadog Extension layer).
datadog-ci lambda instrument -f <YOUR_LAMBDA_FUNCTION_NAME> -r <AWS_REGION> -v 109 -e 78 --llmobs <YOUR_LLMOBS_ML_APP>datadog-ci lambda instrument -f <YOUR_LAMBDA_FUNCTION_NAME> -r <AWS_REGION> -v 125 -e 78 --llmobs <YOUR_LLMOBS_ML_APP>
- Verify that your function was instrumented.
- In the Datadog UI, navigate to
Infrastructure > Serverless - Search for the name of your function.
- Click on it to open the details panel.
- Under the
Configurationtab are the details of the Lambda function, attached layers, and a list ofDD_Datadog-related environment variables under theDatadog Environment Variablessection.
- In the Datadog UI, navigate to
- Invoke your Lambda function and verify that LLM Observability traces are visible in the Datadog UI.
Force flushing traces
For either serverless environments other than AWS Lambda or issues seeing traces from AWS Lambdas, use the flush method to ensure traces are flushed before the process exits.
from ddtrace.llmobs import LLMObs
def handler():
# function body
LLMObs.flush()
import tracer from 'dd-trace';
const llmobs = tracer.llmobs;
export const handler = async (event) => {
// your function body
llmobs.flush();
};
Further Reading
Documentation, liens et articles supplémentaires utiles: