- 重要な情報
- はじめに
- Datadog
- Datadog サイト
- DevSecOps
- AWS Lambda のサーバーレス
- エージェント
- インテグレーション
- コンテナ
- ダッシュボード
- アラート設定
- ログ管理
- トレーシング
- プロファイラー
- タグ
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic モニタリング
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- 用語集
- Standard Attributes
- ガイド
- インテグレーション
- エージェント
- OpenTelemetry
- 開発者
- 認可
- DogStatsD
- カスタムチェック
- インテグレーション
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- サービスのチェック
- IDE インテグレーション
- コミュニティ
- ガイド
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- モバイルアプリケーション
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- アプリ内
- Service Management
- インフラストラクチャー
- アプリケーションパフォーマンス
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- データベース モニタリング
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility (CI/CDの可視化)
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- セキュリティ
- セキュリティの概要
- Cloud SIEM
- クラウド セキュリティ マネジメント
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- ログ管理
- Observability Pipelines(観測データの制御)
- ログ管理
- 管理
Databricks の Data Jobs Monitoring を有効にする
Data Jobs Monitoring は、Apache Spark と Databricks のジョブのパフォーマンスと信頼性を視覚化します。
セットアップ
以下の手順に従って、Databricks の Data Jobs Monitoring を有効にしてください。
- Databricks API トークンを使って Datadog-Databricks インテグレーションを構成します。
- Databricks クラスターに Datadog Agent をインストールします。
Configure the Datadog-Databricks integration
In your Databricks workspace, click on your profile in the top right corner and go to Settings. Select Developer in the left side bar. Next to Access tokens, click Manage.
Click Generate new token, enter “Datadog Integration” in the Comment field, remove the default value in Lifetime (days), and click Generate. Take note of your token.
Important:
- Make sure you delete the default value in Lifetime (days) so that the token doesn’t expire and the integration doesn’t break.
- Ensure the account generating the token has CAN VIEW access for the Databricks jobs and clusters you want to monitor.
As an alternative, follow the official Databricks documentation to generate access token for a service principal.
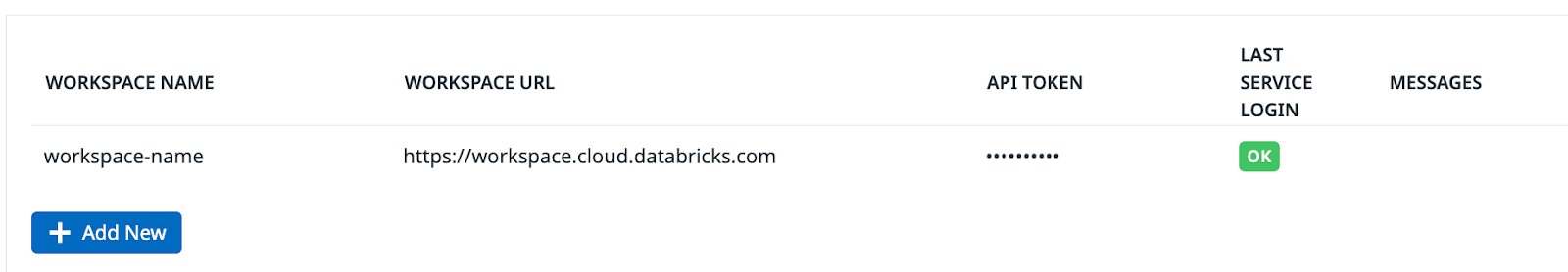
Datadog で、Databricks インテグレーションタイルを開きます。
On the Configure tab, click Add New.
ワークスペース名、Databricks ワークスペース URL、生成した Databricks トークンを入力します。
Datadog Agent を Databricks クラスターにインストールします。
Agent を全体的にインストールするか、特定の Databricks クラスターにインストールするかを選択できます。
In Databricks, click your display name (email address) in the upper right corner of the page.
Select Settings and click the Compute tab.
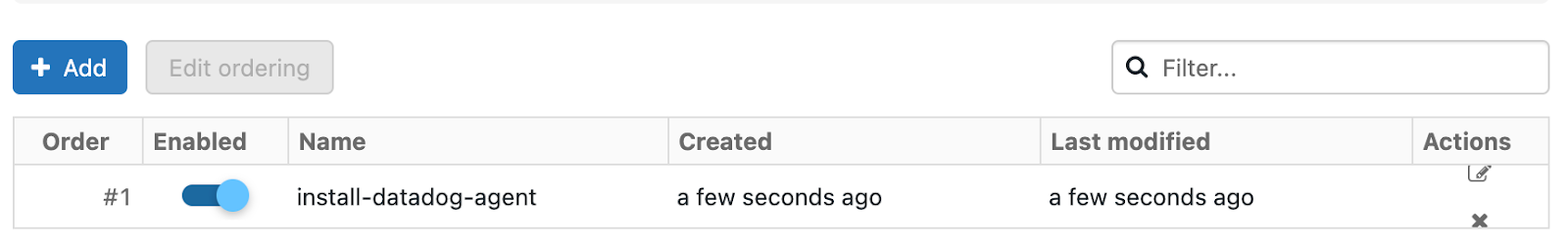
In the All purpose clusters section, next to Global init scripts, click Manage.
Click Add. Name your script. Then, in the Script field, copy and paste the following script, remembering to replace the placeholders with your parameter values.
#!/bin/bash # Required parameters export DD_API_KEY=<YOUR API KEY> export DD_SITE=<YOUR DATADOG SITE> export DATABRICKS_WORKSPACE="<YOUR WORKSPACE NAME>" # Download and run the latest init script bash -c "$(curl -L https://dd-data-jobs-monitoring-setup.s3.amazonaws.com/scripts/databricks/databricks_init_latest.sh)" || trueThe script above sets the required parameters, downloads and runs the latest init script for Data Jobs Monitoring in Databricks. If you want to pin your script to a specific version, you can replace the file name in the URL with
databricks_init_1.3.1.shto use the last stable version.すべての新しいクラスターと再起動したクラスターでスクリプトを有効にするには、Enabled に切り替えます。
Add をクリックします。
Set the required init script parameters
Provide the values for the init script parameters at the beginning of the global init script.
export DD_API_KEY=<YOUR API KEY>
export DD_SITE=<YOUR DATADOG SITE>
export DATABRICKS_WORKSPACE="<YOUR WORKSPACE NAME>"
Optionally, you can also set other init script parameters and Datadog environment variables here, such as DD_ENV and DD_SERVICE. The script can be configured using the following parameters:
| 変数 | 説明 | デフォルト |
|---|---|---|
| DD_API_KEY | Datadog API キー。 | |
| DD_SITE | Your Datadog site. | |
| DATABRICKS_WORKSPACE | Name of your Databricks Workspace. It should match the name provided in the Datadog-Databricks integration step. Enclose the name in double quotes if it contains whitespace. | |
| DRIVER_LOGS_ENABLED | Collect spark driver logs in Datadog. | false |
| WORKER_LOGS_ENABLED | Collect spark workers logs in Datadog. | false |
| DD_DJM_ADD_LOGS_TO_FAILURE_REPORT | Include init script logs for debugging when reporting a failure back to Datadog. | false |
In Databricks, create a init script file in Workspace with the following content. Be sure to make note of the file path.
#!/bin/bash # Download and run the latest init script bash -c "$(curl -L https://dd-data-jobs-monitoring-setup.s3.amazonaws.com/scripts/databricks/databricks_init_latest.sh)" || trueThe script above downloads and runs the latest init script for Data Jobs Monitoring in Databricks. If you want to pin your script to a specific version, you can replace the file name in the URL with
databricks_init_1.3.1.shto use the last stable version.On the cluster configuration page, click the Advanced options toggle.
ページ下部の Init Scripts タブに移動します。
- **Destination** ドロップダウンで、`Workspace` を選択します。 - **Init script path** に、init スクリプトのパスを入力します。 - **Add** をクリックします。
Set the required init script parameters
Databricks のクラスター構成ページで、Advanced options トグルをクリックします。
ページ下部の Spark タブに移動します。
In the Environment variables textbox, provide the values for the init script parameters.
DD_API_KEY=<YOUR API KEY> DD_SITE=<YOUR DATADOG SITE> DATABRICKS_WORKSPACE="<YOUR WORKSPACE NAME>"Optionally, you can also set other init script parameters and Datadog environment variables here, such as
DD_ENVandDD_SERVICE. The script can be configured using the following parameters:
| 変数 | 説明 | デフォルト |
|---|---|---|
| DD_API_KEY | Datadog API キー。 | |
| DD_SITE | Your Datadog site. | |
| DATABRICKS_WORKSPACE | Name of your Databricks Workspace. It should match the name provided in the Datadog-Databricks integration step. Enclose the name in double quotes if it contains whitespace. | |
| DRIVER_LOGS_ENABLED | Collect spark driver logs in Datadog. | false |
| WORKER_LOGS_ENABLED | Collect spark workers logs in Datadog. | false |
| DD_DJM_ADD_LOGS_TO_FAILURE_REPORT | Include init script logs for debugging when reporting a failure back to Datadog. | false |
- Confirm をクリックします。
検証
Datadog で Data Jobs Monitoring ページを表示すると、Databricks の全ジョブのリストが表示されます。
高度な構成
ランタイムでのタグスパン
ランタイムで Spark スパンにタグを設定できます。これらのタグは、タグが追加された後に開始するスパンにのみ適用されます。
// 次のすべての Spark 計算のタグを追加します
sparkContext.setLocalProperty("spark.datadog.tags.key", "value")
spark.read.parquet(...)
ランタイムタグを削除するには
// 次のすべての Spark 計算のタグを削除します
sparkContext.setLocalProperty("spark.datadog.tags.key", null)
Aggregate cluster metrics from one-time job runs
This configuration is applicable if you want cluster resource utilization data about your jobs and create a new job and cluster for each run via the one-time run API endpoint (common when using orchestration tools outside of Databricks such as Airflow or Azure Data Factory).
If you are submitting Databricks Jobs via the one-time run API endpoint, each job run will have a unique job ID. This can make it difficult to group and analyze cluster metrics for jobs that use ephemeral clusters. To aggregate cluster utilization from the same job and assess performance across multiple runs, you must set the DD_JOB_NAME variable inside the spark_env_vars of every new_cluster to the same value as your request payload’s run_name.
Here’s an example of a one-time job run request body:
{
"run_name": "Example Job",
"idempotency_token": "8f018174-4792-40d5-bcbc-3e6a527352c8",
"tasks": [
{
"task_key": "Example Task",
"description": "Description of task",
"depends_on": [],
"notebook_task": {
"notebook_path": "/Path/to/example/task/notebook",
"source": "WORKSPACE"
},
"new_cluster": {
"num_workers": 1,
"spark_version": "13.3.x-scala2.12",
"node_type_id": "i3.xlarge",
"spark_env_vars": {
"DD_JOB_NAME": "Example Job"
}
}
}
]
}その他の参考資料
お役に立つドキュメント、リンクや記事: