- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Google Cloud Platform
Overview
Use this guide to get started monitoring your Google Cloud environment. This approach simplifies the setup for Google Cloud environments with multiple projects, allowing you to maximize your monitoring coverage.
See the full list of Google Cloud integrations
See the full list of Google Cloud integrations
Datadog's Google Cloud integration collects all Google Cloud metrics. Datadog continually updates the docs to show every dependent integration, but the list of integrations is sometimes behind the latest cloud services metrics and services.
If you don’t see an integration for a specific Google Cloud service, reach out to Datadog Support.
| Integration | Description |
|---|---|
| App Engine | PaaS (platform as a service) to build scalable applications |
| BigQuery | Enterprise data warehouse |
| Bigtable | NoSQL Big Data database service |
| Cloud SQL | MySQL database service |
| Cloud APIs | Programmatic interfaces for all Google Cloud Platform services |
| Cloud Armor | Network security service to help protect against denial-of-service and web attacks |
| Cloud Composer | A fully managed workflow orchestration service |
| Cloud Dataproc | A cloud service for running Apache Spark and Apache Hadoop clusters |
| Cloud Dataflow | A fully-managed service for transforming and enriching data in stream and batch modes |
| Cloud Filestore | High-performance, fully managed file storage |
| Cloud Firestore | A flexible, scalable database for mobile, web, and server development |
| Cloud Interconnect | Hybrid connectivity |
| Cloud IoT | Secure device connection and management |
| Cloud Load Balancing | Distribute load-balanced compute resources |
| Cloud Logging | Real-time log management and analysis |
| Cloud Memorystore for Redis | A fully managed in-memory data store service |
| Cloud Router | Exchange routes between your VPC and on-premises networks by using BGP |
| Cloud Run | Managed compute platform that runs stateless containers over HTTP |
| Cloud Security Command Center | Security Command Center is a threat reporting service |
| Cloud Tasks | Distributed task queues |
| Cloud TPU | Train and run machine learning models |
| Compute Engine | High performance virtual machines |
| Container Engine | Kubernetes, managed by Google |
| Datastore | NoSQL database |
| Firebase | Mobile platform for application development |
| Functions | Serverless platform for building event-based microservices |
| Kubernetes Engine | Cluster manager and orchestration system |
| Machine Learning | Machine learning services |
| Private Service Connect | Access managed services with private VPC connections |
| Pub/Sub | Real-time messaging service |
| Spanner | Horizontally scalable, globally consistent, relational database service |
| Storage | Unified object storage |
| Vertex AI | Build, train, and deploy custom machine learning (ML) models |
| VPN | Managed network functionality |
Setup
Set up Datadog’s Google Cloud integration to collect metrics and logs from your Google Cloud services.
Prerequisites
If your organization restricts identities by domain, you must add Datadog’s customer identity as an allowed value in your policy. Datadog’s customer identity:
C0147pk0iService account impersonation and automatic project discovery relies on you having certain roles and APIs enabled to monitor projects. Before you start, ensure the following APIs are enabled for each of the projects you want to monitor:
- Cloud Monitoring API
- Allows Datadog to query your Google Cloud metric data.
- Compute Engine API
- Allows Datadog to discover compute instance data.
- Cloud Asset API
- Allows Datadog to request Google Cloud resources and link relevant labels to metrics as tags.
- Cloud Resource Manager API
- Allows Datadog to append metrics with the correct resources and tags.
- IAM API
- Allows Datadog to authenticate with Google Cloud.
- Cloud Billing API
- Allows developers to manage billing for their Google Cloud Platform projects programmatically. See the Cloud Cost Management (CCM) documentation for more information.
- Ensure that any projects being monitored are not configured as scoping projects that pull in metrics from multiple other projects.
Metric collection
Installation
Best practices for monitoring multiple projects
Enable per-project cost and API quota attribution
By default, Google Cloud attributes the cost of monitoring API calls, as well as API quota usage, to the project containing the service account for this integration. As a best practice for Google Cloud environments with multiple projects, enable per-project cost attribution of monitoring API calls and API quota usage. With this enabled, costs and quota usage are attributed to the project being queried, rather than the project containing the service account. This provides visibility into the monitoring costs incurred by each project, and also helps to prevent reaching API rate limits.
To enable this feature:
- Ensure that the Datadog service account has the Service Usage Consumer role at the desired scope (folder or organization).
- Click the Enable Per Project Quota toggle in the Projects tab of the Google Cloud integration page.
Validation
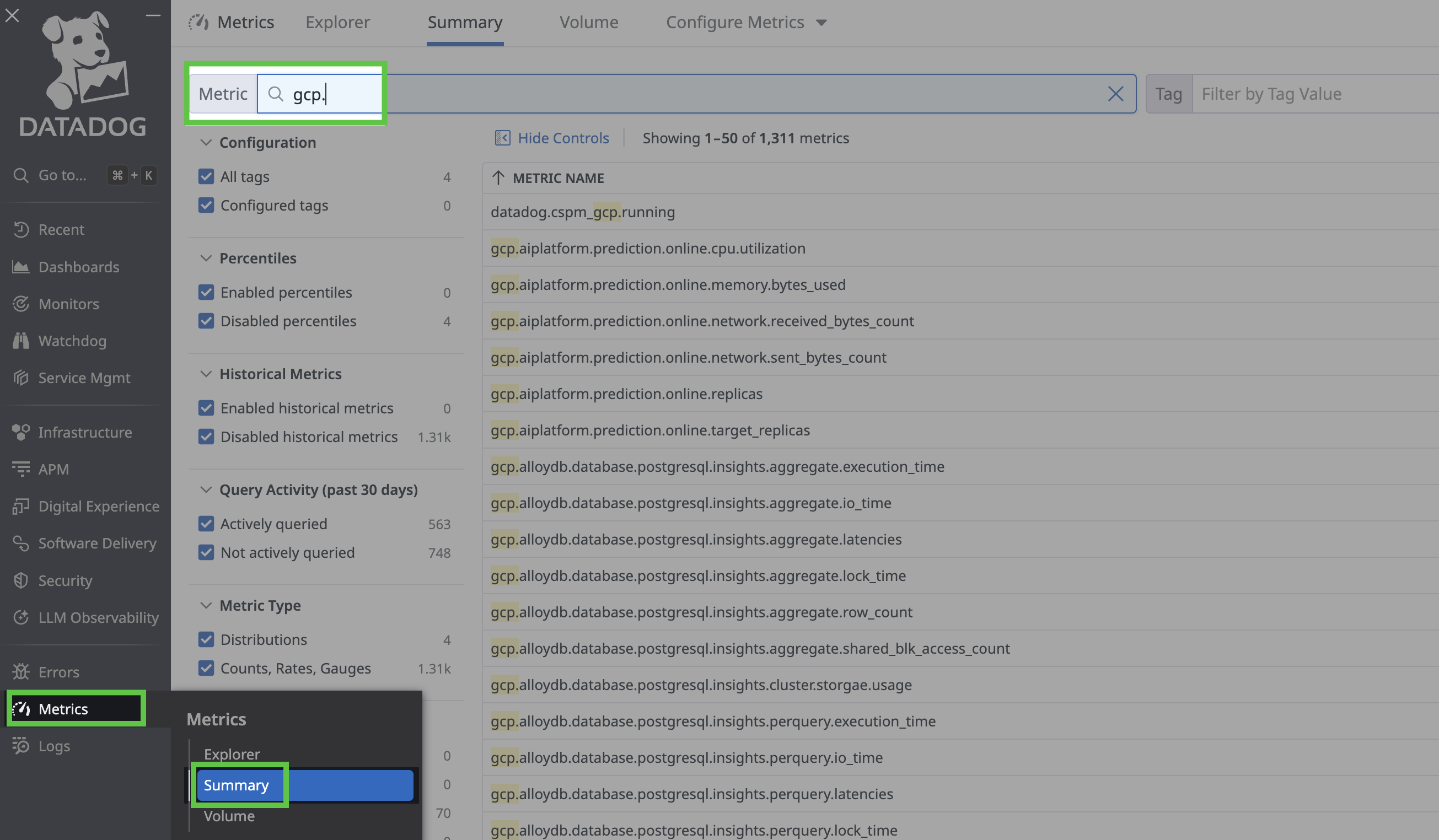
To view your metrics, use the left menu to navigate to Metrics > Summary and search for gcp:
Configuration
Limit metric collection by metric namespace
Limit metric collection by metric namespace
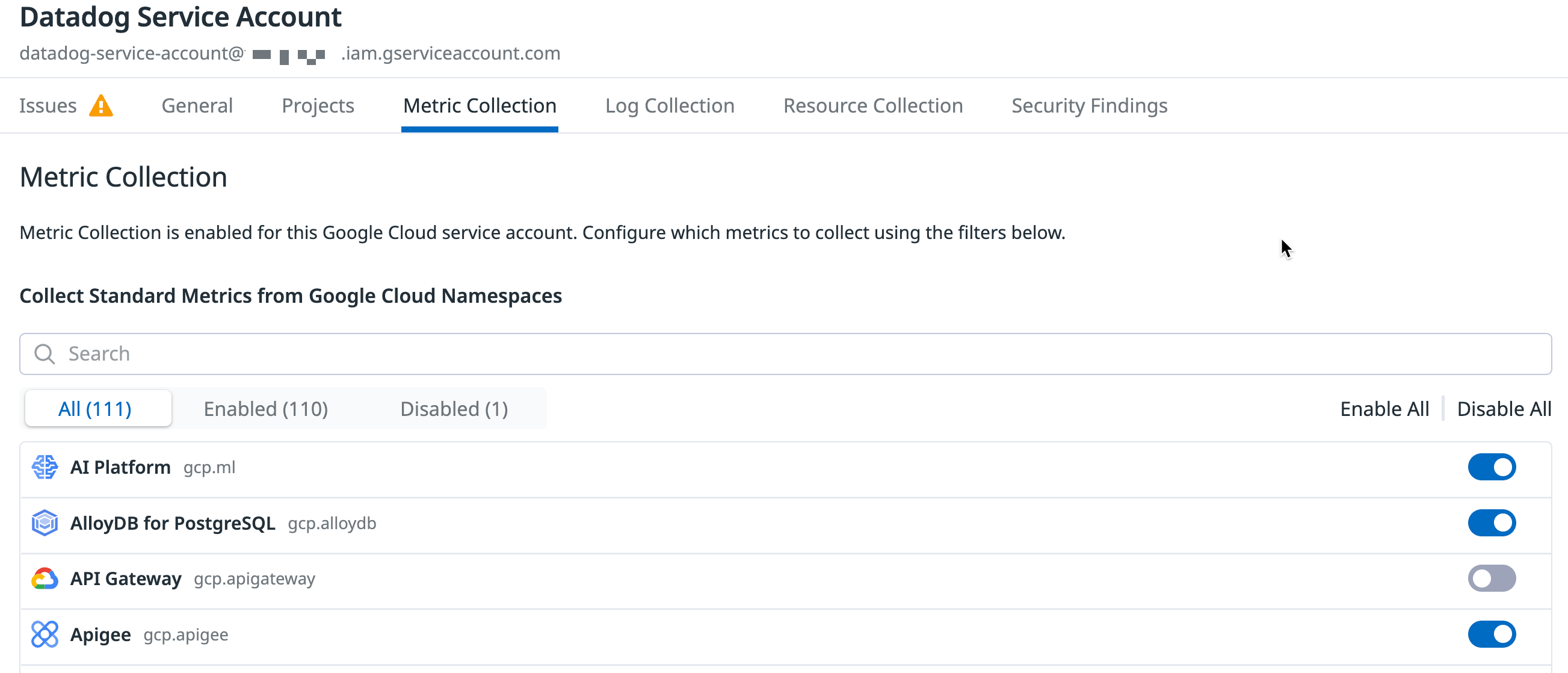
Optionally, you can choose which Google Cloud services you monitor with Datadog. Configuring metrics collection for specific Google services lets you optimize your Google Cloud Monitoring API costs, while retaining visibility into your critical services.
Under the Metric Collection tab in Datadog’s Google Cloud integration page, unselect the metric namespaces to exclude. You can also choose to disable collection of all metric namespaces.
Limit metric collection by tag
Limit metric collection by tag
By default, you’ll see all your Google Compute Engine (GCE) instances in Datadog’s infrastructure overview. Datadog automatically tags them with GCE host tags and any GCE labels you may have added.
Optionally, you can use tags to limit the instances that are pulled into Datadog. Under a project’s Metric Collection tab, enter the tags in the Limit Metric Collection Filters textbox. Only hosts that match one of the defined tags are imported into Datadog. You can use wildcards (? for single character, * for multi-character) to match many hosts, or ! to exclude certain hosts. This example includes all c1* sized instances, but excludes staging hosts:
datadog:monitored,env:production,!env:staging,instance-type:c1.*
See Google’s Organize resources using labels page for more details.
Leveraging the Datadog Agent
Use the Datadog Agent to collect the most granular, low-latency metrics from your infrastructure. Install the Agent on any host, including GKE, to get deeper insights from the traces and logs it can collect. For more information, see Why should I install the Datadog Agent on my cloud instances?
Log collection
Forward logs from your Google Cloud services to Datadog using Google Cloud Dataflow and the Datadog template. This method provides both compression and batching of events before forwarding to Datadog.
You can use the terraform-gcp-datadog-integration module to manage this infrastructure through Terraform, or follow the instructions in this section to:
- Create a Pub/Sub topic and pull subscription to receive logs from a configured log sink
- Create a custom Dataflow worker service account to provide least privilege to your Dataflow pipeline workers
- Create a log sink to publish logs to the Pub/Sub topic
- Create a Dataflow job using the Datadog template to stream logs from the Pub/Sub subscription to Datadog
You have full control over which logs are sent to Datadog through the logging filters you create in the log sink, including GCE and GKE logs. See Google’s Logging query language page for information about writing filters. For a detailed examination of the created architecture, see Stream logs from Google Cloud to Datadog in the Cloud Architecture Center.
Note: You must enable the Dataflow API to use Google Cloud Dataflow. See Enabling APIs in the Google Cloud documentation for more information.
To collect logs from applications running in GCE or GKE, you can also use the Datadog Agent.
1. Create a Cloud Pub/Sub topic and subscription
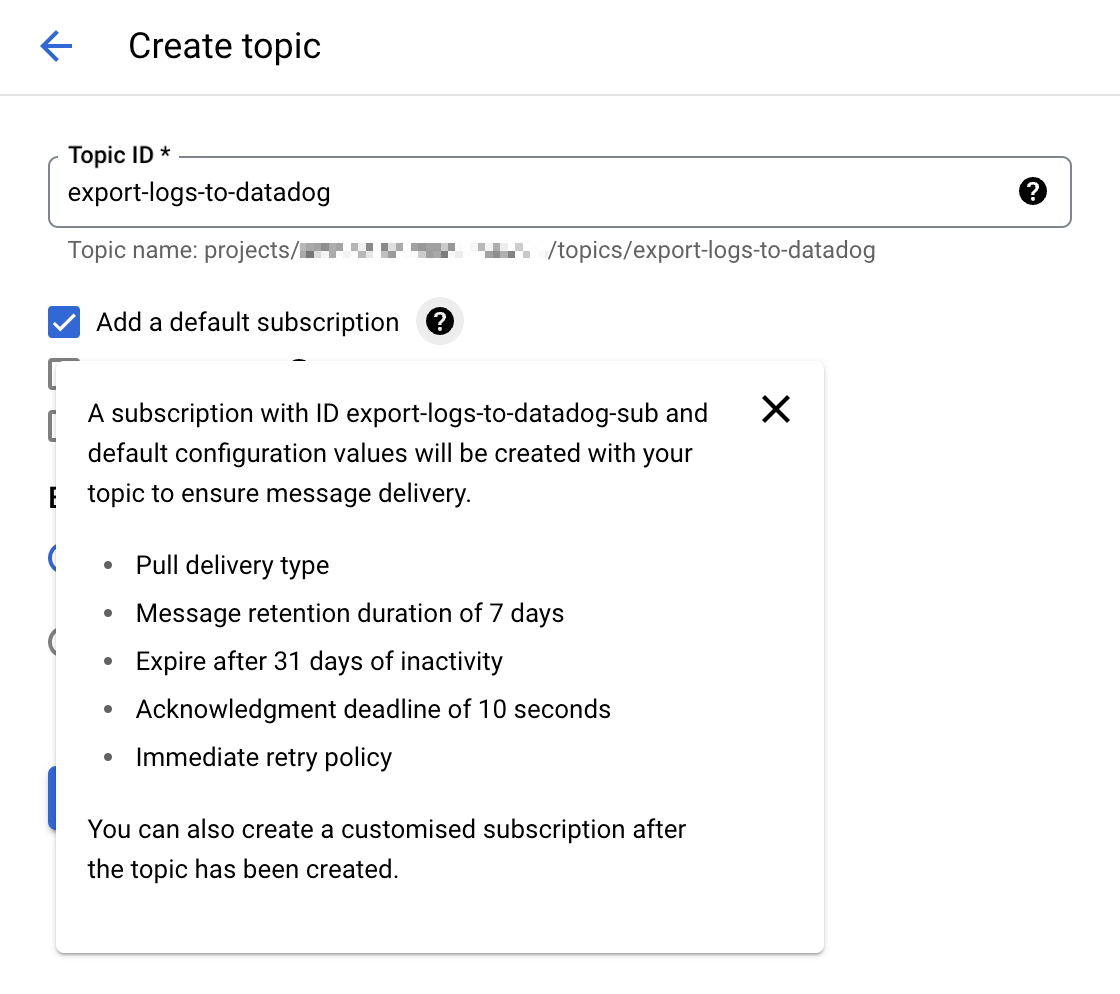
Go to the Cloud Pub/Sub console and create a new topic. Select the option Add a default subscription to simplify the setup.
Note: You can also manually configure a Cloud Pub/Sub subscription with the Pull delivery type. If you manually create your Pub/Sub subscription, leave the
Enable dead letteringbox unchecked. For more details, see Unsupported Pub/Sub features.
Give that topic an explicit name such as
export-logs-to-datadogand click Create.Create an additional topic and default subscription to handle any log messages rejected by the Datadog API. The name of this topic is used within the Datadog Dataflow template as part of the path configuration for the
outputDeadletterTopictemplate parameter. When you have inspected and corrected any issues in the failed messages, send them back to the originalexport-logs-to-datadogtopic by running a Pub/Sub to Pub/Sub template job.Datadog recommends creating a secret in Secret Manager with your valid Datadog API key value, for later use in the Datadog Dataflow template.
Warning: Cloud Pub/Subs are subject to Google Cloud quotas and limitations. If the number of logs you have exceeds those limitations, Datadog recommends you split your logs over several topics. See the Monitor the Pub/Sub Log Forwarding section for information on setting up monitor notifications if you approach those limits.
2. Create a custom Dataflow worker service account
The default behavior for Dataflow pipeline workers is to use your project’s Compute Engine default service account, which grants permissions to all resources in the project. If you are forwarding logs from a Production environment, you should instead create a custom worker service account with only the necessary roles and permissions, and assign this service account to your Dataflow pipeline workers.
- Go to the Service Accounts page in the Google Cloud console and select your project.
- Click CREATE SERVICE ACCOUNT and give the service account a descriptive name. Click CREATE AND CONTINUE.
- Add the roles in the required permissions table and click DONE.
Required permissions
- Dataflow Admin
roles/dataflow.admin
Allow this service account to perform Dataflow administrative tasks.- Dataflow Worker
roles/dataflow.worker
Allow this service account to perform Dataflow job operations.- Pub/Sub Viewer
roles/pubsub.viewer
Allow this service account to view messages from the Pub/Sub subscription with your Google Cloud logs.- Pub/Sub Subscriber
roles/pubsub.subscriber
Allow this service account to consume messages from the Pub/Sub subscription with your Google Cloud logs.- Pub/Sub Publisher
roles/pubsub.publisher
Allow this service account to publish failed messages to a separate subscription, which allows for analysis or resending the logs.- Secret Manager Secret Accessor
roles/secretmanager.secretAccessor
Allow this service account to access the Datadog API key in Secret Manager.- Storage Object Admin
roles/storage.objectAdmin
Allow this service account to read and write to the Cloud Storage bucket specified for staging files.
Note: If you don’t create a custom service account for the Dataflow pipeline workers, ensure that the default Compute Engine service account has the required permissions above.
3. Export logs from Google Cloud Pub/Sub topic
Go to the Logs Explorer page in the Google Cloud console.
From the Log Router tab, select Create Sink.
Provide a name for the sink.
Choose Cloud Pub/Sub as the destination and select the Cloud Pub/Sub topic that was created for that purpose. Note: The Cloud Pub/Sub topic can be located in a different project.
Choose the logs you want to include in the sink with an optional inclusion or exclusion filter. You can filter the logs with a search query, or use the sample function. For example, to include only 10% of the logs with a
severitylevel ofERROR, create an inclusion filter withseverity="ERROR" AND sample(insertId, 0.1).Click Create Sink.
Note: It is possible to create several exports from Google Cloud Logging to the same Cloud Pub/Sub topic with different sinks.
4. Create and run the Dataflow job
Go to the Create job from template page in the Google Cloud console.
Give the job a name and select a Dataflow regional endpoint.
Select
Pub/Sub to Datadogin the Dataflow template dropdown, and the Required parameters section appears. a. Select the input subscription in the Pub/Sub input subscription dropdown. b. Enter the following in the Datadog Logs API URL field:https://
Note: Ensure that the Datadog site selector on the right of the page is set to your Datadog site before copying the URL above.
c. Select the topic created to receive message failures in the Output deadletter Pub/Sub topic dropdown. d. Specify a path for temporary files in your storage bucket in the Temporary location field.
Under Optional Parameters, check
Include full Pub/Sub message in the payload.If you created a secret in Secret Manager with your Datadog API key value as mentioned in step 1, enter the resource name of the secret in the Google Cloud Secret Manager ID field.
See Template parameters in the Dataflow template for details on using the other available options:
apiKeySource=KMSwithapiKeyKMSEncryptionKeyset to your Cloud KMS key ID andapiKeyset to the encrypted API key- Not recommended:
apiKeySource=PLAINTEXTwithapiKeyset to the plaintext API key
- If you created a custom worker service account, select it in the Service account email dropdown.
- Click RUN JOB.
Note: If you have a shared VPC, see the Specify a network and subnetwork page in the Dataflow documentation for guidelines on specifying the Network and Subnetwork parameters.
Validation
New logging events delivered to the Cloud Pub/Sub topic appear in the Datadog Log Explorer.
Note: You can use the Google Cloud Pricing Calculator to calculate potential costs.
Monitor the Cloud Pub/Sub log forwarding
The Google Cloud Pub/Sub integration provides helpful metrics to monitor the status of the log forwarding:
gcp.pubsub.subscription.num_undelivered_messagesfor the number of messages pending deliverygcp.pubsub.subscription.oldest_unacked_message_agefor the age of the oldest unacknowledged message in a subscription
Use the metrics above with a metric monitor to receive alerts for the messages in your input and deadletter subscriptions.
Monitor the Dataflow pipeline
Use Datadog’s Google Cloud Dataflow integration to monitor all aspects of your Dataflow pipelines. You can see all your key Dataflow metrics on the out-of-the-box dashboard, enriched with contextual data such as information about the GCE instances running your Dataflow workloads, and your Pub/Sub throughput.
You can also use a preconfigured Recommended Monitor to set up notifications for increases in backlog time in your pipeline. For more information, read Monitor your Dataflow pipelines with Datadog in the Datadog blog.
Collecting Google Cloud logs with a Pub/Sub Push subscription is in the process of being deprecated.
The above documentation for the Push subscription is only maintained for troubleshooting or modifying legacy setups.
Use a Pull subscription with the Datadog Dataflow template as described under Dataflow Method to forward your Google Cloud logs to Datadog instead.
Expanded BigQuery monitoring
Join the Preview!
Expanded BigQuery monitoring is in Preview. Use this form to sign up to start gaining insights into your query performance.
Request AccessExpanded BigQuery monitoring provides granular visibility into your BigQuery environments.
BigQuery jobs performance monitoring
To monitor the performance of your BigQuery jobs, grant the BigQuery Resource Viewer role to the Datadog service account for each Google Cloud project.
Notes:
- You need to have verified your Google Cloud service account in Datadog, as outlined in the setup section.
- You do not need to set up Dataflow to collect logs for expanded BigQuery monitoring.
- In the Google Cloud console, go to the IAM page.
- Click Grant access.
- Enter the email of your service account in New principals.
- Assign the BigQuery Resource Viewer role.
- Click SAVE.
- In Datadog’s Google Cloud integration page, click into the BigQuery tab.
- Click the Enable Query Performance toggle.
BigQuery data quality monitoring
BigQuery data quality monitoring provides quality metrics from your BigQuery tables (such as freshness and updates to row count and size). Explore the data from your tables in depth on the Data Quality Monitoring page.
To collect quality metrics, grant the BigQuery Metadata Viewer role to the Datadog Service Account for each BigQuery table you are using.
Note: BigQuery Metadata Viewer can be applied at a BigQuery table, dataset, project, or organization level.
- For Data Quality Monitoring of all tables within a dataset, grant access at the dataset level.
- For Data Quality Monitoring of all datasets within a project, grant access at the project level.
- Navigate to BigQuery.
- In the Explorer, search for the desired BigQuery resource.
- Click the three-dot menu next to the resource, then click Share -> Manage Permissions.
- Click ADD PRINCIPAL.
- In the new principals box, enter the Datadog service account set up for the Google Cloud integration.
- Assign the BigQuery Metadata Viewer role.
- Click SAVE.
- In Datadog’s Google Cloud integration page, click into the BigQuery tab.
- Click the Enable Data Quality toggle.
BigQuery jobs log retention
Datadog recommends setting up a new logs index called data-observability-queries, and indexing your BigQuery job logs for 15 days. Use the following index filter to pull in the logs:
service:data-observability @platform:*
See the Log Management pricing page for cost estimation.
Resource changes collection
Join the Preview!
Resource changes collection is in Preview! To request access, use the attached form.
Request AccessSelect Enable Resource Collection in the Resource Collection tab of the Google Cloud integration page. This allows you to receive resource events in Datadog when Google’s Cloud Asset Inventory detects changes in your cloud resources.
Then, follow the steps below to forward change events from a Pub/Sub topic to the Datadog Event Explorer.
Google Cloud CLI
Google Cloud CLI
Create a Cloud Pub/Sub topic and subscription
Create a topic
- In the Google Cloud Pub/Sub topics page, click CREATE TOPIC.
- Give the topic a descriptive name.
- Uncheck the option to add a default subscription.
- Click CREATE.
Create a subscription
- In the Google Cloud Pub/Sub subscriptions page, click CREATE SUBSCRIPTION.
- Enter
export-asset-changes-to-datadogfor the subscription name. - Select the Cloud Pub/Sub topic previously created.
- Select Pull as the delivery type.
- Click CREATE.
Grant access
To read from this Pub/Sub subscription, the Google Cloud service account used by the integration needs the pubsub.subscriptions.consume permission for the subscription. A default role with minimal permissions that allows this is the Pub/Sub subscriber role. Follow the steps below to grant this role:
- In the Google Cloud Pub/Sub subscriptions page, click the
export-asset-changes-to-datadogsubscription. - In the info panel on the right of the page, click the Permissions tab. If you don’t see the info panel, click SHOW INFO PANEL.
- Click ADD PRINCIPAL.
- Enter the service account email used by the Datadog Google Cloud integration. You can find your service accounts listed on the left of the Configuration tab in the Google Cloud integration page in Datadog.
Create an asset feed
Run the command below in Cloud Shell or the gcloud CLI to create a Cloud Asset Inventory Feed that sends change events to the Pub/Sub topic created above.
gcloud asset feeds create <FEED_NAME>
--project=<PROJECT_ID>
--pubsub-topic=projects/<PROJECT_ID>/topics/<TOPIC_NAME>
--asset-names=<ASSET_NAMES>
--asset-types=<ASSET_TYPES>
--content-type=<CONTENT_TYPE>
Update the placeholder values as indicated:
<FEED_NAME>: A descriptive name for the Cloud Asset Inventory Feed.<PROJECT_ID>: Your Google Cloud project ID.<TOPIC_NAME>: The name of the Pub/Sub topic linked with theexport-asset-changes-to-datadogsubscription.<ASSET_NAMES>: Comma-separated list of resource full names to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-types.<ASSET_TYPES>: Comma-separated list of asset types to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-names.<CONTENT_TYPE>: Optional asset content type to receive change events from.
gcloud asset feeds create <FEED_NAME>
--folder=<FOLDER_ID>
--pubsub-topic=projects/<PROJECT_ID>/topics/<TOPIC_NAME>
--asset-names=<ASSET_NAMES>
--asset-types=<ASSET_TYPES>
--content-type=<CONTENT_TYPE>
Update the placeholder values as indicated:
<FEED_NAME>: A descriptive name for the Cloud Asset Inventory Feed.<FOLDER_ID>: Your Google Cloud folder ID.<TOPIC_NAME>: The name of the Pub/Sub topic linked with theexport-asset-changes-to-datadogsubscription.<ASSET_NAMES>: Comma-separated list of resource full names to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-types.<ASSET_TYPES>: Comma-separated list of asset types to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-names.<CONTENT_TYPE>: Optional asset content type to receive change events from.
gcloud asset feeds create <FEED_NAME>
--organization=<ORGANIZATION_ID>
--pubsub-topic=projects/<PROJECT_ID>/topics/<TOPIC_NAME>
--asset-names=<ASSET_NAMES>
--asset-types=<ASSET_TYPES>
--content-type=<CONTENT_TYPE>
Update the placeholder values as indicated:
<FEED_NAME>: A descriptive name for the Cloud Asset Inventory Feed.<ORGANIZATION_ID>: Your Google Cloud organization ID.<TOPIC_NAME>: The name of the Pub/Sub topic linked with theexport-asset-changes-to-datadogsubscription.<ASSET_NAMES>: Comma-separated list of resource full names to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-types.<ASSET_TYPES>: Comma-separated list of asset types to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-names.<CONTENT_TYPE>: Optional asset content type to receive change events from.
Terraform
Terraform
Create an asset feed
Copy the following Terraform template and substitute the necessary arguments:
locals {
project_id = "<PROJECT_ID>"
}
resource "google_pubsub_topic" "pubsub_topic" {
project = local.project_id
name = "<TOPIC_NAME>"
}
resource "google_pubsub_subscription" "pubsub_subscription" {
project = local.project_id
name = "export-asset-changes-to-datadog"
topic = google_pubsub_topic.pubsub_topic.id
}
resource "google_pubsub_subscription_iam_member" "subscriber" {
project = local.project_id
subscription = google_pubsub_subscription.pubsub_subscription.id
role = "roles/pubsub.subscriber"
member = "serviceAccount:<SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL>"
}
resource "google_cloud_asset_project_feed" "project_feed" {
project = local.project_id
feed_id = "<FEED_NAME>"
content_type = "<CONTENT_TYPE>" # Optional. Remove if unused.
asset_names = ["<ASSET_NAMES>"] # Optional if specifying asset_types. Remove if unused.
asset_types = ["<ASSET_TYPES>"] # Optional if specifying asset_names. Remove if unused.
feed_output_config {
pubsub_destination {
topic = google_pubsub_topic.pubsub_topic.id
}
}
}
Update the placeholder values as indicated:
<PROJECT_ID>: Your Google Cloud project ID.<TOPIC_NAME>: The name of the Pub/Sub topic to be linked with theexport-asset-changes-to-datadogsubscription.<SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL>: The service account email used by the Datadog Google Cloud integration.<FEED_NAME>: A descriptive name for the Cloud Asset Inventory Feed.<ASSET_NAMES>: Comma-separated list of resource full names to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-types.<ASSET_TYPES>: Comma-separated list of asset types to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-names.<CONTENT_TYPE>: Optional asset content type to receive change events from.
locals {
project_id = "<PROJECT_ID>"
}
resource "google_pubsub_topic" "pubsub_topic" {
project = local.project_id
name = "<TOPIC_NAME>"
}
resource "google_pubsub_subscription" "pubsub_subscription" {
project = local.project_id
name = "export-asset-changes-to-datadog"
topic = google_pubsub_topic.pubsub_topic.id
}
resource "google_pubsub_subscription_iam_member" "subscriber" {
project = local.project_id
subscription = google_pubsub_subscription.pubsub_subscription.id
role = "roles/pubsub.subscriber"
member = "serviceAccount:<SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL>"
}
resource "google_cloud_asset_folder_feed" "folder_feed" {
billing_project = local.project_id
folder = "<FOLDER_ID>"
feed_id = "<FEED_NAME>"
content_type = "<CONTENT_TYPE>" # Optional. Remove if unused.
asset_names = ["<ASSET_NAMES>"] # Optional if specifying asset_types. Remove if unused.
asset_types = ["<ASSET_TYPES>"] # Optional if specifying asset_names. Remove if unused.
feed_output_config {
pubsub_destination {
topic = google_pubsub_topic.pubsub_topic.id
}
}
}
Update the placeholder values as indicated:
<PROJECT_ID>: Your Google Cloud project ID.<FOLDER_ID>: The ID of the folder this feed should be created in.<TOPIC_NAME>: The name of the Pub/Sub topic to be linked with theexport-asset-changes-to-datadogsubscription.<SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL>: The service account email used by the Datadog Google Cloud integration.<FEED_NAME>: A descriptive name for the Cloud Asset Inventory Feed.<ASSET_NAMES>: Comma-separated list of resource full names to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-types.<ASSET_TYPES>: Comma-separated list of asset types to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-names.<CONTENT_TYPE>: Optional asset content type to receive change events from.
locals {
project_id = "<PROJECT_ID>"
}
resource "google_pubsub_topic" "pubsub_topic" {
project = local.project_id
name = "<TOPIC_NAME>"
}
resource "google_pubsub_subscription" "pubsub_subscription" {
project = local.project_id
name = "export-asset-changes-to-datadog"
topic = google_pubsub_topic.pubsub_topic.id
}
resource "google_pubsub_subscription_iam_member" "subscriber" {
project = local.project_id
subscription = google_pubsub_subscription.pubsub_subscription.id
role = "roles/pubsub.subscriber"
member = "serviceAccount:<SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL>"
}
resource "google_cloud_asset_organization_feed" "organization_feed" {
billing_project = local.project_id
org_id = "<ORGANIZATION_ID>"
feed_id = "<FEED_NAME>"
content_type = "<CONTENT_TYPE>" # Optional. Remove if unused.
asset_names = ["<ASSET_NAMES>"] # Optional if specifying asset_types. Remove if unused.
asset_types = ["<ASSET_TYPES>"] # Optional if specifying asset_names. Remove if unused.
feed_output_config {
pubsub_destination {
topic = google_pubsub_topic.pubsub_topic.id
}
}
}
Update the placeholder values as indicated:
<PROJECT_ID>: Your Google Cloud project ID.<TOPIC_NAME>: The name of the Pub/Sub topic to be linked with theexport-asset-changes-to-datadogsubscription.<SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL>: The service account email used by the Datadog Google Cloud integration.<ORGANIZATION_ID>: Your Google Cloud organization ID.<FEED_NAME>: A descriptive name for the Cloud Asset Inventory Feed.<ASSET_NAMES>: Comma-separated list of resource full names to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-types.<ASSET_TYPES>: Comma-separated list of asset types to receive change events from. Optional if specifyingasset-names.<CONTENT_TYPE>: Optional asset content type to receive change events from.
Datadog recommends setting the asset-types parameter to the regular expression .* to collect changes for all resources.
Note: You must specify at least one value for either the asset-names or asset-types parameter.
See the gcloud asset feeds create reference for the full list of configurable parameters.
Enable resource changes collection
Click to Enable Resource Changes Collection in the Resource Collection tab of the Google Cloud integration page.
Validation
Find your asset change events in the Datadog Event Explorer.
Private Service Connect
Use the Google Cloud Private Service Connect integration to visualize connections, data transferred, and dropped packets through Private Service Connect. This gives you visibility into important metrics from your Private Service Connect connections, both for producers as well as consumers. Private Service Connect (PSC) is a Google Cloud networking product that enables you to access Google Cloud services, third-party partner services, and company-owned applications directly from your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
See Access Datadog privately and monitor your Google Cloud Private Service Connect usage in the Datadog blog for more information.
Data Collected
Metrics
| gcp.gce.instance.cpu.utilization (gauge) | Fraction of the allocated CPU that is currently in use on the instance. Note that some machine types allow bursting above 100% usage. Shown as fraction |
Cumulative metrics
Cumulative metrics are imported into Datadog with a .delta metric for each metric name. A cumulative metric is a metric where the value constantly increases over time. For example, a metric for sent bytes might be cumulative. Each value records the total number of bytes sent by a service at that time. The delta value represents the change since the previous measurement.
For example:
gcp.gke.container.restart_count is a CUMULATIVE metric. While importing this metric as a cumulative metric, Datadog adds the gcp.gke.container.restart_count.delta metric which includes the delta values (as opposed to the aggregate value emitted as part of the CUMULATIVE metric). See Google Cloud metric kinds for more information.
Events
All service events generated by your Google Cloud Platform are forwarded to your Datadog Events Explorer.
Service Checks
The Google Cloud Platform integration does not include any service checks.
Tags
Tags are automatically assigned based on a variety of Google Cloud Platform and Google Compute Engine configuration options. The project_id tag is added to all metrics. Additional tags are collected from the Google Cloud Platform when available, and varies based on metric type.
Additionally, Datadog collects the following as tags:
- Any hosts with
<key>:<value>labels. - Custom labels from Google Pub/Sub, GCE, Cloud SQL, and Cloud Storage.
Troubleshooting
Incorrect metadata for user defined gcp.logging metrics?
For non-standard gcp.logging metrics, such as metrics beyond Datadog’s out of the box logging metrics, the metadata applied may not be consistent with Google Cloud Logging.
In these cases, the metadata should be manually set by navigating to the metric summary page, searching and selecting the metric in question, and clicking the pencil icon next to the metadata.
Need help? Contact Datadog support.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles:
- Improve the compliance and security posture of your Google Cloud environment with Datadog
- Monitor Google Cloud Vertex AI with Datadog
- Monitor your Dataflow pipelines with Datadog
- Create and manage your Google Cloud integration with Terraform
- Monitor BigQuery with Datadog
- Troubleshoot infrastructure changes faster with Recent Changes in the Resource Catalog
- Stream logs from Google Cloud to Datadog