- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Integrations
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- APM Tracing
- Profiler
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic Monitoring
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- API
- Datadog Mobile App
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Infrastructure
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Product Analytics
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Advanced Configuration
Overview
There are various ways you can modify the data and context collected by RUM, to support your needs for:
- Protecting sensitive data like personally identifiable information.
- Connecting a user session with your internal identification of that user, to help with support.
- Reducing how much RUM data you’re collecting, through sampling the data.
- Providing more context than what the default attributes provide about where the data is coming from.
Override default RUM view names
The RUM Browser SDK automatically generates a view event for each new page visited by your users, or when the page URL is changed (for single-page applications). A view name is computed from the current page URL, where variable alphanumeric IDs are removed automatically. For example, /dashboard/1234 becomes /dashboard/?.
Starting with version 2.17.0, you can add view names and assign them to a dedicated service owned by a team by tracking view events manually with the trackViewsManually option:
Set
trackViewsManuallyto true when initializing the RUM Browser SDK.import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum'; datadogRum.init({ ..., trackViewsManually: true, ... });window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() { window.DD_RUM.init({ ..., trackViewsManually: true, ... }) })window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.init({ ..., trackViewsManually: true, ... });You must start views for each new page or route change (for single-page applications). RUM data is collected when the view starts. Starting with version 4.13.0, you can also optionally define the associated service name and version.
- View Name: Defaults to the page URL path.
- Service: Defaults to the default service specified when creating your RUM application.
- Version: Defaults to the default version specified when creating your RUM application.
For more information, see Setup Browser Monitoring.
Latest version
The following example manually tracks the pageviews on thecheckoutpage in a RUM application. Usecheckoutfor the view name and associate thepurchaseservice with version1.2.3.datadogRum.startView({ name: 'checkout', service: 'purchase', version: '1.2.3' })window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() { window.DD_RUM.startView({ name: 'checkout', service: 'purchase', version: '1.2.3' }) })window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.startView({ name: 'checkout', service: 'purchase', version: '1.2.3' })before
The following example manually tracks the pageviews on thev4.13.0checkoutpage in a RUM application. No service or version can be specified.datadogRum.startView('checkout')window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() { window.DD_RUM.startView('checkout') })window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.startView('checkout')
If you are using React, Angular, Vue, or any other frontend framework, Datadog recommends implementing the startView logic at the framework router level.
React router instrumentation
To override default RUM view names so that they are aligned with how you’ve defined them in your React application, you need to follow the below steps.
Note: These instructions are specific to the React Router v6 library.
Set
trackViewsManuallytotruewhen initializing the RUM browser SDK as described above.Start views for each route change.
import { matchRoutes, useLocation } from 'react-router-dom'; import { routes } from 'path/to/routes'; import { datadogRum } from "@datadog/browser-rum"; export default function App() { // Track every route change with useLocation API let location = useLocation(); useEffect(() => { const routeMatches = matchRoutes(routes, location.pathname); const viewName = routeMatches && computeViewName(routeMatches); if (viewName) { datadogRum.startView({name: viewName}); } }, [location.pathname]); ... } // Compute view name out of routeMatches function computeViewName(routeMatches) { let viewName = ""; for (let index = 0; index < routeMatches.length; index++) { const routeMatch = routeMatches[index]; const path = routeMatch.route.path; // Skip pathless routes if (!path) { continue; } if (path.startsWith("/")) { // Handle absolute child route paths viewName = path; } else { // Handle route paths ending with "/" viewName += viewName.endsWith("/") ? path : `/${path}`; } } return viewName || '/'; }import { matchRoutes, useLocation } from 'react-router-dom'; import { routes } from 'path/to/routes'; export default function App() { // Track every route change with useLocation API let location = useLocation(); useEffect(() => { const routeMatches = matchRoutes(routes, location.pathname); const viewName = routeMatches && computeViewName(routeMatches); if (viewName) { DD_RUM.onReady(function() { DD_RUM.startView({name: viewName}); }); } }, [location.pathname]); ... } // Compute view name out of routeMatches function computeViewName(routeMatches) { let viewName = ""; for (let index = 0; index < routeMatches.length; index++) { const routeMatch = routeMatches[index]; const path = routeMatch.route.path; // Skip pathless routes if (!path) { continue; } if (path.startsWith("/")) { // Handle absolute child route paths viewName = path; } else { // Handle route paths ending with "/" viewName += viewName.endsWith("/") ? path : `/${path}`; } } return viewName || '/'; }import { matchRoutes, useLocation } from 'react-router-dom'; import { routes } from 'path/to/routes'; export default function App() { // Track every route change with useLocation API let location = useLocation(); useEffect(() => { const routeMatches = matchRoutes(routes, location.pathname); const viewName = routeMatches && computeViewName(routeMatches); if (viewName) { window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.startView({name: viewName}); } }, [location.pathname]); ... } // Compute view name out of routeMatches function computeViewName(routeMatches) { let viewName = ""; for (let index = 0; index < routeMatches.length; index++) { const routeMatch = routeMatches[index]; const path = routeMatch.route.path; // Skip pathless routes if (!path) { continue; } if (path.startsWith("/")) { // Handle absolute child route paths viewName = path; } else { // Handle route paths ending with "/" viewName += viewName.endsWith("/") ? path : `/${path}`; } } return viewName || '/'; }
Enrich and control RUM data
The RUM Browser SDK captures RUM events and populates their main attributes. The beforeSend callback function gives you access to every event collected by the RUM Browser SDK before it is sent to Datadog.
Intercepting the RUM events allows you to:
- Enrich your RUM events with additional context attributes
- Modify your RUM events to alter their content or redact sensitive sequences (see list of editable properties)
- Discard selected RUM events
Starting with version 2.13.0, beforeSend takes two arguments: the event generated by the RUM Browser SDK, and the context that triggered the creation of the RUM event.
function beforeSend(event, context)
The potential context values are:
| RUM event type | Context |
|---|---|
| View | Location |
| Action | Event |
| Resource (XHR) | XMLHttpRequest and PerformanceResourceTiming |
| Resource (Fetch) | Request, Response, and PerformanceResourceTiming |
| Resource (Other) | PerformanceResourceTiming |
| Error | Error |
| Long Task | PerformanceLongTaskTiming |
For more information, see the Enrich and control RUM data guide.
Enrich RUM events
Along with attributes added with the Global Context API or the Feature Flag data collection, you can add additional context attributes to the event. For example, tag your RUM resource events with data extracted from a fetch response object:
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
datadogRum.init({
...,
beforeSend: (event, context) => {
// collect a RUM resource's response headers
if (event.type === 'resource' && event.resource.type === 'fetch') {
event.context.responseHeaders = Object.fromEntries(context.response.headers)
}
return true
},
...
});
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.init({
...,
beforeSend: (event, context) => {
// collect a RUM resource's response headers
if (event.type === 'resource' && event.resource.type === 'fetch') {
event.context.responseHeaders = Object.fromEntries(context.response.headers)
}
return true
},
...
})
})
window.DD_RUM &&
window.DD_RUM.init({
...,
beforeSend: (event, context) => {
// collect a RUM resource's response headers
if (event.type === 'resource' && event.resource.type === 'fetch') {
event.context.responseHeaders = Object.fromEntries(context.response.headers)
}
return true
},
...
});
If a user belongs to multiple teams, add additional key-value pairs in your calls to the Global Context API.
The RUM Browser SDK ignores:
- Attributes added outside of
event.context - Modifications made to a RUM view event context
Enrich RUM events with feature flags
You can enrich your RUM event data with feature flags to get additional context and visibility into performance monitoring. This lets you determine which users are shown a specific user experience and if it is negatively affecting the user’s performance.
Modify the content of a RUM event
For example, to redact email addresses from your web application URLs:
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
datadogRum.init({
...,
beforeSend: (event) => {
// remove email from view url
event.view.url = event.view.url.replace(/email=[^&]*/, "email=REDACTED")
},
...
});
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.init({
...,
beforeSend: (event) => {
// remove email from view url
event.view.url = event.view.url.replace(/email=[^&]*/, "email=REDACTED")
},
...
})
})
window.DD_RUM &&
window.DD_RUM.init({
...,
beforeSend: (event) => {
// remove email from view url
event.view.url = event.view.url.replace(/email=[^&]*/, "email=REDACTED")
},
...
});
You can update the following event properties:
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
view.url | String | The URL of the active web page. |
view.referrer | String | The URL of the previous web page from which a link to the currently requested page was followed. |
view.name | String | The name of the current view. |
action.target.name | String | The element that the user interacted with. Only for automatically collected actions. |
error.message | String | A concise, human-readable, one-line message explaining the error. |
error.stack | String | The stack trace or complementary information about the error. |
error.resource.url | String | The resource URL that triggered the error. |
resource.url | String | The resource URL. |
context | Object | Attributes added with the Global Context API or when generating events manually (for example, addError and addAction). RUM view events context is read-only. |
The RUM Browser SDK ignores modifications made to event properties not listed above. For more information about event properties, see the RUM Browser SDK GitHub repository.
Discard a RUM event
With the beforeSend API, discard a RUM event by returning false:
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
datadogRum.init({
...,
beforeSend: (event) => {
if (shouldDiscard(event)) {
return false
}
...
},
...
});
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.init({
...,
beforeSend: (event) => {
if (shouldDiscard(event)) {
return false
},
...
},
...
})
})
window.DD_RUM &&
window.DD_RUM.init({
...,
beforeSend: (event) => {
if (shouldDiscard(event)) {
return false
}
...
},
...
});
Note: View events cannot be discarded.
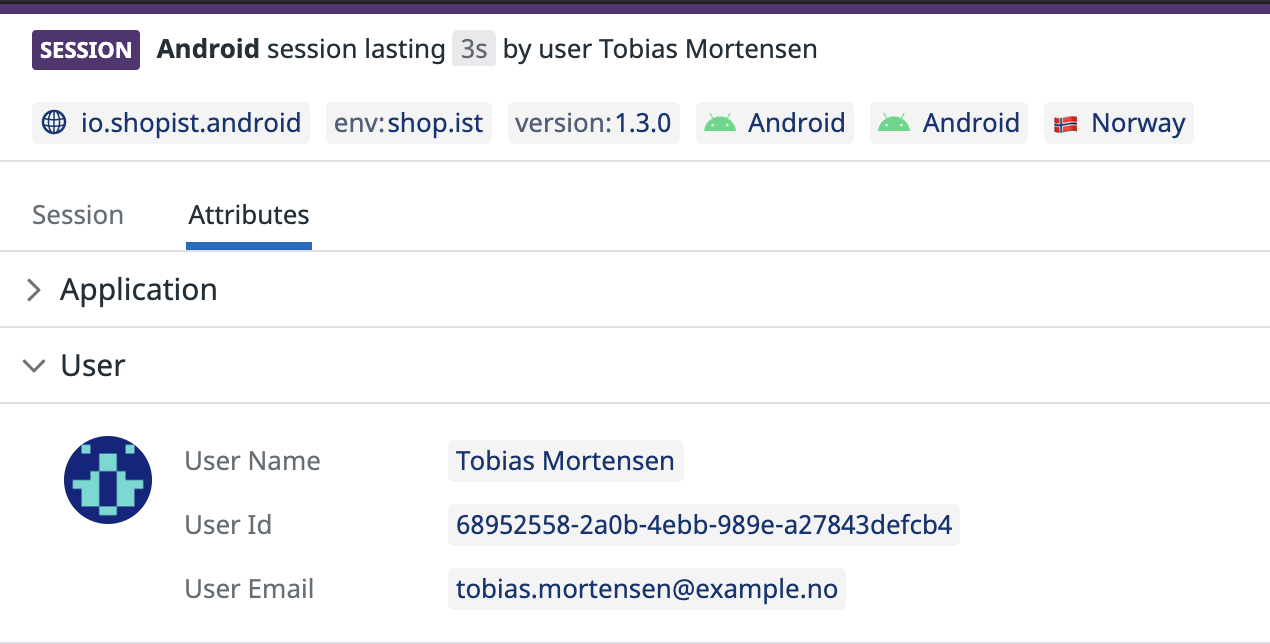
User session
Adding user information to your RUM sessions can help you:
- Follow the journey of a given user
- Know which users are the most impacted by errors
- Monitor performance for your most important users
The following attributes are optional but Datadog recommends providing at least one of them:
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
usr.id | String | Unique user identifier. |
usr.name | String | User friendly name, displayed by default in the RUM UI. |
usr.email | String | User email, displayed in the RUM UI if the user name is not present. It is also used to fetch Gravatars. |
Increase your filtering capabilities by adding extra attributes on top of the recommended ones. For instance, add information about the user plan, or which user group they belong to.
When making changes to the user session object, all RUM events collected after the change contain the updated information.
Note: Deleting the user session information, as in a logout, retains the user information on the last view before the logout, but not on later views or the session level as the session data uses the last view’s values.
Identify user session
datadogRum.setUser(<USER_CONFIG_OBJECT>)
datadogRum.setUser({
id: '1234',
name: 'John Doe',
email: 'john@doe.com',
plan: 'premium',
...
})
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.setUser({
id: '1234',
name: 'John Doe',
email: 'john@doe.com',
plan: 'premium',
...
})
})
window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.setUser({
id: '1234',
name: 'John Doe',
email: 'john@doe.com',
plan: 'premium',
...
})
Access user session
datadogRum.getUser()
datadogRum.getUser()
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.getUser()
})
window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.getUser()
Add/Override user session property
datadogRum.setUserProperty('<USER_KEY>', <USER_VALUE>)
datadogRum.setUserProperty('name', 'John Doe')
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.setUserProperty('name', 'John Doe')
})
window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.setUserProperty('name', 'John Doe')
Remove user session property
datadogRum.removeUserProperty('<USER_KEY>')
datadogRum.removeUserProperty('name')
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.removeUserProperty('name')
})
window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.removeUserProperty('name')
Clear user session property
datadogRum.clearUser()
datadogRum.clearUser()
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.clearUser()
})
window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.clearUser()
Sampling
By default, no sampling is applied on the number of collected sessions. To apply a relative sampling (in percent) to the number of sessions collected, use the sessionSampleRate parameter when initializing RUM.
The following example collects only 90% of all sessions on a given RUM application:
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
datadogRum.init({
applicationId: '<DATADOG_APPLICATION_ID>',
clientToken: '<DATADOG_CLIENT_TOKEN>',
site: '<DATADOG_SITE>',
sessionSampleRate: 90,
});
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.init({
clientToken: '<CLIENT_TOKEN>',
applicationId: '<APPLICATION_ID>',
site: '<DATADOG_SITE>',
sessionSampleRate: 90,
})
})
window.DD_RUM &&
window.DD_RUM.init({
clientToken: '<CLIENT_TOKEN>',
applicationId: '<APPLICATION_ID>',
site: '<DATADOG_SITE>',
sessionSampleRate: 90,
});
For a sampled out session, all pageviews and associated telemetry for that session are not collected.
User tracking consent
To be compliant with GDPR, CCPA, and similar regulations, the RUM Browser SDK lets you provide the tracking consent value at initialization. For more information on tracking consent, see Data Security.
The trackingConsent initialization parameter can be one of the following values:
"granted": The RUM Browser SDK starts collecting data and sends it to Datadog."not-granted": The RUM Browser SDK does not collect any data.
To change the tracking consent value after the RUM Browser SDK is initialized, use the setTrackingConsent() API call. The RUM Browser SDK changes its behavior according to the new value:
- when changed from
"granted"to"not-granted", the RUM session is stopped, data is no longer sent to Datadog. - when changed from
"not-granted"to"granted", a new RUM session is created if no previous session is active, and data collection resumes.
This state is not synchronized between tabs nor persisted between navigation. It is your responsibility to provide the user decision during RUM Browser SDK initialization or by using setTrackingConsent().
When setTrackingConsent() is used before init(), the provided value takes precedence over the initialization parameter.
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
datadogRum.init({
...,
trackingConsent: 'not-granted'
});
acceptCookieBannerButton.addEventListener('click', function() {
datadogRum.setTrackingConsent('granted');
});
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.init({
...,
trackingConsent: 'not-granted'
});
});
acceptCookieBannerButton.addEventListener('click', () => {
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.setTrackingConsent('granted');
});
});
window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.init({
...,
trackingConsent: 'not-granted'
});
acceptCookieBannerButton.addEventListener('click', () => {
window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.setTrackingConsent('granted');
});
Global context
Add global context property
After RUM is initialized, add extra context to all RUM events collected from your application with the setGlobalContextProperty(key: string, value: any) API:
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
datadogRum.setGlobalContextProperty('<CONTEXT_KEY>', <CONTEXT_VALUE>);
// Code example
datadogRum.setGlobalContextProperty('activity', {
hasPaid: true,
amount: 23.42
});
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.setGlobalContextProperty('<CONTEXT_KEY>', '<CONTEXT_VALUE>');
})
// Code example
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.setGlobalContextProperty('activity', {
hasPaid: true,
amount: 23.42
});
})
window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.setGlobalContextProperty('<CONTEXT_KEY>', '<CONTEXT_VALUE>');
// Code example
window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.setGlobalContextProperty('activity', {
hasPaid: true,
amount: 23.42
});
Remove global context property
You can remove a previously defined global context property.
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
datadogRum.removeGlobalContextProperty('<CONTEXT_KEY>');
// Code example
datadogRum.removeGlobalContextProperty('codeVersion');
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.removeGlobalContextProperty('<CONTEXT_KEY>');
})
// Code example
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.removeGlobalContextProperty('codeVersion');
})
window.DD_RUM &&
window.DD_RUM.removeGlobalContextProperty('<CONTEXT_KEY>');
// Code example
window.DD_RUM &&
window.DD_RUM.removeGlobalContextProperty('codeVersion');
Replace global context
Replace the default context for all your RUM events with the setGlobalContext(context: Context) API.
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
datadogRum.setGlobalContext({ '<CONTEXT_KEY>': '<CONTEXT_VALUE>' });
// Code example
datadogRum.setGlobalContext({
codeVersion: 34,
});
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.setGlobalContext({ '<CONTEXT_KEY>': '<CONTEXT_VALUE>' });
})
// Code example
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.setGlobalContext({
codeVersion: 34,
})
})
window.DD_RUM &&
window.DD_RUM.setGlobalContext({ '<CONTEXT_KEY>': '<CONTEXT_VALUE>' });
// Code example
window.DD_RUM &&
window.DD_RUM.setGlobalContext({
codeVersion: 34,
});
Clear global context
You can clear the global context by using clearGlobalContext.
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
datadogRum.clearGlobalContext();
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
window.DD_RUM.clearGlobalContext();
});
window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.clearGlobalContext();
Read global context
Once RUM is initialized, read the global context with the getGlobalContext() API.
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
const context = datadogRum.getGlobalContext();
window.DD_RUM.onReady(function() {
const context = window.DD_RUM.getGlobalContext();
});
const context = window.DD_RUM && window.DD_RUM.getGlobalContext();
Contexts life cycle
By default, global context and user context are stored in the current page memory, which means they are not:
- kept after a full reload of the page
- shared across different tabs or windows of the same session
To add them to all events of the session, they must be attached to every page.
With the introduction of the storeContextsAcrossPages configuration option in the v4.49.0 of the browser SDK, those contexts can be stored in localStorage, allowing the following behaviors:
- Contexts are preserved after a full reload
- Contexts are synchronized between tabs opened on the same origin
However, this feature comes with some limitations:
- Setting Personable Identifiable Information (PII) in those contexts is not recommended, as data stored in
localStorageoutlives the user session - The feature is incompatible with the
trackSessionAcrossSubdomainsoptions becauselocalStoragedata is only shared among the same origin (login.site.com ≠ app.site.com) localStorageis limited to 5 MiB by origin, so the application-specific data, Datadog contexts, and other third-party data stored in local storage must be within this limit to avoid any issues
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: