- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Catalog
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
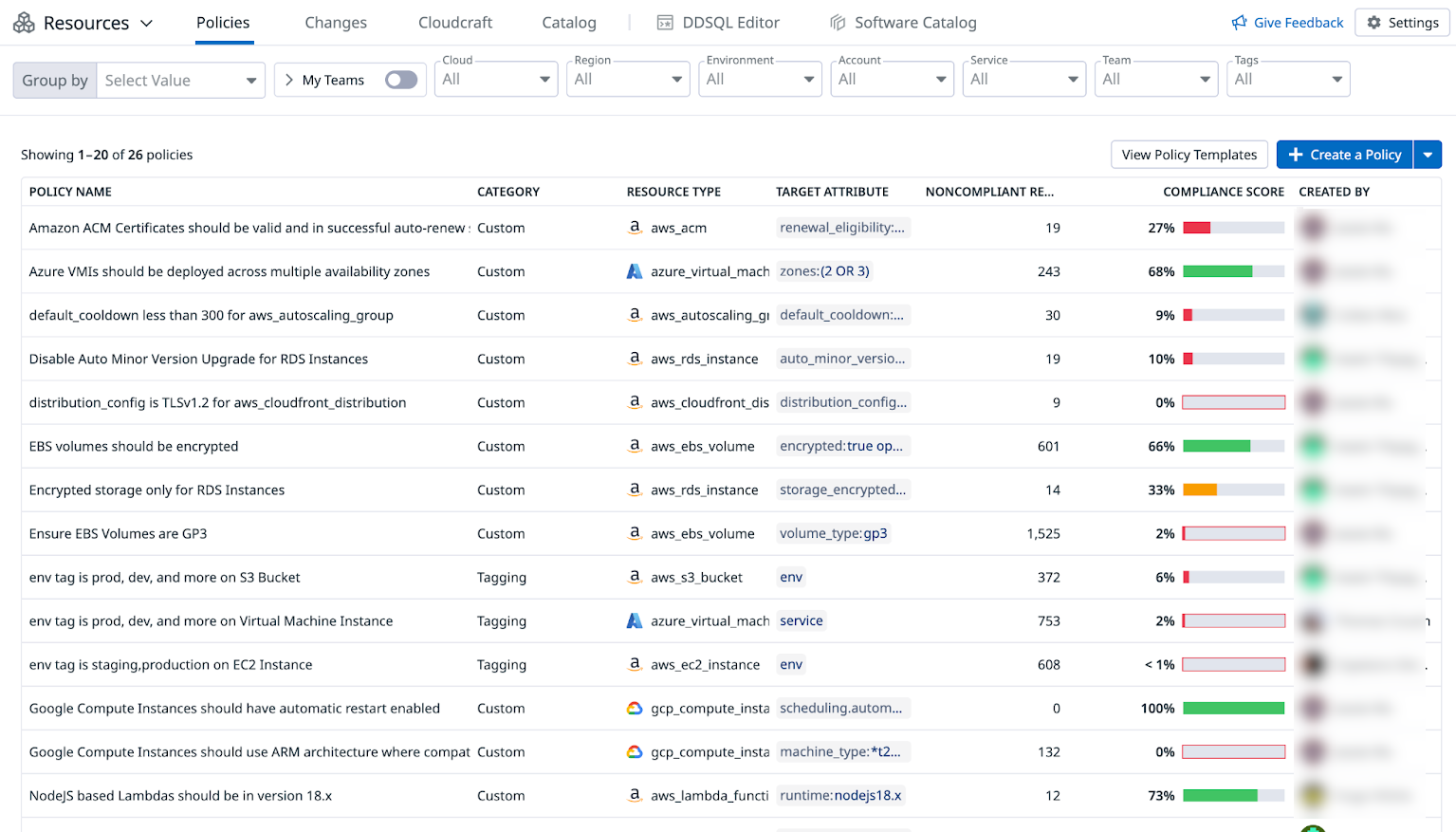
Policies
Resource Catalog is not available for the selected Datadog site ().
Overview
In Resource Policies, you can define policies on the desired optimal configuration of your infrastructure resources based on governance best practices in your organization. Some examples include improving ownership tag coverage on resources, or ensuring versioning on critical resources is up-to-date. Instead of writing custom scripts or Lambdas that scan every resource, Datadog gives you visibility into problematic resources so that you can focus on remediation.
Specifically, you can:
- Define a custom policy, which involves choosing a resource type, the attribute on the resource type, and target values the attribute should have.
- Start from a set of out-of-the-box policy templates that span infrastructure reliability, cost optimization, operational excellence, and versioning.
- Define a tagging policy, which involves a resource type and the desired tag key and value the resource type should have.
- Access a dedicated view for each policy where you can see its list of non-compliant resources and compliance score.
- Filter policies by team (or any custom tag) to create a shareable view for each team.
- Group policies by team (or any custom tag) to assess compliance and prioritize outreach to low-performing teams.
Example Resource Policies
Operational excellence and versioning
- Amazon EC2 instances should only use approved Golden AMIs.
- Amazon RDS instances running Postgres should use the latest compatible engine versions.
- AWS Lambda functions should not run deprecated runtimes.
- Amazon ElastiCache should use the latest engine version.
Reliability
- Amazon RDS instances should have at least 1 day of backup retention configured.
- Amazon ECS services should have desired task count > 1.
- Amazon ACM certificates should be in successful auto-renewal state.
- Google Compute Engine instances should have automatic restart enabled.
- Azure Virtual Machines should be deployed across multiple Availability Zones.
Security
- Amazon RDS instances should be encrypted.
- Amazon CloudFront distributions should use TLS protocol version 1.2.
- Amazon EBS volumes should be encrypted.
Cost optimization
- Amazon EBS volumes should use GP3 instead of GP2.
- Google Compute Engine instances should use ARM architecture where possible.
- Azure Managed Disks should be in the attached state.
Create a custom policy
Custom policies require specific values in your cloud resource attributes within Datadog based on your organization’s infrastructure best practices.
To create a custom policy:
- In the side navigation, click on Resources > Policies.
- Click the New Custom Policy button.
- Select a resource type from the dropdown menu.
- Optionally, search for additional dataset filters, such as
env: prodto only include resources in production. - Select a target resource attribute and desired value.
- Optionally, add instructions for remediation.
- A name is automatically generated based on the data entered, but you can modify it.
- Click Create Custom Policy.
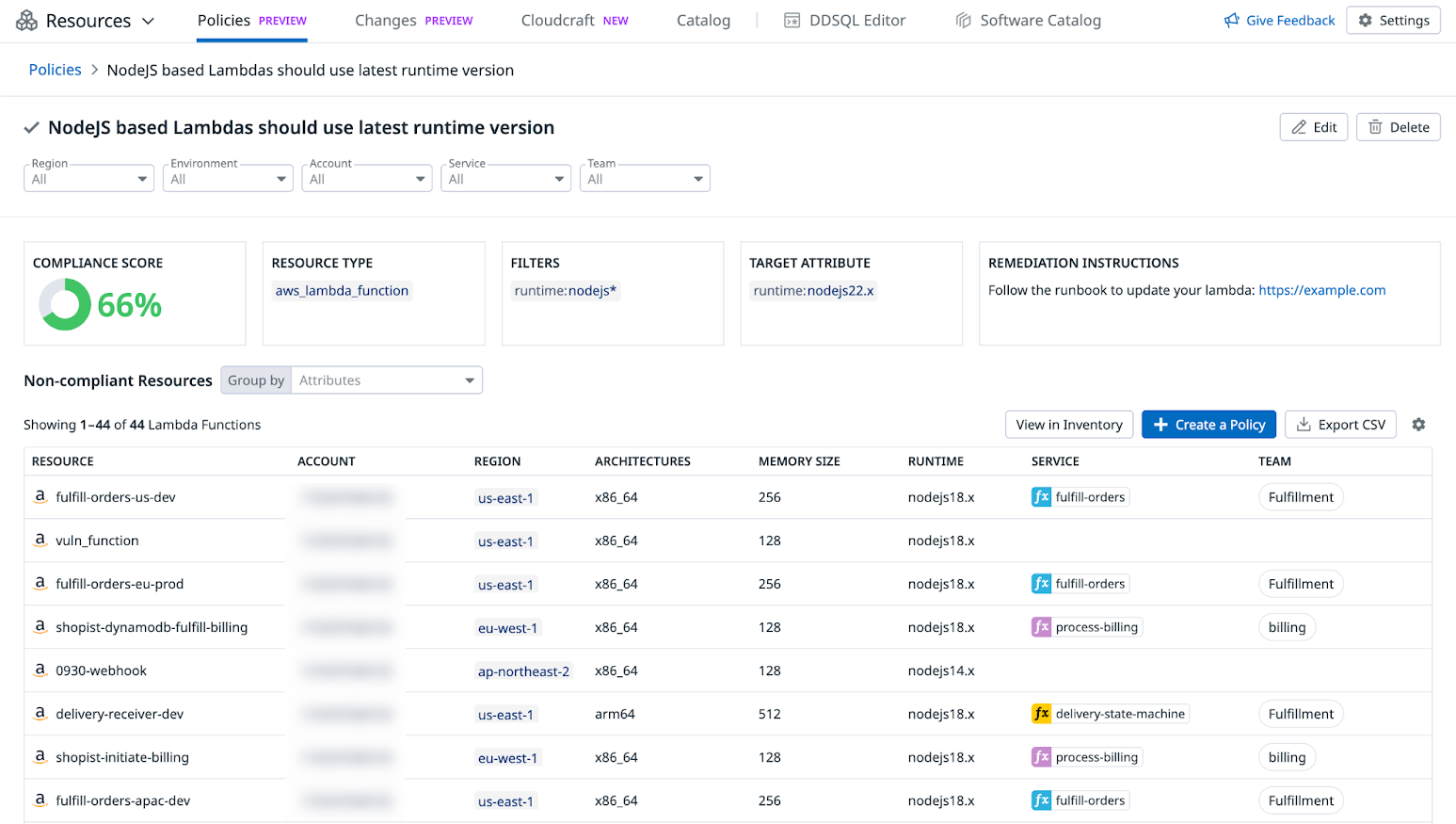
Click the new policy to review all non-compliant resources and filter them by region, environment, account, service, or team. You can also group them by attributes or tags.
Selecting values for your target attribute
Custom policies let you define a target resource attribute and a desired value, providing flexibility in creating policies for your cloud resources without requiring complex query languages. The following features are available:
- Access data in nested attributes:
Validate more of your configurations (for example, require that
TLS 1.2, which is data stored in a multi-level property, is used for Amazon CloudFront). - Use advanced condition matching:
Use operators like
>,<, or!=(for example, enforcing Kubernetes version > 1.25). - Use multi-attribute logic: Chain multiple attributes in one policy (for example, require AWS CloudTrail logging and multi-region to be enabled).
Start with an out-of-the-box policy template
For insights into your infrastructure’s reliability, cost optimization, operational excellence, and versioning, Datadog provides out-of-the-box policy templates. These templates are curated using cloud provider best practices and customer stories. Since each organization has unique requirements, filters can be applied to limit the set of resources evaluated against a policy, and an attribute’s target values can be customized as needed.
Remediate with Native Actions
All policy templates come equipped with suggested remediation steps based on industry best practices, as well as Datadog Native Actions in some cases. Using Native Actions, you can remediate misconfigurations without ever leaving Datadog for the following policy templates:
- Amazon RDS instances should be configured with Multi-AZ deployment
- Amazon EBS volume type should be upgraded from GP2 to GP3
- Amazon DynamoDB point-in-time recovery should be enabled
- Google Compute instances should have automatic restart enabled
As shown in the video below, some policy templates allow you to enable actions and provide instructions for the responsible team to remediate non-compliant resources. This enables them to update cloud resource configurations directly from Datadog. To ensure the team can perform these actions, verify they have read/write permissions for the required cloud accounts.
Create a tagging policy
Tagging policies require specific tag keys and tag value formats on your infrastructure resources across Datadog.
To create a tagging policy:
- In the side navigation, click on Resources > Policies.
- Click the New Tagging Policy button.
- Choose the resource types the policy applies to.
- Define the required tag key and its allowed values.
- A name is automatically generated based on the data entered, but you can modify it.
- Click Create Tagging Policy.
Click the new policy to review all non-compliant resources and filter them by cloud, region, environment, account, service, team, or tag. You can also group them by attributes or tags.
Updating policies
To update a policy, click the policy, then click the Edit button and modify as needed.
Deleting policies
To delete a custom or tagging policy, click the policy, then click the Delete button.
Exporting policies
To export the list of non-compliant resources for a policy, click the policy, then click the Export as CSV button.
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: