- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Integrations
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- APM Tracing
- Profiler
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic Monitoring
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Test Impact Analysis
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Datadog Mobile App
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Infrastructure
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Product Analytics
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Optimization
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Weaviate
Supported OS
Integration version3.1.0
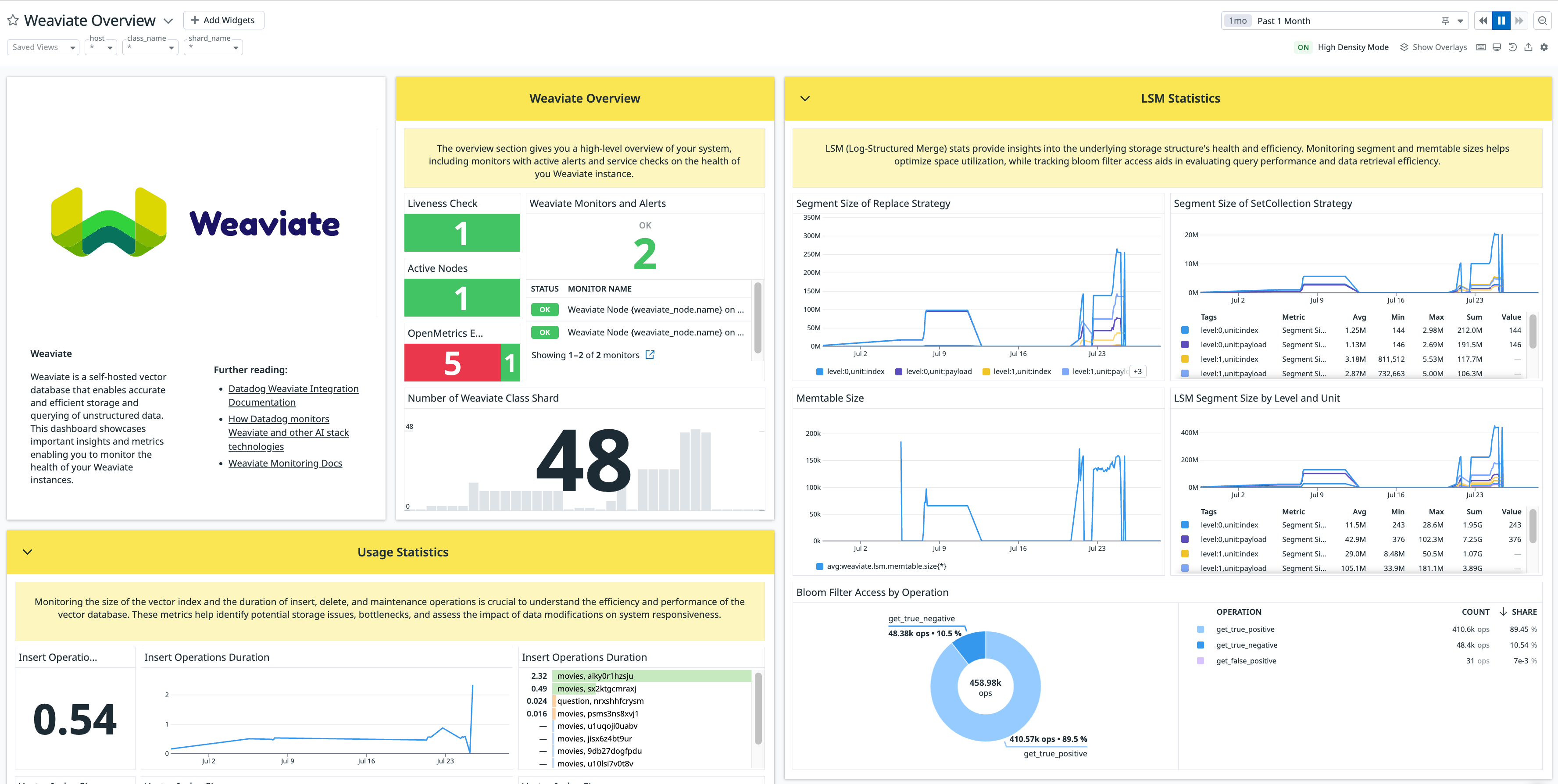
Overview
Weaviate is an open source, AI-native vector database that helps create AI-powered applications. With Datadog’s Weaviate integration, you can:
- Monitor usage statistics (such as duration of insert, delete, and maintenance operations) to identify potential storage issues, bottlenecks, and assess the impact of data modifications on system responsiveness.
- Track query latency, rate, and concurrent read/write requests to gain insight into the vector database’s overall responsiveness and load handling capabilities.
- Optimize write-heavy workloads with object statistics, like the average time taken for “put” (write) operations.
- Ensure smooth and efficient data ingestion with import-related metrics that offer insights into operations like data loading process.
This check monitors Weaviate through the Datadog Agent. For more information, see Weaviate monitoring. To learn more about Datadog’s suite of AI integrations, see this blog.
Setup
Follow the instructions below to install and configure this check for an Agent running on a host. For containerized environments, see the Autodiscovery Integration Templates for guidance on applying these instructions.
Installation
Starting from Agent release 7.47.0, the Weaviate check is included in the Datadog Agent package.
Note: This check requires Agent v7.47.0 or later.
Configuration
Weaviate can be configured to expose Prometheus-formatted metrics. The Datadog Agent can collect these metrics using the integration described below. Follow the instructions to configure data collection for your Weaviate instances. For the required configurations to expose the Prometheus metrics, see the Monitoring page in the Weaviate documentation.
In addition, a small subset of metrics can be collected by communicating with different API endpoints. Specifically:
/v1/meta: Version information/v1/nodes: Node-specific metrics such as objects and shards/v1/.well-known/live: HTTP response time and service liveness
Note: This check uses OpenMetrics for metric collection, which requires Python 3.
Containerized
Metric collection
Make sure that the Prometheus-formatted metrics are exposed in your Weaviate cluster. You can configure and customize this by following the instructions on the Monitoring page in the Weaviate documentation. For the Agent to start collecting metrics, the Weaviate pods need to be annotated. For more information about annotations, refer to the Autodiscovery Integration Templates for guidance. You can find additional configuration options by reviewing the sample weaviate.d/conf.yaml
Note: The listed metrics can only be collected if they are available. Some metrics are generated only when certain actions are performed. For example, the object deletion metric is exposed only when an object is deleted.
The two most important parameters for configuring the Weaviate check are as follows:
openmetrics_endpoint: This parameter should be set to the location where the Prometheus-formatted metrics are exposed. The default port is2112, but it can be configured using thePROMETHEUS_MONITORING_PORTenvironment variable. In containerized environments,%%host%%should be used for host autodetection.weaviate_api_endpoint: This parameter is optional. By default, this parameter is set to<hostname>:8080and it specifies the configuration of the RESTful API.
If authentication is required for the RESTful API endpoints, the check can be configured to provide an API key as part of the request header.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
# (...)
metadata:
name: '<POD_NAME>'
annotations:
ad.datadoghq.com/weaviate.checks: |
{
"weaviate": {
"init_config": {},
"instances": [
{
"openmetrics_endpoint": "http://%%host%%:2112/metrics",
"weaviate_api_endpoint": "http://%%host%%:8080",
"headers": {'Authorization': 'Bearer if_needed_for_auth'}
}
]
}
}
# (...)
spec:
containers:
- name: 'weaviate'
# (...)
Note: You can set these annotations directly in your Weaviate Helm chart using annotations key.
Validation
Run the Agent’s status subcommand and look for weaviate under the Checks section.
Data Collected
Metrics
| weaviate.async.operations.running (gauge) | The number of currently running async operations. The operation itself is defined through the operation label Shown as operation |
| weaviate.backup.restore.class.ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration of restoring a class Shown as operation |
| weaviate.backup.restore.class.ms.sum (count) | The duration of restoring a class Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.backup.restore.data.transferred (count) | The total number of bytes transferred during a backup restore Shown as byte |
| weaviate.backup.restore.from.backend.ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration of the file transfer stage of a backup restore Shown as operation |
| weaviate.backup.restore.from.backend.ms.sum (count) | The duration of the file transfer stage of a backup restore Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.backup.restore.init.ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration of the startup phase of a backup restore Shown as operation |
| weaviate.backup.restore.init.ms.sum (count) | The duration of the startup phase of a backup restore Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.backup.restore.ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration of backup restores Shown as operation |
| weaviate.backup.restore.ms.sum (count) | The duration of backup restores Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.backup.store.data.transferred (count) | The total number of bytes transferred during a backup store Shown as byte |
| weaviate.backup.store.to.backend.ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration of the file transfer stage of a backup store Shown as operation |
| weaviate.backup.store.to.backend.ms.sum (count) | The duration of the file transfer stage of a backup store Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.batch.delete.durations_ms.bucket (count) | The number of operations observed for the batch delete duration histogram by upper_bound bucketsShown as operation |
| weaviate.batch.delete.durations_ms.count (count) | The count of operations observed in the batch delete duration histogram Shown as operation |
| weaviate.batch.delete.durations_ms.sum (count) | The sum of the duration of a batch delete in ms. The operation label further defines what operation as part of the batch delete is being measured. Granularity is a shard of a class Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.batch.durations_ms.bucket (count) | The number of operations observed for the batch operation duration histogram by upper_bound bucketsShown as operation |
| weaviate.batch.durations_ms.count (count) | The count of operations observed in the batch operation duration histogram Shown as operation |
| weaviate.batch.durations_ms.sum (count) | The sum of the duration of a single batch operation in ms. The operation label further defines what operation as part of the batch (e.g. object, inverted, vector) is being used. Granularity is a shard of a class Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.bucket.pause.durations.ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration of bucket pauses Shown as operation |
| weaviate.bucket.pause.durations.ms.sum (count) | The duration of bucket pauses Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.concurrent.goroutines (gauge) | The number of concurrently running goroutines |
| weaviate.concurrent.queries (gauge) | The number of concurrently running query operations Shown as operation |
| weaviate.go.gc.duration.seconds.count (count) | The summary count of garbage collection cycles in the Weaviate instance Shown as second |
| weaviate.go.gc.duration.seconds.quantile (gauge) | A summary of the pause duration of garbage collection cycles in the Weaviate instance Shown as second |
| weaviate.go.gc.duration.seconds.sum (count) | The sum of the pause duration of garbage collection cycles in the Weaviate instance Shown as second |
| weaviate.go.goroutines (gauge) | The number of goroutines that currently exist in the Weaviate instance |
| weaviate.go.info (gauge) | Metric containing the Go version as a tag |
| weaviate.go.memstats.alloc_bytes (gauge) | The number of bytes allocated and still in use in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.alloc_bytes.count (count) | The monotonic count of bytes allocated and still in use in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.buck_hash.sys_bytes (gauge) | The number of bytes used by the profiling bucket hash table in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.frees.count (count) | The total number of frees in the Weaviate instance |
| weaviate.go.memstats.gc.cpu_fraction (gauge) | The fraction of this program's available CPU time used by the GC since the program started in the Weaviate instance Shown as fraction |
| weaviate.go.memstats.gc.sys_bytes (gauge) | The number of bytes used for garbage collection system metadata in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.heap.alloc_bytes (gauge) | The number of heap bytes allocated and still in use in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.heap.idle_bytes (gauge) | The number of heap bytes waiting to be used in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.heap.inuse_bytes (gauge) | The number of heap bytes that are in use in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.heap.objects (gauge) | The number of allocated objects in the Weaviate instance Shown as object |
| weaviate.go.memstats.heap.released_bytes (gauge) | The number of heap bytes released to the OS in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.heap.sys_bytes (gauge) | The number of heap bytes obtained from system in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.lookups.count (count) | The number of pointer lookups |
| weaviate.go.memstats.mallocs.count (count) | The number of mallocs |
| weaviate.go.memstats.mcache.inuse_bytes (gauge) | The number of bytes in use by mcache structures in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.mcache.sys_bytes (gauge) | The number of bytes used for mcache structures obtained from system in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.mspan.inuse_bytes (gauge) | The number of bytes in use by mspan structures in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.mspan.sys_bytes (gauge) | The number of bytes used for mspan structures obtained from system in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.next.gc_bytes (gauge) | The number of heap bytes when next garbage collection takes place in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.other.sys_bytes (gauge) | The number of bytes used for other system allocations in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.stack.inuse_bytes (gauge) | The number of bytes in use by the stack allocator in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.stack.sys_bytes (gauge) | The number of bytes obtained from system for stack allocator in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.memstats.sys_bytes (gauge) | The number of bytes obtained from system in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.go.threads (gauge) | The number of OS threads created in the Weaviate instance Shown as thread |
| weaviate.http.latency_ms (gauge) | The HTTP request response time latency in ms Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.lsm.active.segments (gauge) | The number of currently present segments per shard. Granularity is shard of a class. Grouped by strategy Shown as segment |
| weaviate.lsm.bloom.filters.duration_ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration of a bloom operation Shown as operation |
| weaviate.lsm.bloom.filters.duration_ms.sum (count) | The duration of a bloom filter operation per shard in ms. Granularity is shard of a class. Grouped by strategy Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.lsm.memtable.durations_ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration of a sync or async vector index maintenance operation Shown as operation |
| weaviate.lsm.memtable.durations_ms.sum (count) | The duration of a sync or async vector index maintenance operation. The operation itself is defined through the operation label Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.lsm.memtable.size (gauge) | The size of memtable by path |
| weaviate.lsm.segment.objects (gauge) | The number of entries per LSM segment by level. Granularity is shard of a class. Grouped by strategy and level Shown as object |
| weaviate.lsm.segment.size (gauge) | The size of LSM segment by level and unit |
| weaviate.lsm.segments (gauge) | The number of segments by level Shown as segment |
| weaviate.node.shard.objects (gauge) | The number of objects inside a Weaviate shard Shown as object |
| weaviate.node.stats.objects (gauge) | The number of objects inside a Weaviate node Shown as object |
| weaviate.node.stats.shards (gauge) | The number of shard inside a Weaviate shard Shown as shard |
| weaviate.node.status (gauge) | The current status of a Weaviate Node. 0:HEALTHY, 1:UNHEALTHY, 2:UNAVAILABLE, and 3:UNKNOWN |
| weaviate.objects (gauge) | The numbers of objects present. Granularity is a shard of a class Shown as object |
| weaviate.objects.durations_ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration of an individual object operation Shown as operation |
| weaviate.objects.durations_ms.sum (count) | The duration of an individual object operation, such as put, delete, etc. as indicated by the operation label, also as part of a batch. The step label adds additional precisions to each operation. Granularity is a shard of a class Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.process.cpu.seconds.count (count) | The total user and system CPU time spent in seconds in the Weaviate instance Shown as second |
| weaviate.process.max_fds (gauge) | The maximum number of open file descriptors in the Weaviate instance |
| weaviate.process.open_fds (gauge) | The number of open file descriptors in the Weaviate instance |
| weaviate.process.resident_memory.bytes (gauge) | The resident memory size in bytes in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.process.start_time.seconds (gauge) | The start time of the process since unix epoch in seconds in the Weaviate instance Shown as second |
| weaviate.process.virtual_memory.bytes (gauge) | The virtual memory size in bytes in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.process.virtual_memory.max_bytes (gauge) | The maximum amount of virtual memory available in bytes in the Weaviate instance Shown as byte |
| weaviate.promhttp.metric_handler.requests.count (count) | The total number of scrapes by HTTP status code Shown as request |
| weaviate.promhttp.metric_handler.requests_in_flight (gauge) | The current number of scrapes being served Shown as request |
| weaviate.queries.durations_ms.bucket (count) | The number of operations observed in the query duration histogram by upper_bound bucketsShown as operation |
| weaviate.queries.durations_ms.count (count) | The count of operations observed in the query duration histogram Shown as operation |
| weaviate.queries.durations_ms.sum (count) | The sum of query durations in milliseconds Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.queries.filtered.vector.durations_ms.count (count) | The count of the duration of queries summary |
| weaviate.queries.filtered.vector.durations_ms.sum (count) | The duration of queries in milliseconds Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.query.dimensions.count (count) | The vector dimensions used by any read-query that involves vectors |
| weaviate.requests (gauge) | The number of requests tagged by a given status(ok, usererror, servererror). Available only on Weaviate version 1.20.0+ Shown as request |
| weaviate.startup.diskio.throughput.bucket (count) | The number of operations observed for the the disk I/O throughput duration by upper_bound bucketsShown as operation |
| weaviate.startup.diskio.throughput.count (count) | The count of operations observed in the disk I/O throughput duration histogram Shown as operation |
| weaviate.startup.diskio.throughput.sum (count) | The sum of disk I/O throughput startup operations in bytes/s, such as reading back the HNSW index or recovering LSM segments. The operation itself is defined by the operation label Shown as byte |
| weaviate.startup.durations_ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration individual startup operation Shown as operation |
| weaviate.startup.durations_ms.sum (count) | The duration of individual startup operations in ms. The operation itself is defined through the operation label Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.startup.progress (gauge) | The ratio (percentage) of startup progress for a particular component in a shard |
| weaviate.vector.dimensions.count (count) | The total dimensions in a shard |
| weaviate.vector.index.durations_ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration of a sync or async vector index operation Shown as operation |
| weaviate.vector.index.durations_ms.sum (count) | The duration of regular vector index operation, such as insert or delete. The operation itself is defined through the operation label. The step label adds more granularity to each operation Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.vector.index.maintenance.durations_ms.count (count) | The number of samples used to calculate the duration of a sync or async vector index operation Shown as operation |
| weaviate.vector.index.maintenance.durations_ms.sum (count) | The duration of a sync or async vector index maintenance operation. The operation itself is defined through the operation label Shown as millisecond |
| weaviate.vector.index.operations (gauge) | The total number of mutating operations on the vector index. The operation itself is defined by the operation label Shown as operation |
| weaviate.vector.index.size (gauge) | The total capacity of the vector index. Typically larger than the number of vectors imported as it grows proactively |
| weaviate.vector.index.tombstone.cleaned.count (count) | The total number of deleted and removed vectors after repair operations |
| weaviate.vector.index.tombstone.cleanup.threads (gauge) | The number of currently active threads for repairing/cleaning up the vector index after deletes have occurred |
| weaviate.vector.index.tombstones (gauge) | The number of active vector index tombstones |
Events
The Weaviate integration does not include any events.
Service Checks
weaviate.openmetrics.health
Returns CRITICAL if the Agent is unable to connect to the Weaviate OpenMetrics endpoint, otherwise returns OK.
Statuses: ok, critical
weaviate.node.status
Returns CRITICAL if the node is UNAVAILABLE, WARNING if UNHEALTHY and OK if HEALTHY.
Statuses: ok, warning, critical
weaviate.liveness.status
Returns OK if liveness endpoint returns a 200 response, otherwise returns CRITICAL.
Statuses: ok, critical
Troubleshooting
Need help? Contact Datadog support.
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles:
