- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Integrations
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- APM Tracing
- Profiler
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic Monitoring
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Test Impact Analysis
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Datadog Mobile App
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Infrastructure
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Product Analytics
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Optimization
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Timeshift
Here is a set of functions performing a time shift of your data. These functions display the values from the corresponding time period on the graph. On their own, they may not be of high value, but together with the current values they may provide useful insight into the performance of your application.
Timeshift
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
timeshift() | Graph values from an arbitrary <TIME_IN_SECOND> before the current timestamp for the metric. | timeshift(<METRIC_NAME>{*}, -<TIME_IN_SECOND>) |
For example, if you wanted to use this to compare current system load with load from 2 weeks ago (60*60*24*14 = 1209600), your query would be:
timeshift(avg:system.load.1{*}, -1209600)
Calendar shift
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
calendar_shift() | Graph values from the previous day, week, or month from the current timestamp for the metric. | calendar_shift(<METRIC_NAME>{*}, "<TIME_SHIFT_STRING>", "<TIME_ZONE_CODE>") |
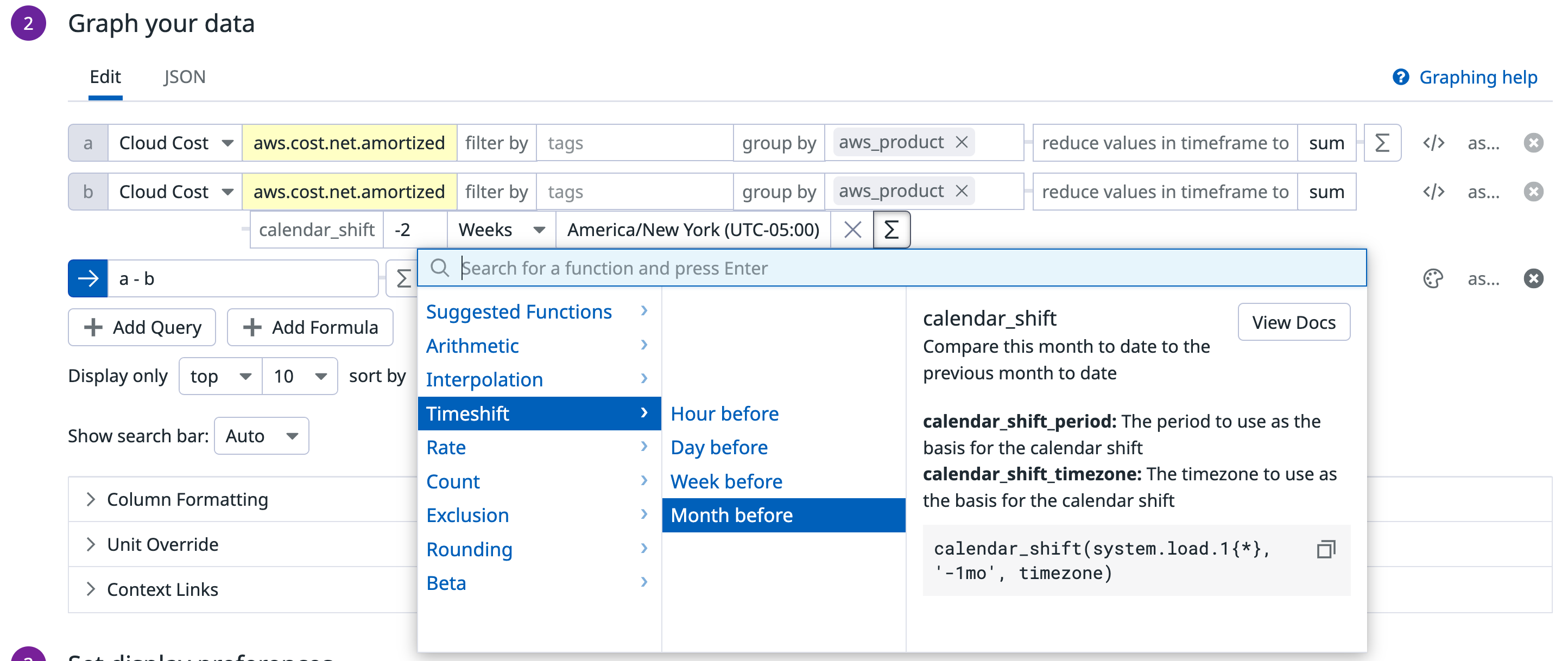
To access the calendar_shift() function click the Add function button, select Timeshift > Month before. The calendar shift allows you to compare the same metric across equivalent time frames. Below is an example of cloud cost metric aws.cost.net.amortized with the calendar_shift() value from two weeks ago compared to the current value.
Valid TIME_SHIFT_STRING values are negative integers followed by “d” for days, “w” for weeks, or “mo” for months.
Some examples are -1d, -7d, -1mo, -30d, and -4w.
Valid TIME_ZONE_CODE values are the IANA time zone codes for a specific city, or UTC.
For example, UTC, America/New_York, Europe/Paris, or Asia/Tokyo.
Hour before
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
hour_before() | Graph values from an hour before the current timestamp for the metric. | hour_before(<METRIC_NAME>{*}) |
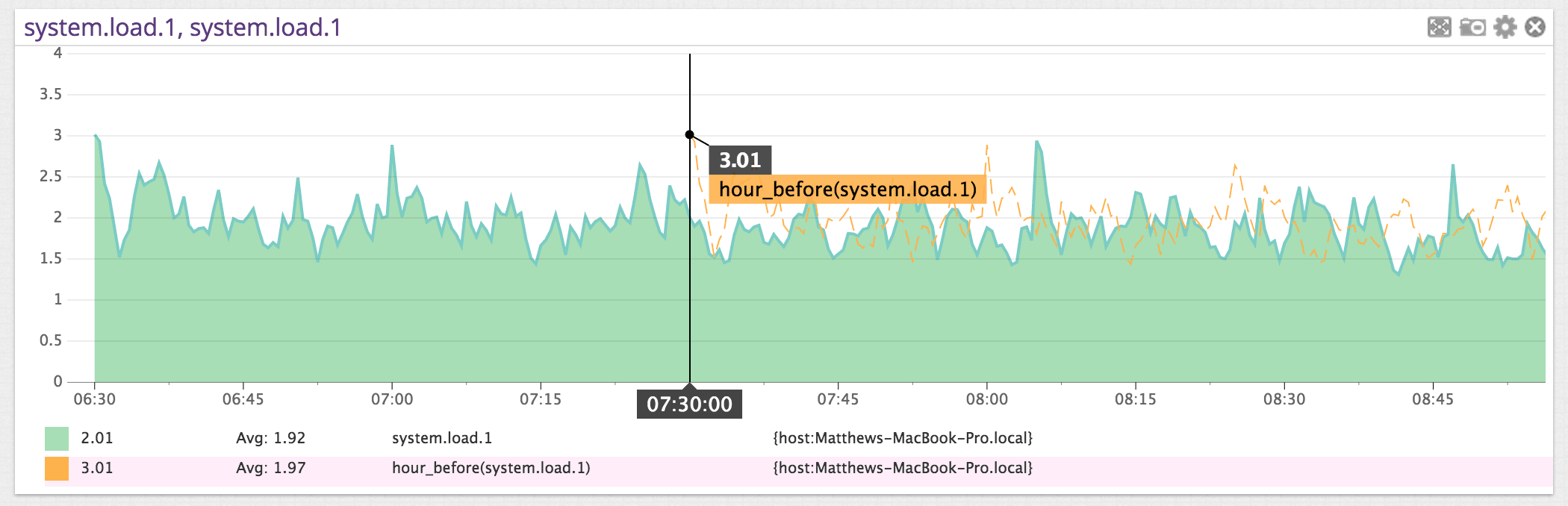
Here is an example of system.load.1 with the hour_before() value shown as a dotted line. In this particular example, you can see the machine was started at 6:30am and the hour_before() values show up at the 7:30 mark. Of course, this example was created specifically so that you can see the hour_before() values match up with the actual values.
Day before
The day before feature is being deprecated. Use calendar shift with a value of "-1d" instead.
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
day_before() | Graph values from a day before the current timestamp for the metric. | day_before(<METRIC_NAME>{*}) |
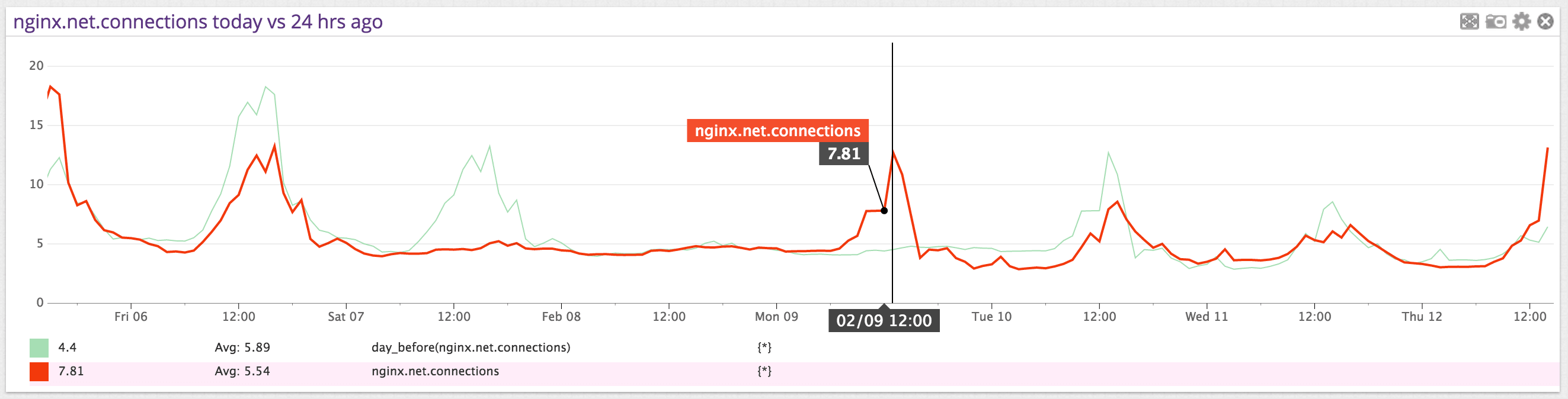
Here is an example of nginx.net.connections with the day_before() value shown as a lighter, thinner line. In this example, you can see a week’s worth of data, which makes the day_before() data easier to identify.
Week before
The week before feature is being deprecated. Use calendar shift with a value of "-7d" instead.
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
week_before() | Graph values from a week (7 days) before the current timestamp for the metric. | week_before(<METRIC_NAME>{*}) |
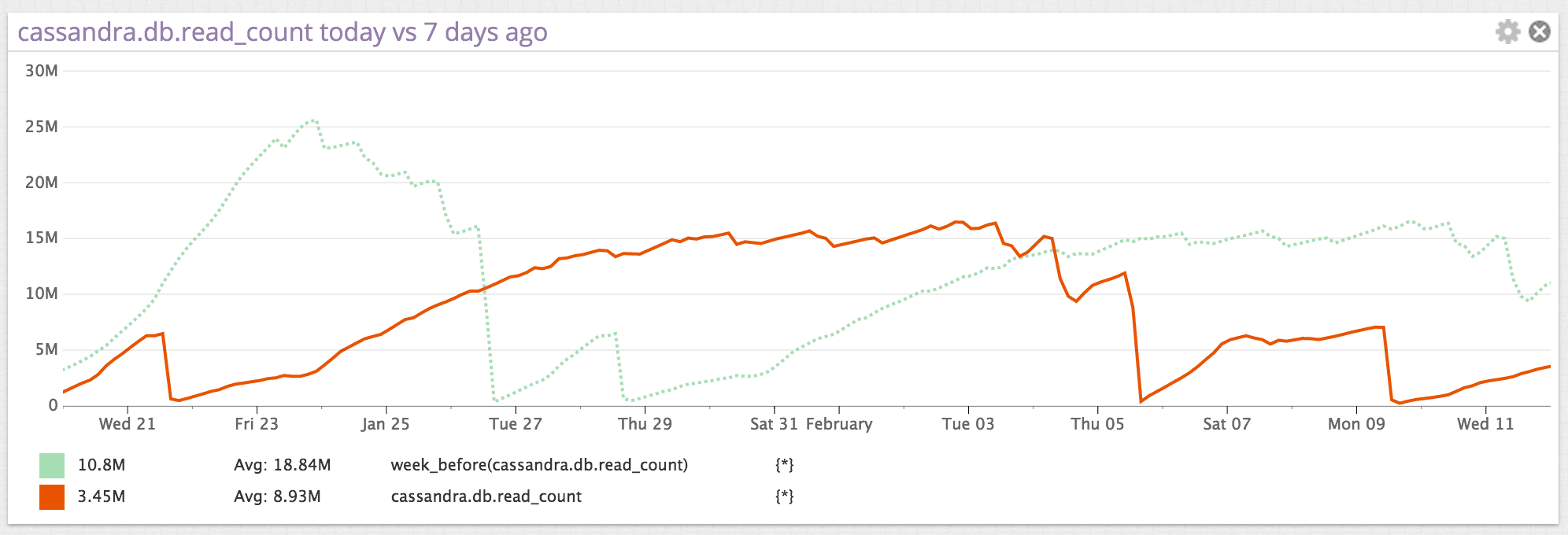
Here is an example of cassandra.db.read_count with the week_before() value shown as a dotted line. In this example, you can see about three weeks’ worth of data, which makes the week_before() data easier to identify.
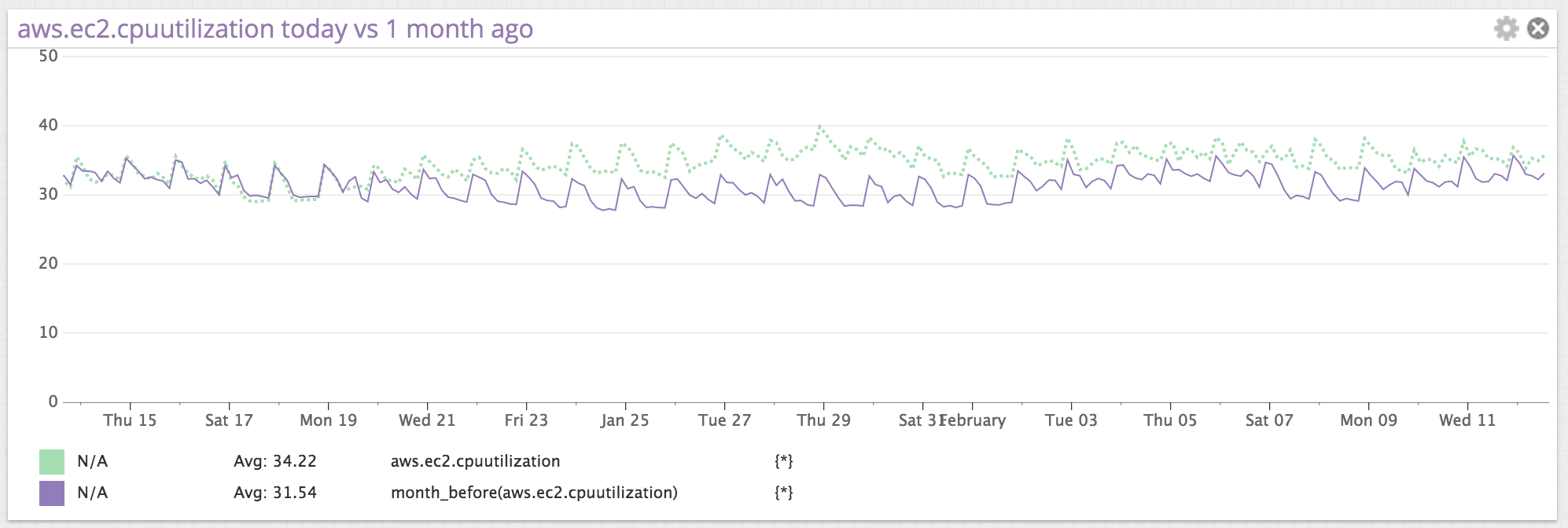
Month before
The month before feature is being deprecated. Use calendar shift with a value of "-1mo", "-30d" or "-4w" instead, depending on your use case.
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
month_before() | Graph values from a month (28 days / 4 weeks) before the current timestamp for the metric. | month_before(<METRIC_NAME>{*}) |
Here is an example of aws.ec2.cpuutilization with the month_before() value shown as a thin, solid line.
Other functions
Consult the other available functions:
- Algorithmic: Implement Anomaly or Outlier detection on your metric.
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: