- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Integrations
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- APM Tracing
- Profiler
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic Monitoring
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Test Impact Analysis
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- API
- Datadog Mobile App
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Infrastructure
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Product Analytics
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Optimization
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Remote Configuration
Remote Configuration is not supported for your selected Datadog site ().
Overview
Remote Configuration is a Datadog capability that allows you to remotely configure and change the behavior of Datadog components (for example, Agents, tracing libraries, and Observability Pipelines Worker) deployed in your infrastructure, for select product features. Use Remote Configuration to apply configurations to Datadog components in your environment on demand, decreasing management costs, reducing friction between teams, and accelerating issue resolution times.
For Datadog security products, Application Security Management and Cloud Security Management Threats (CSM Threats), Remote Configuration-enabled Agents and compatible tracing libraries provide real-time security updates and responses, enhancing security posture for your applications and cloud infrastructure.
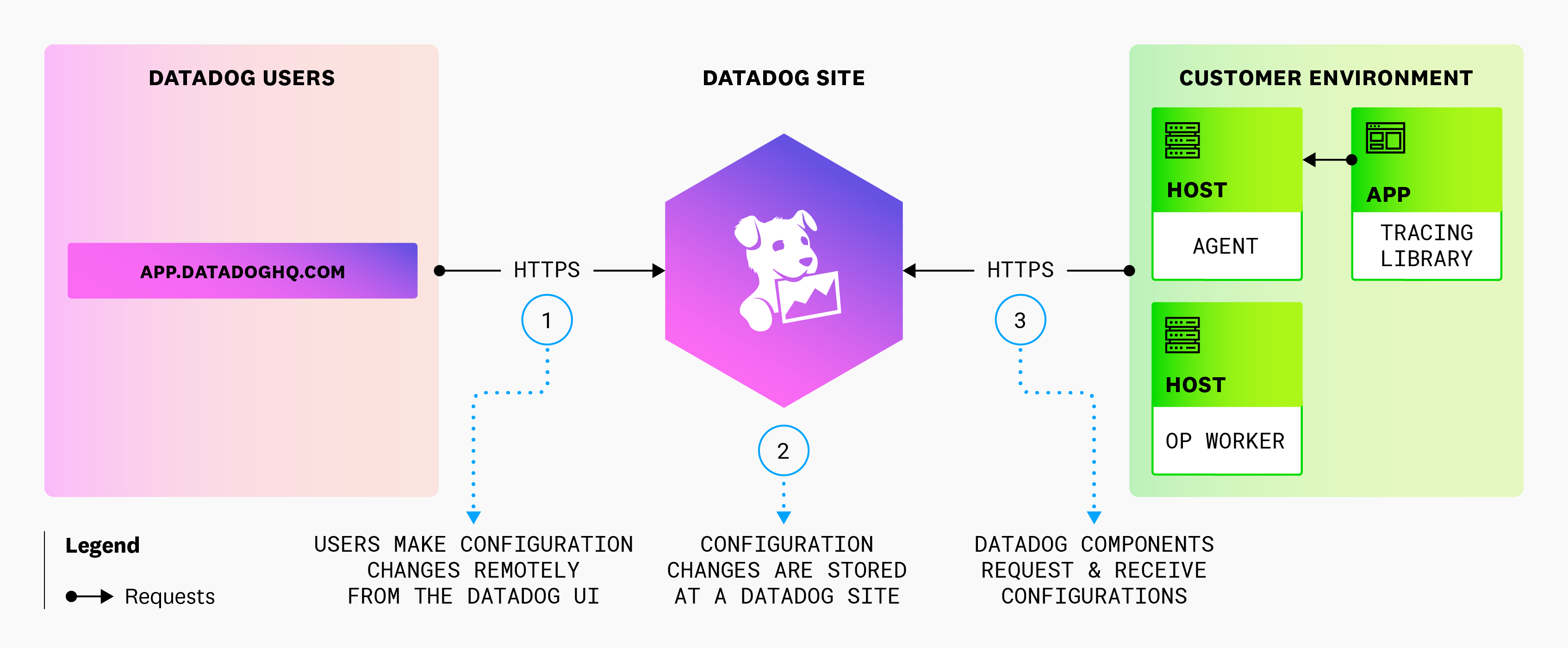
How it works
When Remote Configuration is enabled on the Datadog Agent, it periodically polls the configured Datadog site, to determine whether there are configuration changes to apply to your Remote Configuration-enabled Agents or tracing libraries.
After you submit configuration changes in the respective Datadog product UI for a Remote Configuration-enabled product feature, the changes are stored in Datadog.
The following diagram illustrates how Remote Configuration works:
- You configure select product features in the Datadog UI.
- The product feature configurations are securely stored within Datadog.
- Agents in your environments securely poll, receive, and automatically apply configuration updates from Datadog. Tracing libraries, deployed in your environments, communicate with Agents to request and receive configuration updates from Datadog.
Configuration order precedence
Configurations set by higher-priority sources take precedence in the active configuration displayed in Fleet Automation.
Sources from highest to lowest priority:
- Remote Configuration
Note: Configuration changes applied through Remote Configuration are not shown in your local configuration file (
datadog.yaml). - Environment variables set by tools like Helm
- Configuration files (
datadog.yaml) that are managed locally or by configuration management tools like Ansible, Chef, or Puppet
Configurations issued by higher-priority sources override configurations issued by lower-priority sources.
Supported products and feature capabilities
The following products and features are supported with Remote Configuration:
Fleet Automation
Send flares directly from the Datadog site. Seamlessly troubleshoot the Datadog Agent without directly accessing the host.
Application Security Management (ASM)
- 1-click ASM activation: Enable ASM in 1-click from the Datadog UI.
- In-App attack patterns updates: Receive the newest Web Application Firewall (WAF) attack patterns automatically as Datadog releases them, following newly disclosed vulnerabilities or attack vectors.
- Protect: Block attackers’ IPs, authenticated users, and suspicious requests that are flagged in ASM Security Signals and Traces temporarily or permanently through the Datadog UI.
Application Performance Monitoring (APM)
- Configuration at runtime (Beta): Change a service’s trace sampling rate, Log Injection enablement, and HTTP header tags from within the Service Catalog UI, without having to restart the service. Read Configuration at Runtime for more information.
- Remotely set Agent sampling rate (Public Beta): Remotely configure the Datadog Agent to change its trace sampling rates and set rules to scale your organization’s trace ingestion according to your needs, without needing to restart your Datadog Agent.
Dynamic Instrumentation
- Send critical metrics, traces, and logs from your live applications with no code changes.
CSM Threats
- Automatic default Agent rule updates: Automatically receive and update the default Agent rules maintained by Datadog as new Agent detections and enhancements are released. See Setting Up CSM Threats for more information.
- Automatic deployment of custom Agent rules: Automatically deploy your custom Agent rules to designated hosts (all hosts or a defined subset of hosts).
Observability Pipelines
- Remotely deploy and update Observability Pipelines Workers (OPW): Build and edit pipelines in the Datadog UI, rolling out your configuration changes to OPW instances running in your environment.
Sensitive Data Scanner (SDS) through the Datadog Agent
- Redact sensitive information in your logs within your premises (Private Beta): Remotely configure and deploy OOTB Sensitive Data Scanning rules to the Datadog Agent in your environment. See Sensitive Data Scanner for more information.
Security considerations
Datadog implements the following safeguards to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of configurations received and applied by your Datadog components:
- Agents deployed in your infrastructure request configurations from Datadog.
- Datadog never sends configurations unless requested by Agents, and only sends configurations relevant to the requesting Agent.
- Because the configuration requests are initiated from your Agents to Datadog over HTTPS (port 443), there is no need to open additional ports in your network firewall.
- The communication between your Agents and Datadog is encrypted using HTTPS, and is authenticated and authorized using your Datadog API key.
- Only users with the
api_keys_writepermissions are authorized to enable or disable Remote Configuration capability on the API key and use the supported product features. - Your configuration changes submitted through the Datadog UI are signed and validated on the Agent and requesting Datadog components, verifying integrity of the configuration.
Enabling Remote Configuration
Prerequisites
- Datadog Agent version
7.41.1(7.42.0for APM sampling rate,7.43.0for APM Remote Instrumentation) or higher installed on your hosts or containers. - For Datadog products that use tracing libraries, you also need to upgrade your tracing libraries to a Remote Configuration-compatible version. For ASM Protection capabilities and ASM 1-click activation, see ASM compatibility requirements. For Dynamic Instrumentation, see Dynamic Instrumentation prerequisites.
Setup
To enable Remote Configuration:
Ensure your RBAC permissions include
org_management, so you can enable Remote Configuration for your organization.Ensure your RBAC permissions include
api_keys_write, so you can create a new API key with the Remote Configuration capability, or add the capability to an existing API key. Contact your organization’s Datadog administrator to update your permissions if you don’t have it. A key with this capability allows you to authenticate and authorize your Agent to use Remote Configuration.On the Remote Configuration page, enable Remote Configuration. This enables Datadog components across your organization to receive configurations from Datadog. Note: Beginning April 8, 2024, Remote Configuration is on-by-default for:
- New child organizations that are created by existing Datadog customers who already have enabled Remote Configuration at the parent organization level and are in the same Datadog site as their parent organization.
- Organizations created by new Datadog customers.
To opt-out of Remote Configuration use, see the opt-out section.
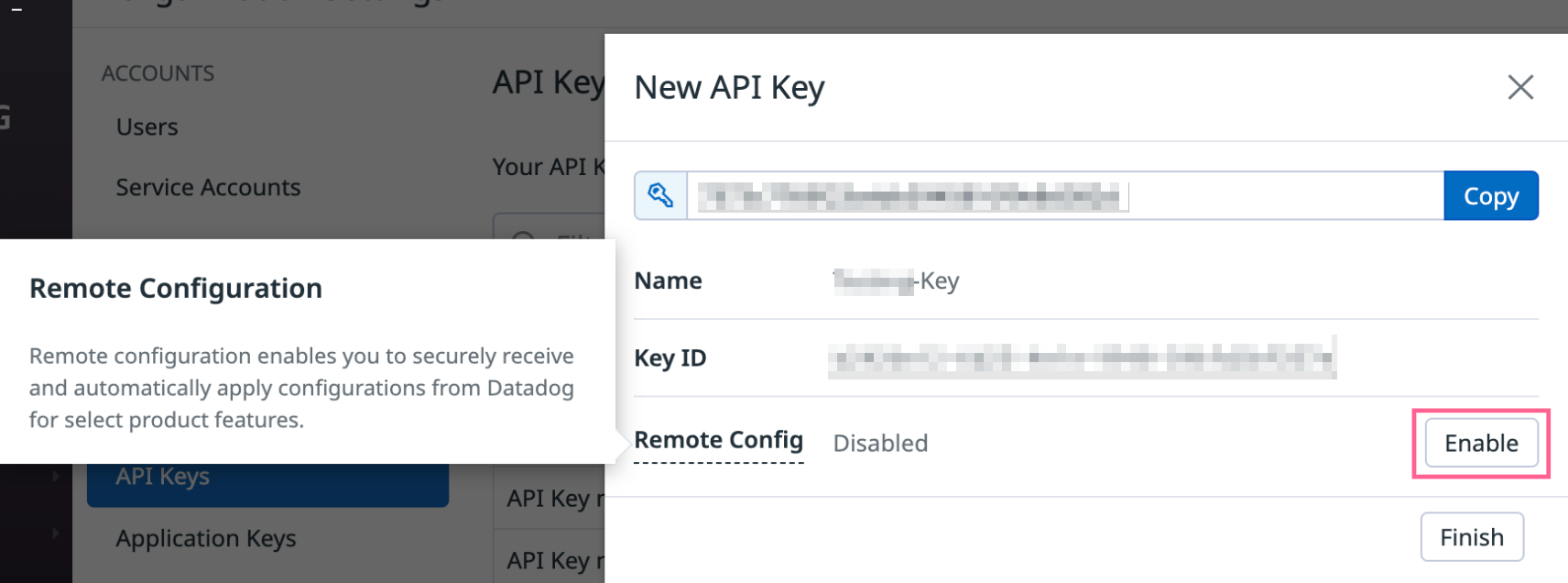
Select an existing API key or create a new API key, and enable the Remote Configuration capability on the key. If your new organization fulfills the conditions mentioned in step 3, Remote Configuration is enabled on your API keys be default.
Update your Agent configuration file: Note: This step is required only for Agent versions 7.46.0 or lower. Starting with Agent version 7.47.0,
remote_configuration.enabledis set totrueby default in the Agent. To opt-out of Remote Configuration use, see the opt-out section.
Add the following to your configuration YAML file, specifying the API key that has Remote Configuration capability enabled:
api_key: xxx
remote_configuration:
enabled: true
Add the following to your Datadog Agent manifest, specifying the API key that has Remote Configuration capability enabled:
DD_API_KEY=xxx
DD_REMOTE_CONFIGURATION_ENABLED=true
Add the following to your Helm chart, specifying the API key that has Remote Configuration capability enabled:
datadog:
apiKey: xxx
remoteConfiguration:
enabled: true
- Restart your Agent for the changes to take effect.
After you perform these steps, your Agent requests its configuration from Datadog, and the features that use remote configuration are enabled:
- CSM Threats default agent rules update automatically as released.
- APM Agent-level sampling rates are applied.
- Dynamic Instrumentation is enabled.
- ASM 1-Click enablement, IP blocking, and attack pattern updates are enabled.
Best practices
Datadog Audit Trail
Use Datadog Audit Trail to monitor organization access and Remote Configuration enabled events. Audit Trail allows your administrators and security teams to track the creation, deletion, and modification of Datadog API and application keys. After Audit Trail is configured, you can view events related to Remote Configuration enabled features and who has requested these changes. Audit Trail allows you to reconstruct sequences of events, and establish robust Datadog monitoring for Remote Configuration.
Monitors
Configure monitors to receive notifications when an event of interest is encountered.
Troubleshooting
If you experience issues using Remote Configuration, use the following troubleshooting guidelines. If you need further assistance, contact Datadog support.
Restart the Agent
After the Agent configuration is updated in the datadog.yaml file, restart the Agent for this change to take effect.
Ensure Datadog Remote Configuration endpoints are reachable from your environment
To use Remote Configuration, both the Agent and the Observability Pipelines Worker deployed in your environment communicate to Datadog Remote Configuration endpoints. For private network connection between your environment and Datadog, you can also connect to Remote Configuration Virtual Private Cloud endpoints. Ensure that outbound HTTPS has access to Remote Configuration endpoints from your environment. If you also have a proxy in between Datadog and your environment, update your proxy settings to incorporate Remote Configuration endpoints.
Enable Remote Configuration at the organization level
To enable Remote Configuration at the Organization level in the Datadog UI, go to the Remote Configuration Setup page in your Organization Settings. This allows your authenticated and authorized Datadog components to remotely receive configurations and security detection rules of supported features from Datadog. Only users who have the org_management RBAC permission can enable Remote Configuration at the Organization level.
Enable Remote Configuration on the API key
To authenticate and authorize the Agent to receive configurations and security detection rules, and to allow the Observability Pipelines Worker to receive configurations, enable Remote Configuration on the relevant API Key. Only users who have the api_keys_write RBAC permission can enable Remote Configuration on the API Key.
Note: If you have api_keys_write RBAC permission, but are missing Remote Configuration Organization level permissions, you cannot enable Remote Configuration on a new or an existing API Key. You only have permission to disable Remote Configuration on an existing API Key.
Review Remote Configuration status of Agents and Tracing libraries
Gain visibility into the Remote Configuration status of your Agent and Tracing library through the Remote Configuration UI.
The following table describes the meaning of each Agent status:
| Agent Status | Description |
|---|---|
| CONNECTED | The Agent deployed in your environment is able to reach, authenticate, and authorize successfully to Datadog. This is the optimal state you want your Agents to be in for Remote Configuration. |
| UNAUTHORIZED | The Agent deployed in your environment is able to reach Datadog but is not able to authenticate and authorize with Datadog for Remote Configuration operation. The most likely cause is the API Key used by the Agent is not Remote Configuration-enabled. To fix the issue, enable Remote Configuration capability on the API Key used by the Agent. |
| CONNECTION ERROR | The Agent deployed in your environment has remote_config.enabled set to true in its datadog.yaml configuration file, however, the Agent cannot be found in the Remote Configuration service. The most likely cause is that the Agent is unable to reach Remote Configuration endpoints. To fix the issue, allow outbound HTTPS access to Remote Configuration endpoints from your environment. This status displays when the Agent version is 7.45.0 or higher. |
| DISABLED | The Agent deployed in your environment has remote_config.enabled set to false in its datadog.yaml configuration file. Set remote_config.enabled to true if you want to enable Remote Configuration on the Agent. This status displays when the Agent version is 7.45.0 or higher. |
| NOT CONNECTED | The Agent cannot be found in the Remote Configuration service and could have remote_config.enabled set to true or false in its datadog.yaml configuration file. Check your local Agent configuration or your proxy settings. This status displays when the Agent version is higher than 7.41.1 but lower than 7.45.0. |
| UNSUPPORTED AGENT | The Agent is on a version that is not Remote Configuration capable. To fix this issue, update the Agent to the latest available version. |
The following table describes the meaning of each Tracing library status:
| Tracing library Status | Description |
|---|---|
| CONNECTED | The Tracing library is successfully connected to the Remote Configuration service through the associated Agent. This is the optimal state you want your Tracing library to be in for Remote Configuration. |
| UNAUTHORIZED | The Tracing library is associated with an Agent which doesn’t have Remote Config Read permission on its API key. To fix the issue, you need to enable Remote Configuration capability on the API Key used by the Agent associated with the Tracing library. |
| CONNECTION ERROR | The Tracing library deployed in your environment is associated with an Agent that has remote_config.enabled set to true in its datadog.yaml configuration file, however, the agent cannot be found in the Remote Configuration service. The most likely cause of this is that the associated Agent is unable to reach Remote Configuration endpoints. To fix the issue, you need to allow outbound HTTPS access to Remote Configuration endpoints from your environment. |
| DISABLED | The Tracing library deployed in your environment is associated with an Agent that has remote_config.enabled set to false in its datadog.yaml configuration file. This could be set deliberately or mistakenly. To enable Remote Configuration on the associated Agent, set remote_config.enabled to true. |
| NOT CONNECTED | The Tracing library cannot be found in the Remote Configuration service and is associated with an Agent that could have remote_config.enabled set to true or false in its datadog.yaml configuration file. Check your local Agent configuration or your proxy settings. |
| UNSUPPORTED AGENT | The Tracing library is associated with an Agent which is not Remote Configuration capable. To fix this issue, update the associated Agent software to the latest available version. |
| NOT DETECTED | The Tracing library does not support Remote Configuration. To fix this issue, update the Tracing library software to the latest available version. |
| UNKNOWN | The Tracing library status is unknown, and it can’t be determined if an Agent is associated with the Tracing library. For example, this could be because the Agent is deployed on a fully managed serverless container service like AWS Fargate. |
Opting out of Remote Configuration
To opt-out of Remote Configuration use, you can disable Remote Configuration at the organization level. Optionally, you can also disable Remote Configuration capability at the API key level and Agent level.
At the Organization level
Disable Remote Configuration at the organization level on the Remote Configuration page. This disables Datadog components across your organization to receive configurations from Datadog. You need the org_management permission to disable Remote Configuration at the organization level.
At the API key level
Disable the API key of your choice on the API Keys page. You need the api_keys_write permission to disable Remote Configuration on an API key.
At the Agent level
Starting with Agent version 7.47.0, remote_configuration.enabled is set to true by default in the Agent. This setting causes the Agent to request configuration updates from the Datadog site.
To receive configurations from Datadog, you also need to take the following steps:
- Enable Remote Configuration at the organization level.
- Enable Remote Configuration capability on your API Key from the Datadog UI.
- Allow outbound HTTPS access to Remote Configuration endpoints from your environment.
If you don’t want your Agent to send configuration requests to Datadog, you can set remote_configuration.enabled to false in the Agent.
Change remote_configuration.enabled from true to false in your configuration YAML file:
remote_configuration:
enabled: false
Add the following to your Datadog Agent manifest:
DD_REMOTE_CONFIGURATION_ENABLED=false
Add the following to your Helm chart:
datadog:
remoteConfiguration:
enabled: false
Supported environments
Remote Configuration works in environments where the Datadog Agent is deployed. Remote Configuration supports serverless container cloud services such as AWS Fargate. Remote Configuration does not support serverless container managed apps (AWS App Runner, Azure Container Apps, Google Cloud Run) and functions deployed with container packaging (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions).
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: