- Esenciales
- Empezando
- Datadog
- Sitio web de Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless para Lambda AWS
- Agent
- Integraciones
- Contenedores
- Dashboards
- Monitores
- Logs
- Rastreo de APM
- Generador de perfiles
- Etiquetas (tags)
- API
- Catálogo de servicios
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Monitorización Synthetic
- Gestión de incidencias
- Monitorización de bases de datos
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Análisis de código
- Centro de aprendizaje
- Compatibilidad
- Glosario
- Atributos estándar
- Guías
- Agent
- Uso básico del Agent
- Arquitectura
- IoT
- Plataformas compatibles
- Recopilación de logs
- Configuración
- Configuración remota
- Automatización de flotas
- Actualizar el Agent
- Solucionar problemas
- Detección de nombres de host en contenedores
- Modo de depuración
- Flare del Agent
- Estado del check del Agent
- Problemas de NTP
- Problemas de permisos
- Problemas de integraciones
- Problemas del sitio
- Problemas de Autodiscovery
- Problemas de contenedores de Windows
- Configuración del tiempo de ejecución del Agent
- Consumo elevado de memoria o CPU
- Guías
- Seguridad de datos
- Integraciones
- OpenTelemetry
- Desarrolladores
- Autorización
- DogStatsD
- Checks personalizados
- Integraciones
- Crear una integración basada en el Agent
- Crear una integración API
- Crear un pipeline de logs
- Referencia de activos de integración
- Crear una oferta de mercado
- Crear un cuadro
- Crear un dashboard de integración
- Crear un monitor recomendado
- Crear una regla de detección Cloud SIEM
- OAuth para integraciones
- Instalar la herramienta de desarrollo de integraciones del Agente
- Checks de servicio
- Complementos de IDE
- Comunidad
- Guías
- API
- Aplicación móvil de Datadog
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- En la aplicación
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- Editor DDSQL
- Hojas
- Monitores y alertas
- Infraestructura
- Métricas
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Catálogo de servicios
- Catálogo de APIs
- Error Tracking
- Gestión de servicios
- Objetivos de nivel de servicio (SLOs)
- Gestión de incidentes
- De guardia
- Gestión de eventos
- Gestión de casos
- Workflow Automation
- App Builder
- Infraestructura
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Contenedores
- Serverless
- Monitorización de red
- Coste de la nube
- Rendimiento de las aplicaciones
- APM
- Términos y conceptos de APM
- Instrumentación de aplicación
- Recopilación de métricas de APM
- Configuración de pipelines de trazas
- Correlacionar trazas (traces) y otros datos de telemetría
- Trace Explorer
- Observabilidad del servicio
- Instrumentación dinámica
- Error Tracking
- Seguridad de los datos
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Gastos generales de integración del Agent
- Arquitecturas de configuración
- Configuración de Postgres
- Configuración de MySQL
- Configuración de SQL Server
- Configuración de Oracle
- Configuración de MongoDB
- Conexión de DBM y trazas
- Datos recopilados
- Explorar hosts de bases de datos
- Explorar métricas de consultas
- Explorar ejemplos de consulta
- Solucionar problemas
- Guías
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Experiencia digital
- Real User Monitoring
- Monitorización del navegador
- Configuración
- Configuración avanzada
- Datos recopilados
- Monitorización del rendimiento de páginas
- Monitorización de signos vitales de rendimiento
- Monitorización del rendimiento de recursos
- Recopilación de errores del navegador
- Rastrear las acciones de los usuarios
- Señales de frustración
- Error Tracking
- Solucionar problemas
- Monitorización de móviles y TV
- Plataforma
- Session Replay
- Exploración de datos de RUM
- Feature Flag Tracking
- Error Tracking
- Guías
- Seguridad de los datos
- Monitorización del navegador
- Análisis de productos
- Pruebas y monitorización de Synthetics
- Continuous Testing
- Entrega de software
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Configuración
- Tests en contenedores
- Búsqueda y gestión
- Explorador
- Monitores
- Flujos de trabajo de desarrolladores
- Cobertura de código
- Instrumentar tests de navegador con RUM
- Instrumentar tests de Swift con RUM
- Detección temprana de defectos
- Reintentos automáticos de tests
- Correlacionar logs y tests
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- Métricas de DORA
- Seguridad
- Información general de seguridad
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Observabilidad de la IA
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Gestión de logs
- Administración
- Gestión de cuentas
- Seguridad de los datos
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Ayuda
Code Security Setup
This page is not yet available in Spanish. We are working on its translation.
If you have any questions or feedback about our current translation project, feel free to reach out to us!
If you have any questions or feedback about our current translation project, feel free to reach out to us!
Prerequisites
Before setting up Code Security, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- Datadog Agent Installation: The Datadog Agent is installed and configured for your application’s operating system or container, cloud, or virtual environment.
- Datadog APM Configuration: Datadog APM is configured for your application or service, and web traces (
type:web) are being received by Datadog. - Supported Tracing Library: The Datadog Tracing Library used by your application or service supports Code Security capabilities for the language of your application or service. For more details, refer to the Library Compatibility page.
Code Security Enablement Types
There are two main approaches to enable Code Security on your tracing libraries: Single-Step Instrumentation and Datadog Tracing Libraries.
Single-Step Instrumentation
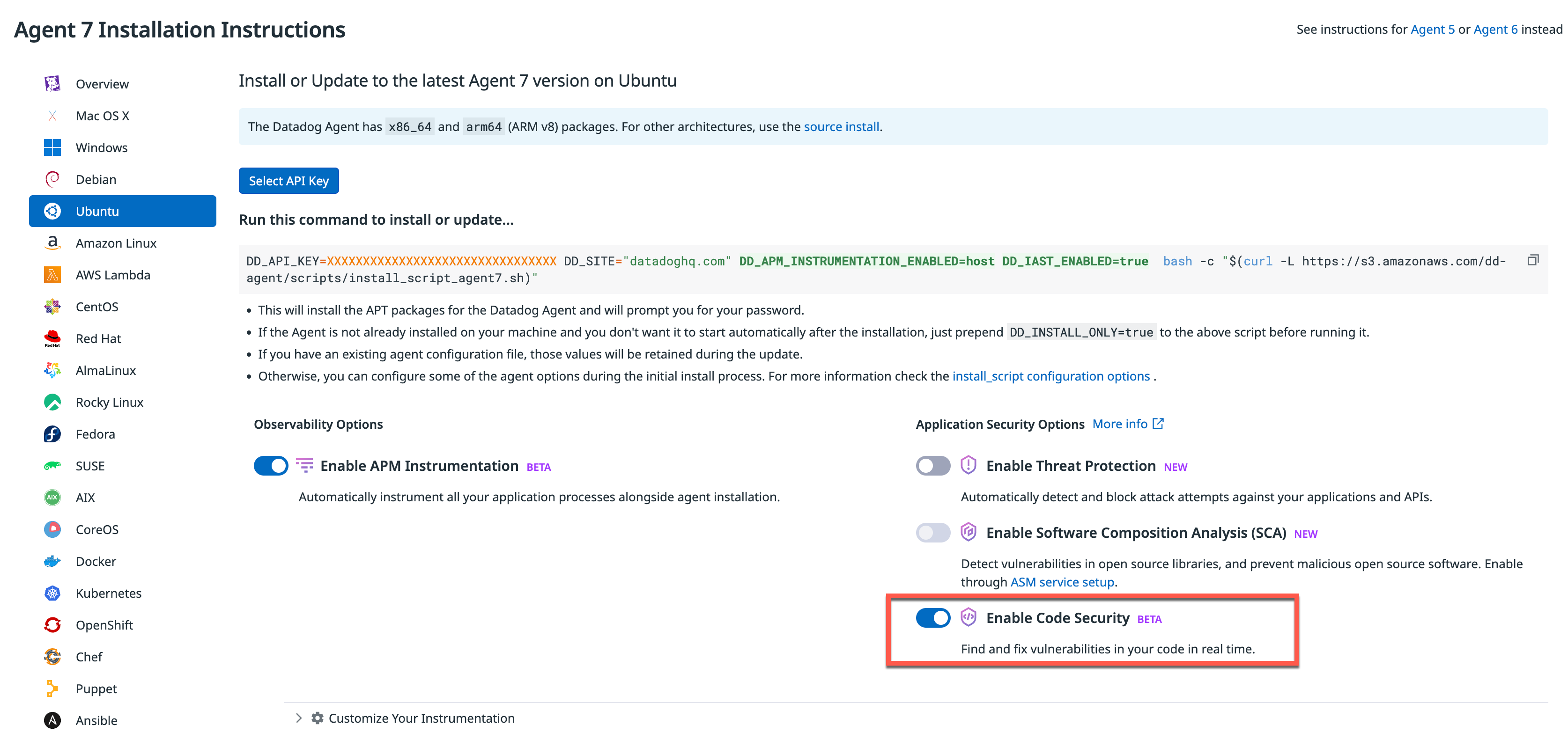
Run a one-line install command to install the Datadog Agent, and enable Code Security with Single-Step Instrumentation.
Datadog Tracing Libraries
Add an environment variable or a new argument to your Datadog Tracing Library configuration.
By following these steps, you’ll successfully set up Code Security for your application or service, ensuring comprehensive monitoring and identification of code-level vulnerabilities at runtime.
Enabling Code Security using single step instrumentation
Enabling Code Security using single step instrumentation is in beta.
Requirements
- Minimum Agent version 7.53.0
- Minimum Datadog Helm chart version 3.62.0 (for Kubernetes deployments).
- Languages and architectures: Single step instrumentation for Code Security only supports tracing Java, Node.js, .NET Core services on
x86_64andarm64architectures, and Python (support available in private beta). - Operating systems: Linux VMs (Debian, Ubuntu, Amazon Linux, CentOS/Red Hat, Fedora), Docker, Kubernetes clusters with Linux containers.
Enabling in one step
If you install or update a Datadog Agent with the Enable Code Security option selected, the Agent is installed and configured to enable detection of code-level vulnerabilities in your applications. This allows you to automatically instrument your application, without any additional installation or configuration steps. Restart services for this instrumentation to take effect.
The following examples show how it works on each infrastructure type.
With one command, you can install, configure, and start the Agent, while also instrumenting your services with Application Security options.
For an Ubuntu host:
Run the one-line installation command:
DD_API_KEY=<YOUR_DD_API_KEY> DD_SITE="<YOUR_DD_SITE>" DD_APM_INSTRUMENTATION_ENABLED=host DD_IAST_ENABLED=true bash -c "$(curl -L https://install.datadoghq.com/scripts/install_script_agent7.sh)"a. Replace
<YOUR_DD_API_KEY>with your Datadog API key.b. Replace
<YOUR_DD_SITE>with your Datadog site.You can also optionally configure the following:Exit your current shell session.
Start a new shell session.
Restart the services on the host or VM.
Explore the performance observability of your services in Datadog.
Note: To configure single-step for both Code Security and Threat Protection, add both the DD_IAST_ENABLED=true and DD_APPSEC_ENABLED=true environment variables to your one-line installation command.
Specifying tracing library versions
By default, enabling APM on your server installs support for Java, Node.js, .NET Core, and Python services. If you only have services implemented in some of these languages, set DD_APM_INSTRUMENTATION_LIBRARIES in your one-line installation command:
DD_APM_INSTRUMENTATION_LIBRARIES="java:1.25.0,python" DD_API_KEY=<YOUR_DD_API_KEY> DD_SITE="<YOUR_DD_SITE>" DD_APM_INSTRUMENTATION_ENABLED=host DD_IAST_ENABLED=true DD_ENV=staging bash -c "$(curl -L https://install.datadoghq.com/scripts/install_script_agent7.sh)"
You can optionally provide a version number for the tracing library by placing a colon after the language name and specifying the tracing library version. If you don’t specify a version, it defaults to the latest version. Language names are comma-separated.
Supported languages include:
- Java (
java) - Node.js (
js) - .NET (
dotnet) - Python (
python)
Note: For the Node.js tracing library, different versions of Node.js are compatible with different versions of the Node.js tracing library. See DataDog/dd-trace-js: JavaScript APM Tracer for more information.
Tagging observability data by environment
Set DD_ENV in your one-line installation command for Linux to automatically tag instrumented services and other telemetry that pass through the Agent with a specific environment. For example, if the Agent is installed in your staging environment, set DD_ENV=staging to associate your observability data with staging.
For example:
DD_API_KEY=<YOUR_DD_API_KEY> DD_SITE="<YOUR_DD_SITE>" DD_APM_INSTRUMENTATION_ENABLED=host DD_IAST_ENABLED=true DD_ENV=staging bash -c "$(curl -L https://install.datadoghq.com/scripts/install_script_agent7.sh)"
For a Docker Linux container:
Install the library injector:
DD_IAST_ENABLED=true DD_APM_INSTRUMENTATION_ENABLED=docker DD_NO_AGENT_INSTALL=true bash -c "$(curl -L https://install.datadoghq.com/scripts/install_script_agent7.sh)"Configure the Agent in Docker:
docker run -d --name dd-agent \ -e DD_API_KEY=${YOUR_DD_API_KEY} \ -e DD_SITE=${YOUR_DD_SITE} \ -e DD_APM_ENABLED=true \ -e DD_APM_NON_LOCAL_TRAFFIC=true \ -e DD_APM_RECEIVER_SOCKET=/var/run/datadog/apm.socket \ -e DD_DOGSTATSD_SOCKET=/var/run/datadog/dsd.socket \ -v /var/run/datadog:/var/run/datadog \ -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \ -v /proc/:/host/proc/:ro \ -v /sys/fs/cgroup/:/host/sys/fs/cgroup:ro \ -v /var/lib/docker/containers:/var/lib/docker/containers:ro \ gcr.io/datadoghq/agent:7a. Replace
<YOUR_DD_API_KEY>with your Datadog API.b. Replace
<YOUR_DD_SITE>with your Datadog site.You can also optionally configure the following:Restart the Docker containers.
Explore the performance observability of your services in Datadog.
Specifying tracing library versions
By default, enabling APM on your server installs support for Java, Python, Node.js, and .NET services. If you only have services implemented in some of these languages, set DD_APM_INSTRUMENTATION_LIBRARIES when running the installation script.
For example, to install support for only v1.25.0 of the Java tracing library and the latest Python tracing library, add the following to the installation command:
DD_APM_INSTRUMENTATION_LIBRARIES="java:1.25.0,python" bash -c "$(curl -L https://install.datadoghq.com/scripts/install_script_docker_injection.sh)"
You can optionally provide a version number for the tracing library by placing a colon after the language name and specifying the tracing library version. If you don’t specify a version, it defaults to the latest version. Language names are comma-separated.
Supported languages include:
- Java (
java) - Node.js (
js) - .NET (
dotnet) - Python (
python)
Note: For the Node.js tracing library, different versions of Node.js are compatible with different versions of the Node.js tracing library. See DataDog/dd-trace-js: JavaScript APM Tracer for more information.
Tagging observability data by environment
Set DD_ENV in the library injector installation command for Docker to automatically tag instrumented services and other telemetry that pass through the Agent with a specific environment. For example, if the Agent is installed in your staging environment, set DD_ENV=staging to associate your observability data with staging.
For example:
docker run -d --name dd-agent \
-e DD_API_KEY=${YOUR_DD_API_KEY} \
-e DD_APM_ENABLED=true \
-e DD_ENV=staging \
-e DD_APM_NON_LOCAL_TRAFFIC=true \
-e DD_DOGSTATSD_NON_LOCAL_TRAFFIC=true \
-e DD_APM_RECEIVER_SOCKET=/opt/datadog/apm/inject/run/apm.socket \
-e DD_DOGSTATSD_SOCKET=/opt/datadog/apm/inject/run/dsd.socket \
-v /opt/datadog/apm:/opt/datadog/apm \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \
gcr.io/datadoghq/agent:7You can enable APM by installing the Agent with the Datadog Helm chart. This deploys the Datadog Agent across all nodes in your Linux-based Kubernetes cluster with a DaemonSet.
Single step instrumentation doesn't instrument applications in the namespace where you install the Datadog Agent. It's recommended to install the Agent in a separate namespace in your cluster where you don't run your applications.
Requirements
- Make sure you have Helm installed.
Installation
To enable single step instrumentation with Helm:
Add the Helm Datadog repo:
helm repo add datadog https://helm.datadoghq.com helm repo updateCreate a Kubernetes Secret to store your Datadog API key:
kubectl create secret generic datadog-secret --from-literal api-key=$DD_API_KEYCreate
datadog-values.yamland add the following configuration:datadog: apiKeyExistingSecret: datadog-secret site: <DATADOG_SITE> apm: instrumentation: enabled: true asm: iast: enabled: trueReplace
<DATADOG_SITE>with your Datadog site.Run the following command:
helm install datadog-agent -f datadog-values.yaml datadog/datadogDo a rolling restart on your applications for instrumentation to take effect.
For more information on Kubernetes single step instrumentation, see the following:
Removing Single Step APM and Application Security instrumentation from your Agent
If you don’t want to collect trace data for a particular service, host, VM, or container, complete the follow steps:
Removing instrumentation for specific services
Run the following commands and restart the service to stop injecting the library into the service and stop producing traces from that service.
Add the
DD_INSTRUMENT_SERVICE_WITH_APMenvironment variable to the service startup command:DD_INSTRUMENT_SERVICE_WITH_APM=false <service_start_command>Restart the service.
To disable Code Security, remove the
DD_IAST_ENABLED=trueenvironment variable from your application configuration, and restart your service.
Add the
DD_INSTRUMENT_SERVICE_WITH_APMenvironment variable to the service startup command:docker run -e DD_INSTRUMENT_SERVICE_WITH_APM=false <service_start_command>Restart the service.
To disable Code Security, remove the
DD_IAST_ENABLED=trueenvironment variable from your application configuration, and restart your service.
Set the
admission.datadoghq.com/enabled:label to"false"for the pod spec:spec: template: metadata: labels: admission.datadoghq.com/enabled: "false"
You can disable Code Security while keeping APM up by adding the
DD_IAST_ENABLED=false environment variable to your deployments.Removing APM for all services on the infrastructure
To stop producing traces, remove library injectors and restart the infrastructure:
- Run:
dd-host-install --uninstall - Restart your host.
- Uninstall local library injection:
dd-container-install --uninstall - Restart Docker:Or use the equivalent for your environment.
systemctl restart docker
Under
apm:, removeinstrumentation:and all following configuration indatadog-values.yaml.Under
asm:, removeiast:and all following configuration indatadog-values.yaml.Run the following command:
helm upgrade datadog-agent -f datadog-values.yaml datadog/datadog
Using Datadog Tracing Libraries
Select your application language for details on how to enable Code Security for your language and infrastructure types.