- Esenciales
- Empezando
- Datadog
- Sitio web de Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless para Lambda AWS
- Agent
- Integraciones
- Contenedores
- Dashboards
- Monitores
- Logs
- Rastreo de APM
- Generador de perfiles
- Etiquetas (tags)
- API
- Catálogo de servicios
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Monitorización Synthetic
- Gestión de incidencias
- Monitorización de bases de datos
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Análisis de código
- Centro de aprendizaje
- Compatibilidad
- Glosario
- Atributos estándar
- Guías
- Agent
- Uso básico del Agent
- Arquitectura
- IoT
- Plataformas compatibles
- Recopilación de logs
- Configuración
- Configuración remota
- Automatización de flotas
- Actualizar el Agent
- Solucionar problemas
- Detección de nombres de host en contenedores
- Modo de depuración
- Flare del Agent
- Estado del check del Agent
- Problemas de NTP
- Problemas de permisos
- Problemas de integraciones
- Problemas del sitio
- Problemas de Autodiscovery
- Problemas de contenedores de Windows
- Configuración del tiempo de ejecución del Agent
- Consumo elevado de memoria o CPU
- Guías
- Seguridad de datos
- Integraciones
- OpenTelemetry
- Desarrolladores
- Autorización
- DogStatsD
- Checks personalizados
- Integraciones
- Crear una integración basada en el Agent
- Crear una integración API
- Crear un pipeline de logs
- Referencia de activos de integración
- Crear una oferta de mercado
- Crear un cuadro
- Crear un dashboard de integración
- Crear un monitor recomendado
- Crear una regla de detección Cloud SIEM
- OAuth para integraciones
- Instalar la herramienta de desarrollo de integraciones del Agente
- Checks de servicio
- Complementos de IDE
- Comunidad
- Guías
- API
- Aplicación móvil de Datadog
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- En la aplicación
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- Editor DDSQL
- Hojas
- Monitores y alertas
- Infraestructura
- Métricas
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Catálogo de servicios
- Catálogo de APIs
- Error Tracking
- Gestión de servicios
- Objetivos de nivel de servicio (SLOs)
- Gestión de incidentes
- De guardia
- Gestión de eventos
- Gestión de casos
- Workflow Automation
- App Builder
- Infraestructura
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Contenedores
- Serverless
- Monitorización de red
- Coste de la nube
- Rendimiento de las aplicaciones
- APM
- Términos y conceptos de APM
- Instrumentación de aplicación
- Recopilación de métricas de APM
- Configuración de pipelines de trazas
- Correlacionar trazas (traces) y otros datos de telemetría
- Trace Explorer
- Observabilidad del servicio
- Instrumentación dinámica
- Error Tracking
- Seguridad de los datos
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Gastos generales de integración del Agent
- Arquitecturas de configuración
- Configuración de Postgres
- Configuración de MySQL
- Configuración de SQL Server
- Configuración de Oracle
- Configuración de MongoDB
- Conexión de DBM y trazas
- Datos recopilados
- Explorar hosts de bases de datos
- Explorar métricas de consultas
- Explorar ejemplos de consulta
- Solucionar problemas
- Guías
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Experiencia digital
- Real User Monitoring
- Monitorización del navegador
- Configuración
- Configuración avanzada
- Datos recopilados
- Monitorización del rendimiento de páginas
- Monitorización de signos vitales de rendimiento
- Monitorización del rendimiento de recursos
- Recopilación de errores del navegador
- Rastrear las acciones de los usuarios
- Señales de frustración
- Error Tracking
- Solucionar problemas
- Monitorización de móviles y TV
- Plataforma
- Session Replay
- Exploración de datos de RUM
- Feature Flag Tracking
- Error Tracking
- Guías
- Seguridad de los datos
- Monitorización del navegador
- Análisis de productos
- Pruebas y monitorización de Synthetics
- Continuous Testing
- Entrega de software
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Configuración
- Tests en contenedores
- Búsqueda y gestión
- Explorador
- Monitores
- Flujos de trabajo de desarrolladores
- Cobertura de código
- Instrumentar tests de navegador con RUM
- Instrumentar tests de Swift con RUM
- Detección temprana de defectos
- Reintentos automáticos de tests
- Correlacionar logs y tests
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- Métricas de DORA
- Seguridad
- Información general de seguridad
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Observabilidad de la IA
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Gestión de logs
- Administración
- Gestión de cuentas
- Seguridad de los datos
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Ayuda
Metrics Summary
This page is not yet available in Spanish. We are working on its translation.
If you have any questions or feedback about our current translation project, feel free to reach out to us!
If you have any questions or feedback about our current translation project, feel free to reach out to us!
Overview
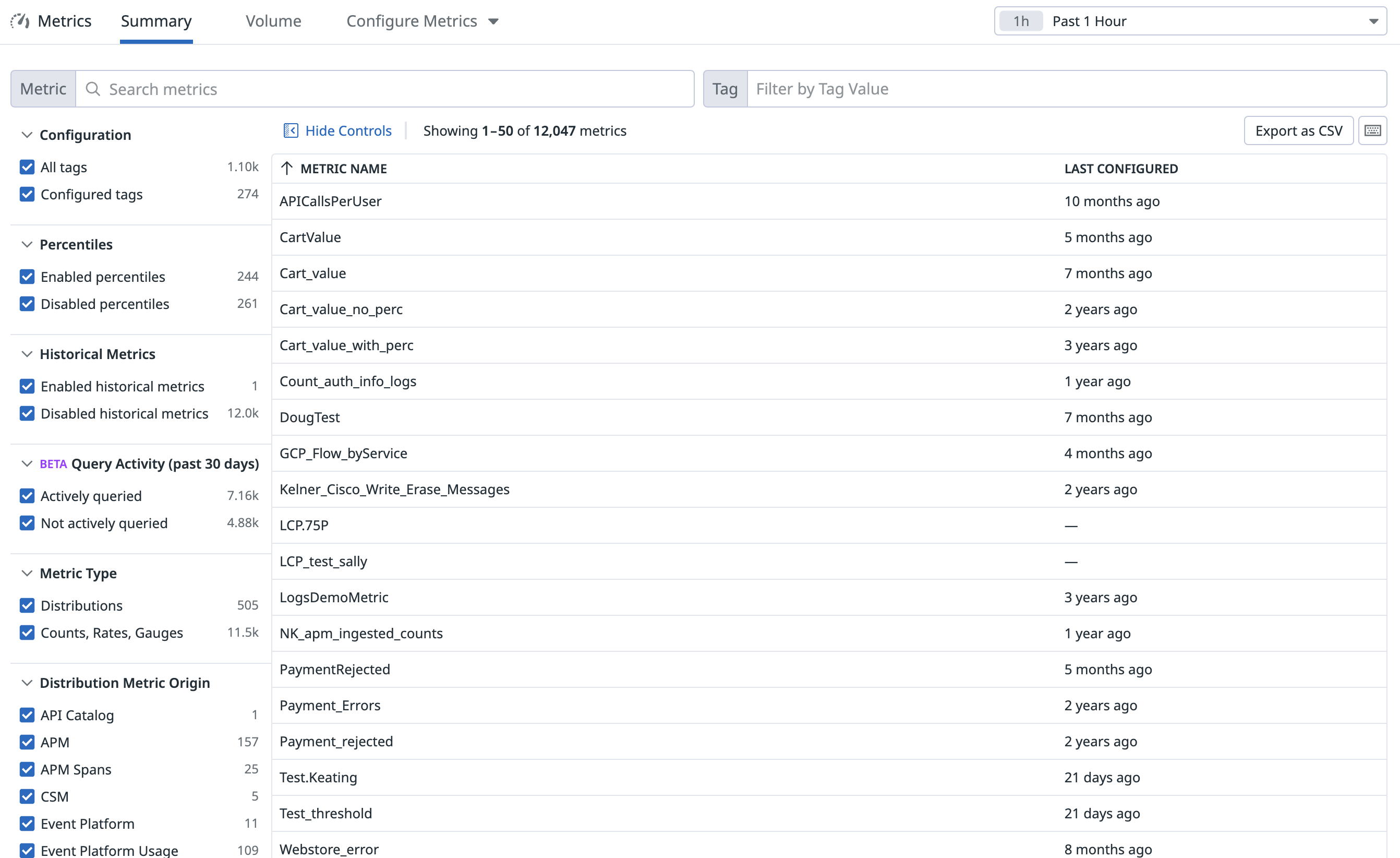
The Metrics Summary page displays a list of your metrics reported to Datadog under a specified time frame: the past hour, day, or week.
Search your metrics by metric name or tag using the Metric or Tag search fields:
Tag filtering supports boolean and wildcard syntax so that you can quickly identify:
- Metrics that are tagged with a particular tag key, for example,
team:team:* - Metrics that are missing a particular tag key, for example,
team:NOT team:*
Facet panel
The search bars provide the most comprehensive set of actions to filter the list of metrics. But facets can also filter your metrics by:
- Configuration: Metrics with tag configurations
- Percentiles: Distribution metrics enabled by percentiles/advanced query capabilities
- Historical Metrics: Metrics that have historical metrics ingestion enabled
- Query Activity (Beta): Metrics not queried in the app or by the API in the past 30 days
- Metric Type: Differentiate between distribution and non-distribution metrics (counts, gauges, rates)
- Metric Origin: The product from which the metric originated (for example, metrics generated from Logs or APM Spans). To learn more about the different metric origin types, see Metric origin definitions.
Note: A metric included on a Dashboard that has not been loaded by a user in the last 30 days would not be considered actively queried.
Configuration of multiple metrics
Clicking on Configure Metrics gives you multiple options that you can use to configure more than one metric at a time:
- Manage tags: Configure tags on multiple custom metrics matching a namespace using Metrics without Limits™.
- Enable or disable percentiles: Manage percentile aggregations across multiple distribution metrics. See the Distributions page for more information.
- Enable or disable historical metrics ingestion: Manage the ingestion of historical metric data. See the Historical Metrics Ingestion page for more information.
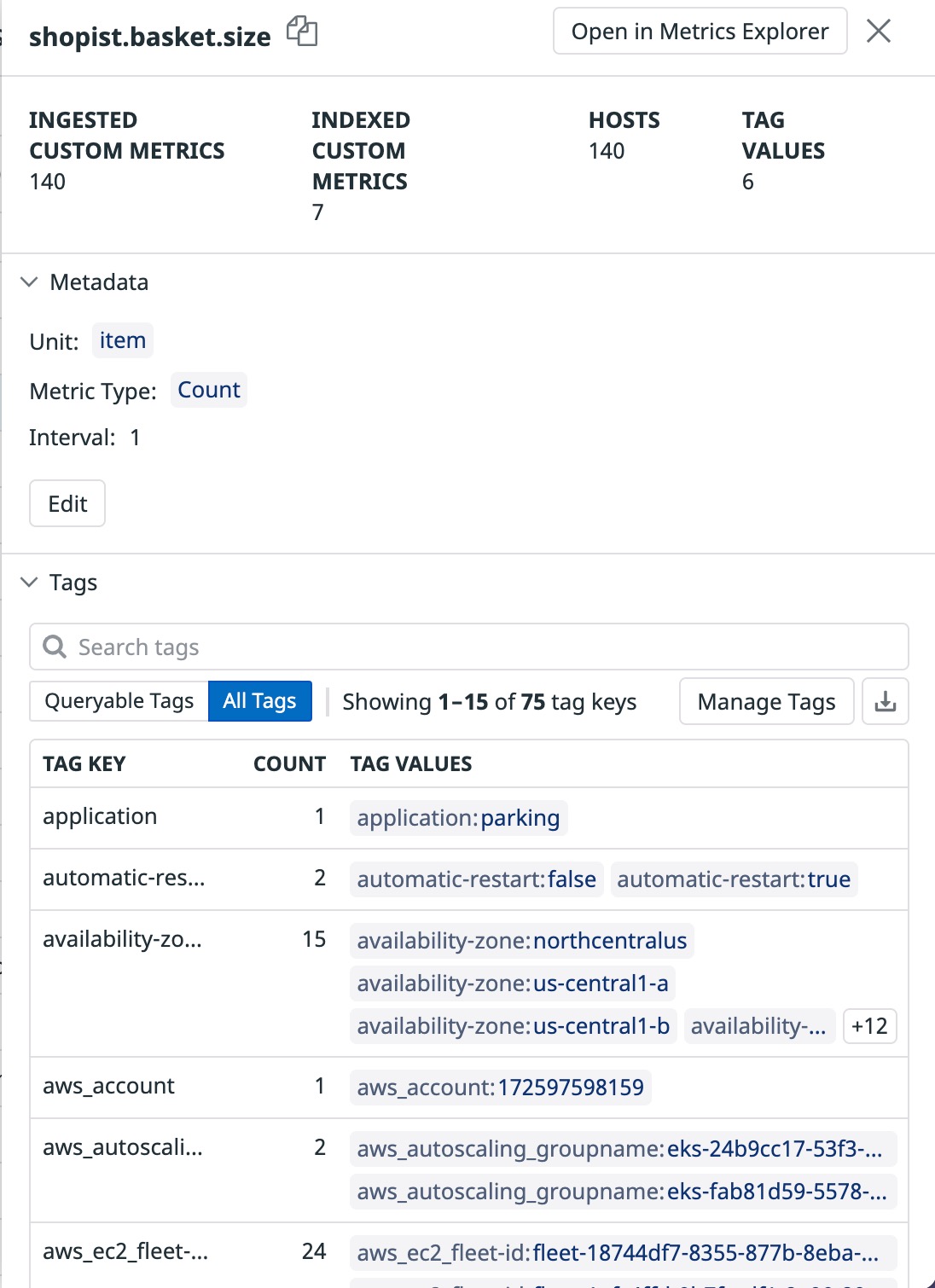
Metric details sidepanel
Click on any metric name to display its details sidepanel for more information regarding the metric’s metadata and tags:
Metric name
The name of your metric in the Metrics Explorer, dashboards, etc.
Ingested custom metrics
A metric name may emit multiple ingested custom metrics depending on its associated tag value combinations. Ingested custom metrics represent all of the data originally submitted with code.
Learn more in the custom metrics documentation.
Indexed custom metrics
Unlike ingested custom metrics, indexed custom metrics represent those that remain queryable across the Datadog platform. This number may be impacted by adding or removing percentile aggregations or by use of Metrics without Limits™. Learn more in the Metrics without Limits™ documentation.
Hosts
The total number of hosts reporting a metric.
Tag values
The total number of unique tag values attached to a metric.
Metrics metadata
The metadata attached to your metric. Most of the metadata can be edited on the metric summary page or with the Datadog API.
Metric unit
The unit for your metric (byte, second, request, query, etc.). See the metric unit page for more details.
When submitting custom metrics to Datadog, it is possible to change the unit of measurement that displays when hovering over the metric in your graph.
Note: This does not change how a metric graph is displayed. It only changes the units of measurement that raw values are considered as when you hover over a metric. Formatting is automatically applied for readability. For example, bytes (B) may be displayed as kilobytes (KiB).
Metric type
The type for your metric (gauge, rate, count, distribution). See the metric type page for more details.
Warning: Editing the metric type changes that metric’s behavior for ALL your dashboards and monitors.
Integration name
If the metric is coming from a supported integration, the metadata lists the integration name. This information cannot be edited.
Interval
The collection interval for the metric in seconds.
Metric description
The metric description helps you understand what a metric does. Descriptions are pre-populated for metrics coming from supported integrations. Use this field to update the descriptions for your custom metrics.
Tags table
The tags table offers multiple ways to explore all of the tag keys and tag values that are actively reporting in your metric’s data.
Use the tags table to:
- Sort tag keys by the Count column (count of unique tag values).
- Search through the paginated table of tags for a particular tag key.
- Export the tags table as a downloadable CSV.
- Toggle between tags you’ve configured on your metric vs the metric’s originally submitted tags
For any particular tag key, you can:
- Inspect all tag values of that tag key.
- Use a specific tag
key:valueto further filter the list of metrics displayed on the Metrics Summary page. - Open a graph of this metric filtered by your tag
key:valuepair in the Metrics Explorer. - Copy any tag
key:valuefor filtering across the application.
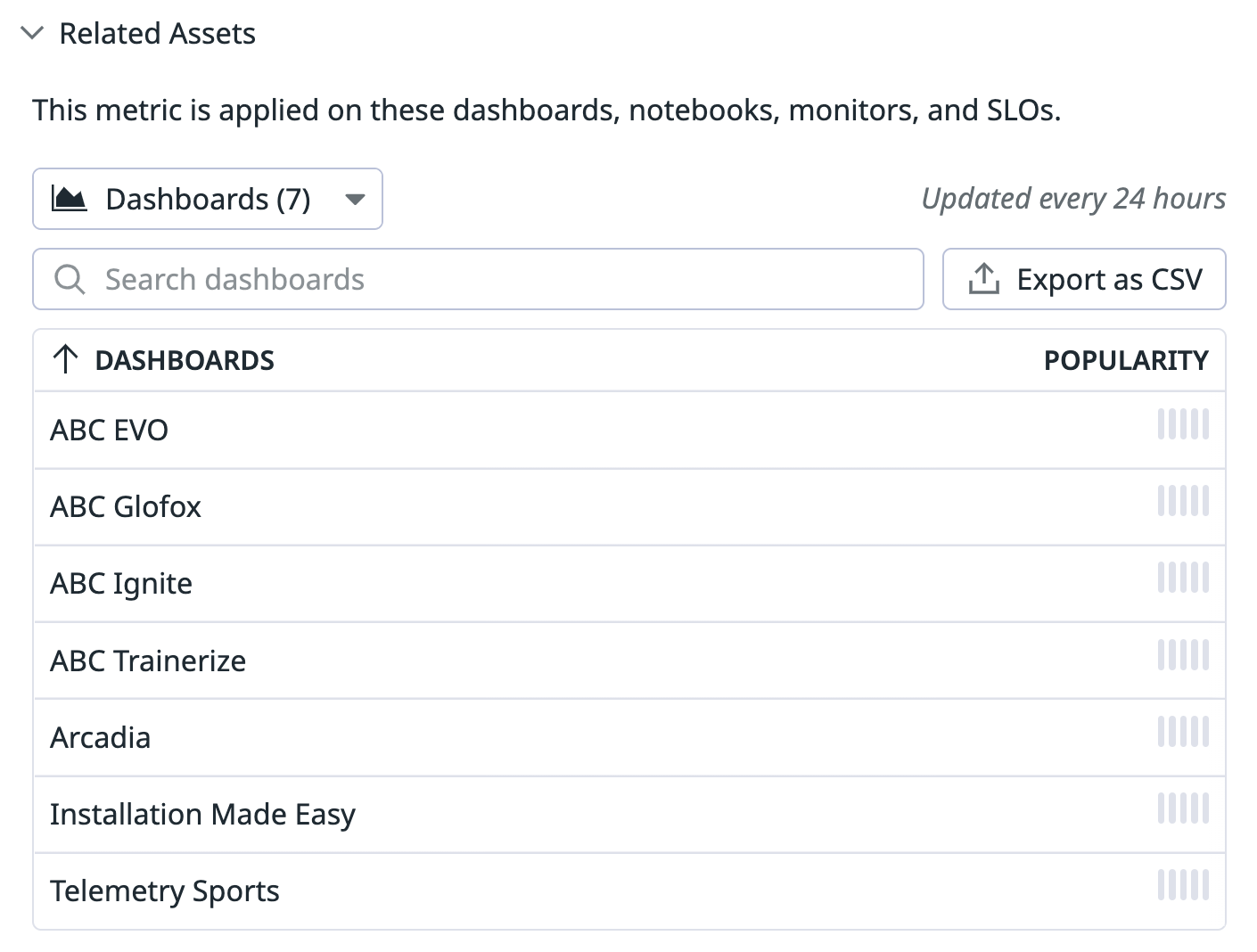
Metrics Related Assets
To determine the value of any metric name to your organization, use Metrics Related Assets. Metrics related assets refers to any dashboard, notebook, monitor, or SLO that queries a particular metric.
- Scroll to the bottom of the metric’s details side panel to the “Related Assets” section.
- Click the dropdown button to view the type of related asset you are interested in (dashboards, monitors, notebooks, SLOs). You can additionally leverage the search bar to validate specific assets.
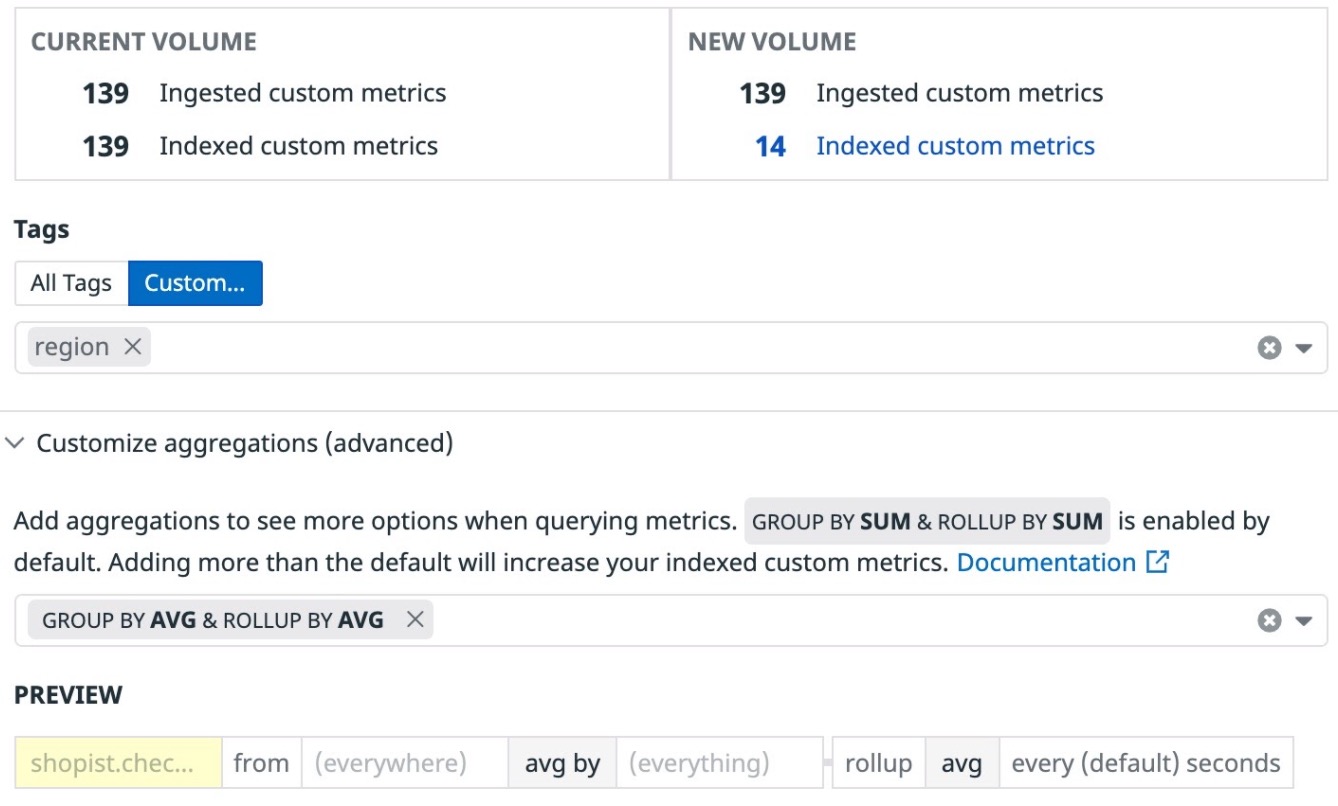
Metrics without Limits™
Metrics without Limits™ provides you control over the size of your custom metrics without requiring any agent or code-level changes.
Note: Metrics without Limits™ is only available for custom metrics.
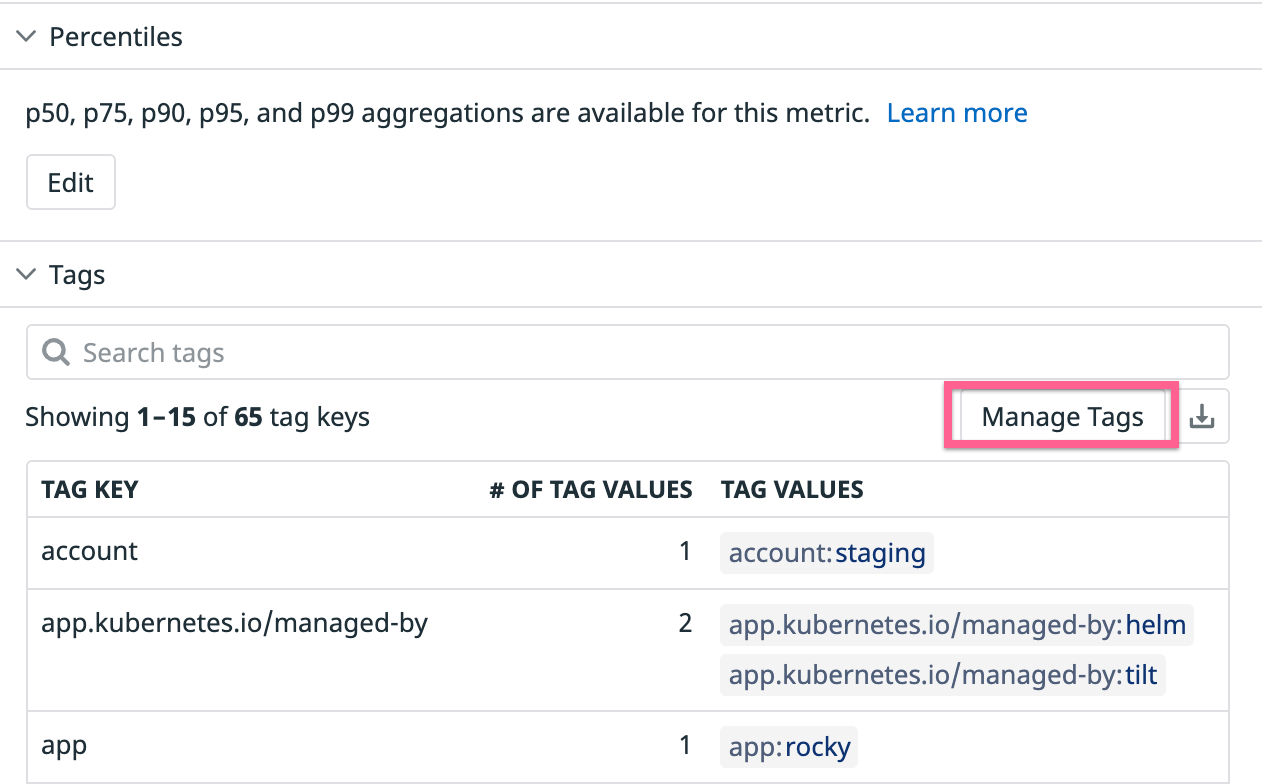
You can configure tags using the bulk metric tag configuration button or the Manage Tags button in a metric’s details side panel.
Click on your custom distribution metric name in the Metrics Summary table to open the metrics details side panel.
Click the Manage Tags button to open the tag configuration modal.
Select Include tags… or Exclude tags… to customize the tags you do or don’t want to query for. For more information on tag configuration, see the Metrics without Limits documentation.
Preview the effects of your proposed tag configuration with the cardinality estimator before selecting Save.
Note: The cardinality estimator requires the metric to be older than 48 hours.
Queryable tags
Once your metric has been configured with Metrics without Limits™, you can view which tags remain Queryable – ultimately those that contribute to Indexed Custom Metrics volume. And you can toggle back to all originally submitted and ingested tags that contribute to your Ingested Custom Metrics volume.
Optimize your metric with aggregations in Advanced Mode
For custom metrics of the count, gauge, or rate metric type, you can further refine your metric’s configurations by optionally including additional aggregations with the advanced mode of Metrics without Limits™. By default, Datadog stores the most frequently queried aggregation combination depending on the metric’s type to preserve the mathematical accuracy of your configured metric’s query as listed below:
- Configured counts/rates are queryable with time/space aggregations of
SUM - Configured gauges are queryable in time/space aggregations of
AVG
More aggregations are available should they be valuable to you. You can add or remove aggregations at any time with no required Agent or code-level changes.
Note: Configuring your count, rate, or gauge metric and removing an aggregation may impact existing dashboards and monitors.
Metric origin definitions
This table shows the mapping between the metric origin as seen in the facet and where it was submitted from:
| Metric Origin | Submitted from |
|---|---|
| API Catalog | Timeseries sent by the Datadog API Catalog product from the APIM Endpoint. |
| APM | Timeseries sent by the Datadog APM product for metrics generated from traces and span metrics. |
| Agent | Timeseries sent by the Datadog Agent, collected from Agent integrations, built-in integrations, DogStatsD, or custom Agent checks. |
| CSM | Timeseries sent by the Datadog Cloud Security Monitoring product. |
| Cloud Integrations | Timeseries collected from cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud etc. from their respective integrations. |
| DBM | Timeseries sent by the Datadog Database Monitoring product, including insights into MySQL, Oracle, and Postgres activities/queries/locks. |
| DSM | Timeseries sent by the Datadog Data Streams Monitoring product, for metrics generated from the DSM spans and traces. |
| Datadog Exporter | Timeseries sent by the OpenTelemetry Collector or the Datadog Exporter. |
| Datadog Platform | Timeseries sent by metrics intake that are used to report metrics usage. |
| Events | Timeseries generated from the Datadog Events platform. |
| LLM Observability | Timeseries emitted by the LLM Observability product using the lmobs_to_metrics service. |
| Logs | Timeseries generated from the Datadog Logs platform. |
| Metrics API | Timeseries sent using Datadog’s OTLP Ingestion endpoint and OTel receiver with a Datadog integration counterparts or points for estimated usage metrics or Datadog API Client. |
| NPM | Timeseries sent by the Datadog Network Performance Monitoring product. |
| Observability Pipelines | Timeseries sent by the Datadog Observability Pipielines including error and performance metrics. |
| Other | Timeseries that don’t have a DD integration counterpart. |
| Processes | Timeseries generated from the Datadog Processes product. |
| RUM | Timeseries generated from the Datadog Real User Monitoring product. |
| SAAS Integrations | Timeseries collected from popular SAAS platforms like Slack, Docker, PagerDuty etc. |
| Serverless | Timeseries sent by the Datadog Serverless platform including Function, App Services, Cloud Run, and Container App Metrics. |
| Service Catalog | Timeseries sent by the Datadog Service Catalog product including Scorecard metrics. |
| Synthetic Monitoring | Synthetic monitoring and continuous testing metrics generated from the Datadog Synthetic Monitoring product. |
| USM | Timeseries generated from the Datadog Universal Service Monitoring product. |
Further reading
Más enlaces, artículos y documentación útiles: