- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Integrations
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- APM Tracing
- Profiler
- Tags
- API
- Software Catalog
- Session Replay
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- Software Delivery
- Code Security
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Datadog Mobile App
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Software Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Product Analytics
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Code Security
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
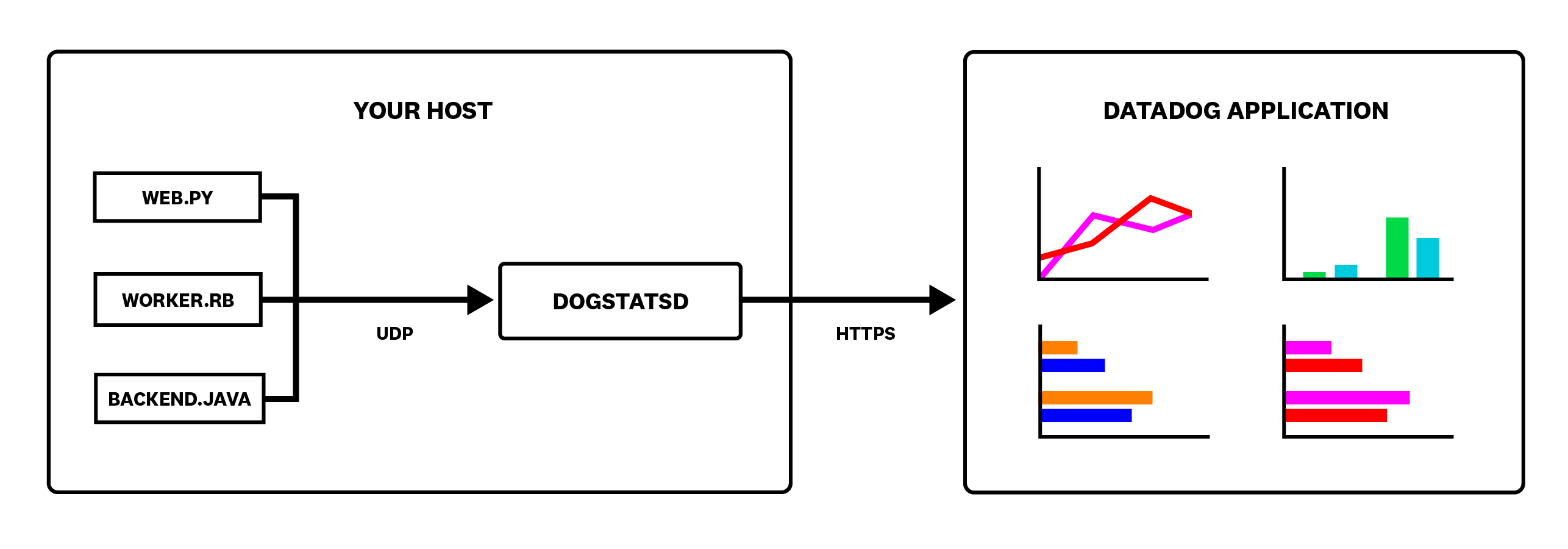
DogStatsD
The easiest way to get your custom application metrics into Datadog is to send them to DogStatsD, a metrics aggregation service bundled with the Datadog Agent. DogStatsD implements the StatsD protocol and adds a few Datadog-specific extensions:
- Histogram metric type
- Service checks
- Events
- Tagging
Any compliant StatsD client works with DogStatsD and the Agent, but does not include the Datadog-specific extensions.
Note: DogStatsD does NOT implement timers from StatsD as a native metric type (though it does support them through histograms).
DogStatsD is available on Docker Hub and GCR:
Docker Hub is subject to image pull rate limits. If you are not a Docker Hub customer, Datadog recommends that you update your Datadog Agent and Cluster Agent configuration to pull from GCR or ECR. For instructions, see Changing your container registry.
How it works
DogStatsD accepts custom metrics, events, and service checks over UDP and periodically aggregates and forwards them to Datadog.
Because it uses UDP, your application can send metrics to DogStatsD and resume its work without waiting for a response. If DogStatsD ever becomes unavailable, your application doesn’t experience an interruption.
As it receives data, DogStatsD aggregates multiple data points for each unique metric into a single data point over a period of time called the flush interval. DogStatsD uses a flush interval of 10 seconds.
Setup
DogStatsD consists of a server, which is bundled with the Datadog Agent, and a client library, which is available in multiple languages. The DogStatsD server is enabled by default over UDP port 8125 for Agent v6+. You can set a custom port for the server if necessary. Configure your client to match the address and port of the Datadog Agent DogStatsD server.
Datadog Agent DogStatsD server
If you need to change the port, configure the dogstatsd_port option in the main Agent configuration file, and restart the Agent. You can also configure DogStatsD to use a UNIX domain socket.
To enable a custom Agent DogStatsD server UDP port:
Set the
dogstatsd_portparameter:## @param dogstatsd_port - integer - optional - default: 8125 ## Override the Agent DogStatsD port. ## Note: Make sure your client is sending to the same UDP port. # dogstatsd_port: 8125
By default, DogStatsD listens on UDP port 8125, so you need to bind this port to your host port when running the Agent in a container. If your StatsD metrics come from outside of localhostyou must set DD_DOGSTATSD_NON_LOCAL_TRAFFIC to true to allow metric collection. In order to run the Agent with the DogStatsd server up, execute the following command:
docker run -d --cgroupns host \
--pid host \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \
-v /proc/:/host/proc/:ro \
-v /sys/fs/cgroup/:/host/sys/fs/cgroup:ro \
-e DD_API_KEY=<DATADOG_API_KEY> \
-e DD_DOGSTATSD_NON_LOCAL_TRAFFIC="true" \
-p 8125:8125/udp \
gcr.io/datadoghq/agent:latest
If you need to change the port used to collect StatsD metrics, use the DD_DOGSTATSD_PORT="<NEW_DOGSTATSD_PORT> environment variable. You can also configure DogStatsD to use a UNIX domain socket.
Origin detection over UDP
Origin detection is supported in Agent v6.10.0+, and allows DogStatsD to detect where the container metrics come from and automatically tag metrics. When this mode is enabled, all metrics received through UDP are tagged by the same pod tags as Autodiscovery metrics.
Origin detection in non-Kubernetes environments is based on an extension of the DogStatsD protocol in Datagram Format and Shell Usage. To enable the feature in the Agent, set the DD_DOGSTATSD_ORIGIN_DETECTION_CLIENT environment variable to true.
Note: Origin detection is not supported for Fargate environments.
StatsD metrics collection is enabled by default on UNIX domain socket. To start collecting your StatsD metrics over UDP, you need to activate the DogStatsD feature in the Operator settings.
Add
features.dogstatsd.hostPortConfig.enabledto yourdatadog-agent.yamlmanifest:features: dogstatsd: hostPortConfig: enabled: trueThis is an example
datadog-agent.yamlmanifest:apiVersion: datadoghq.com/v2alpha1 kind: DatadogAgent metadata: name: datadog spec: global: credentials: apiSecret: secretName: datadog-secret keyName: api-key features: dogstatsd: hostPortConfig: enabled: trueThis enables the Agent to collect StatsD metrics over UDP on port
8125.Apply the change:
kubectl apply -f datadog-agent.yaml
Warning: The features.dogstatsd.hostPortConfig.hostPort parameter opens a port on your host. Make sure your firewall only allows access from your applications or trusted sources. If your network plugin doesn’t support hostPorts, so add hostNetwork: true in your Agent pod specifications. This shares the network namespace of your host with the Datadog Agent. It also means that all ports opened on the container are opened on the host. If a port is used both on the host and in your container, they conflict (since they share the same network namespace) and the pod does not start. Some Kubernetes installations do not allow this.
Send StatsD metrics to the Agent
Your application needs a reliable way to determine the IP address of its host. This is made simple in Kubernetes 1.7, which expands the set of attributes you can pass to your pods as environment variables. In versions 1.7 and above, you can pass the host IP to any pod by adding an environment variable to the PodSpec. For instance, your application manifest might look like this:
env:
- name: DD_AGENT_HOST
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.hostIP
With this, any pod running your application is able to send DogStatsD metrics with port 8125 on $DD_AGENT_HOST.
Note: As a best practice, Datadog recommends using unified service tagging when assigning attributes. Unified service tagging ties Datadog telemetry together through the use of three standard tags: env, service, and version. To learn how to unify your environment, see unified service tagging.
Origin detection over UDP
Origin detection is supported in Agent 6.10.0+ and allows DogStatsD to detect where the container metrics come from, and tag metrics automatically. When this mode is enabled, all metrics received through UDP are tagged by the same pod tags as Autodiscovery metrics.
To activate origin detection, add the
global.originDetectionUnified.enabledsetting to yourdatadog-agent.yamlmanifest:global: originDetectionUnified: enabled: true
Notes:
- An alternative to UDP is UNIX Domain Sockets.
- Origin detection with UDP can use the pod ID as the entity ID.
To use pod ID as the entity ID, add the following lines to your application manifest:
env:
- name: DD_ENTITY_ID
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.uid
To set tag cardinality for the metrics collected using origin detection, set the setting features.dogstatsd.tagCardinality to either low (default), orchestrator or high.
Note: For UDP, pod_name tags are not added by default to avoid creating too many custom metrics.
To gather custom metrics with DogStatsD with helm:
Update your datadog-values.yaml file to enable DogStatsD:
dogstatsd: port: 8125 useHostPort: true nonLocalTraffic: trueNote:
hostPortfunctionality requires a networking provider that adheres to the CNI specification, such as Calico, Canal, or Flannel. For more information, including a workaround for non-CNI network providers, see the Kubernetes documentation: HostPort services do not work.Warning: The
hostPortparameter opens a port on your host. Make sure your firewall only allows access from your applications or trusted sources. If your network plugin doesn’t supporthostPorts, so addhostNetwork: truein your Agent pod specifications. This shares the network namespace of your host with the Datadog Agent. It also means that all ports opened on the container are opened on the host. If a port is used both on the host and in your container, they conflict (since they share the same network namespace) and the pod does not start. Some Kubernetes installations do not allow this.Upgrade your Agent configuration:
helm upgrade -f datadog-values.yaml <RELEASE_NAME> datadog/datadogUpdate your application pods: Your application needs a reliable way to determine the IP address of its host. This is made simple in Kubernetes 1.7, which expands the set of attributes you can pass to your pods as environment variables. In versions 1.7 and above, you can pass the host IP to any pod by adding an environment variable to the PodSpec. For instance, your application manifest might look like this:
env: - name: DD_AGENT_HOST valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: status.hostIPWith this, any pod running your application is able to send DogStatsD metrics through port
8125on$DD_AGENT_HOST.
DogStatsD client
Install the DogStatsD client library for your preferred language and configure it to match the address and port of the Datadog Agent DogStatsD server.
Install the DogStatsD client
Official Datadog-DogStatsD client libraries are available for the following languages. Any compliant StatsD client works with DogStatsD and the Agent, but does not include the Datadog-specific features mentioned above:
go get github.com/DataDog/datadog-go/v5/statsd
Instantiate the DogStatsD client
Once your DogStatsD client is installed, instantiate it in your code:
dogstatsd_client, err := statsd.New("127.0.0.1:8125")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
For more options, see Datadog’s GoDoc.
Client instantiation parameters
Note: As a best practice, Datadog recommends using unified service tagging when assigning tags. Unified service tagging ties Datadog telemetry together through the use of three standard tags: env, service, and version. To learn how to unify your environment, see unified service tagging.
In addition to the required DogStatsD configuration (url and port), the following optional parameters are available for your DogStatsD client:
The Go client has multiple options for configuring the behavior of your client.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
WithNamespace() | String | Configure a namespace to prefix to all metrics, events, and service checks. |
WithTags() | List of strings | Global tags applied to every metric, event, and service check. |
For all available options, see Datadog’s GoDoc.
Dive into DogStatsD
DogStatsD and StatsD are broadly similar, however, DogStatsD contains advanced features which are specific to Datadog, including available data types, events, service checks, and tags:
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles:
If you’re interested in learning more about the datagram format used by DogStatsD, or want to develop your own Datadog library, see the datagram and shell usage section, which also explains how to send metrics and events straight from the command line.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: