- 重要な情報
- はじめに
- Datadog
- Datadog サイト
- DevSecOps
- AWS Lambda のサーバーレス
- エージェント
- インテグレーション
- コンテナ
- ダッシュボード
- アラート設定
- ログ管理
- トレーシング
- プロファイラー
- タグ
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic モニタリング
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- 用語集
- Standard Attributes
- ガイド
- インテグレーション
- エージェント
- OpenTelemetry
- 開発者
- 認可
- DogStatsD
- カスタムチェック
- インテグレーション
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- サービスのチェック
- IDE インテグレーション
- コミュニティ
- ガイド
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- モバイルアプリケーション
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- アプリ内
- Service Management
- インフラストラクチャー
- アプリケーションパフォーマンス
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- データベース モニタリング
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility (CI/CDの可視化)
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- セキュリティ
- セキュリティの概要
- Cloud SIEM
- クラウド セキュリティ マネジメント
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- ログ管理
- Observability Pipelines(観測データの制御)
- ログ管理
- 管理
Google Cloud Run Functions
このページは日本語には対応しておりません。随時翻訳に取り組んでいます。
翻訳に関してご質問やご意見ございましたら、お気軽にご連絡ください。
翻訳に関してご質問やご意見ございましたら、お気軽にご連絡ください。
Overview
Google Cloud Run is a fully managed serverless platform for deploying and scaling container-based applications. Datadog provides monitoring and log collection for Cloud Run functions (formerly Cloud Functions) through the Google Cloud integration.
Datadog Serverless Monitoring is supported for Cloud Run functions (2nd gen). If you want to monitor 1st gen functions, contact your technical account manager.
Setup
Application
Tracing
In your main application, add the dd-trace-js library. See Tracing Node.js applications for instructions.
Set ENV NODE_OPTIONS="--require dd-trace/init". This specifies that the dd-trace/init module is required when the Node.js process starts.
Profiling
The profiler is shipped within Datadog tracing libraries. If you are already using APM to collect traces for your application, you can skip installing the library and proceed to enabling the profiler. See Enabling the Node.js Profiler to add the environment variables.
Metrics
The tracing library also collects custom metrics. See the code examples.
Logs
The Datadog sidecar collects logs through a shared volume. To forward logs from your main container to the sidecar, configure your application to write all logs to a location such as shared-volume/logs/*.log using the steps below. You must follow the setup in the GCP UI to add the environment variable DD_SERVERLESS_LOG_PATH and a shared Volume Mount to both the main and sidecar container.
To set up logging in your application, see Node.js Log Collection. To set up trace log correlation, see Correlating Node.js Logs and Traces.
Tracing
In your main application, add the dd-trace-py library. See Tracing Python Applications for instructions. You can also use Tutorial - Enabling Tracing for a Python Application and Datadog Agent in Containers.
Profiling
The profiler is shipped within Datadog tracing libraries. If you are already using APM to collect traces for your application, you can skip installing the library and proceed to enabling the profiler. See Enabling the Python Profiler to add the environment variables.
Metrics
The tracing library also collects custom metrics. See the code examples.
Logs
The Datadog sidecar collects logs through a shared volume. To forward logs from your main container to the sidecar, configure your application to write all logs to a location such as shared-volume/logs/*.log using the steps below. You must follow the setup in the GCP UI to add the environment variable DD_SERVERLESS_LOG_PATH and a shared Volume Mount to both the main and sidecar container.
To set up logging in your application, see Python Log Collection. Python Logging Best Practices can also be helpful. To set up trace log correlation, see Correlating Python Logs and Traces.
Tracing
Add
functions-framework-apiand other dependencies likejava-dogstatsd-clientto yourpom.xml.Example
pom.xml:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>functions</groupId> <artifactId>functions-hello-world</artifactId> <version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <artifactId>libraries-bom</artifactId> <groupId>com.google.cloud</groupId> <scope>import</scope> <type>pom</type> <version>26.32.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <properties> <maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target> <maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- Required for Function primitives --> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.cloud.functions</groupId> <artifactId>functions-framework-api</artifactId> <version>1.1.4</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.cloud.functions.invoker</groupId> <artifactId>java-function-invoker</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.datadoghq</groupId> <artifactId>java-dogstatsd-client</artifactId> <version>4.4.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId> <version>2.19.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId> <version>2.19.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <!-- Google Cloud Functions Framework Maven plugin This plugin allows you to run Cloud Functions Java code locally. Use the following terminal command to run a given function locally: mvn function:run -Drun.functionTarget=your.package.yourFunction --> <groupId>com.google.cloud.functions</groupId> <artifactId>function-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>0.11.0</version> <configuration> <functionTarget>functions.HelloWorld</functionTarget> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.2.4</version> <executions> <execution> <phase>package</phase> <goals> <goal>shade</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>Run
mvn clean packageto update thetargetdirectory with the new.jarused in your Dockerfile.As an alternative to the provided Dockerfile, you can use Artifact Registry to store the images built from your function source code. You can use Google Cloud Build or Buildpacks to build and deploy your image.
For example:gcloud builds submit --pack image=LOCATION-docker.pkg.dev/PROJECT_ID/REPO_NAME/IMAGE_NAMEAdd
dd-java-agent.jarandjava-function-invoker.jarto your Dockerfile. Cloud Run Function code runs with a classpath that includes the function code and its dependencies. The Maven plugin automatically determines the classpath based on the dependencies inpom.xml. If invoking the Functions Framework directly with the Datadog Agent, update your DockerfileENTRYPOINTto include the--classpathand--targetoptions, along with the Java agent flag-javaagent:dd-java-agent.jar:java -javaagent:dd-java-agent.jar -jar java-function-invoker-1.3.2 \ --classpath 'FUNCTION_JAR' \ --target 'FUNCTION_TARGET'- Replace
FUNCTION_JARwith the target JAR generated from the Maven build, including all dependencies. - Replace
FUNCTION_TARGETwith the function’s entry point (for example,gcfv2.HelloworldApplication).
Example
Dockerfile:# Download Datadog Java Agent FROM maven:3.8.3-openjdk-17 AS build # Set working directory WORKDIR / # Download the required Maven dependency RUN mvn dependency:get -Dartifact=com.google.cloud.functions.invoker:java-function-invoker:1.4.0 \ && mvn dependency:copy -Dartifact=com.google.cloud.functions.invoker:java-function-invoker:1.4.0 -DoutputDirectory=/ FROM openjdk:17-jdk # Set the working directory in the container WORKDIR / ADD 'https://dtdg.co/latest-java-tracer' dd-java-agent.jar COPY --from=build java-function-invoker-1.4.0.jar java-function-invoker.jar # Copy the JAR file into the container COPY target/functions-hello-world-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar helloworld.jar ENV JAVA_OPTS=-javaagent:dd-java-agent.jar # Expose the port (Cloud Run automatically assigns the actual port via $PORT) ENV PORT=8080 EXPOSE 8080 8125/udp ENTRYPOINT ["java","-javaagent:/dd-java-agent.jar", "-jar", "/java-function-invoker.jar","--classpath", "/helloworld.jar","--target", "functions.HelloWorld"]- Replace
To deploy the Java function, run the following command from the top-level directory containing your
pom.xmlandDockerfile:gcloud beta run deploy FUNCTION_NAME \ --source . \ --function FUNCTION_TARGET \ --clear-base-image \ --region REGION- Replace
REGIONwith the region where you want to deploy the function. - Replace
FUNCTION_TARGETwith your function entry point. For example,gcfv2.HelloworldApplication. - Replace
FUNCTION_NAMEwith the name of your Cloud Run function. - Ensure that you set –clear-base-image to deploy your Cloud Function with the Dockerfile.
- Replace
When setting up your containers, use the same container image deployed in the previous steps.
Profiling
The profiler is shipped within Datadog tracing libraries. If you are already using APM to collect traces for your application, you can skip installing the library and proceed to enabling the profiler. See Enabling the Java Profiler to add the environment variables.
Metrics
To collect custom metrics, install the Java DogStatsD client.
Logs
The Datadog sidecar collects logs through a shared volume. To forward logs from your main container to the sidecar, configure your application to write all logs to a location such as shared-volume/logs/*.log using the steps below. You must follow the setup in the GCP UI to add the environment variable DD_SERVERLESS_LOG_PATH and a shared Volume Mount to both the main and sidecar container.
To set up logging in your application, see Java Log Collection. To set up trace log correlation, see Correlating Java Logs and Traces.
Tracing
In your main application, add the dd-trace-go library. See Tracing Go Applications for instructions.
Profiling
The profiler is shipped within Datadog tracing libraries. If you are already using APM to collect traces for your application, you can skip installing the library and proceed to enabling the profiler. See Enabling the Go Profiler to add the environment variables.
Metrics
The tracing library also collects custom metrics. See the code examples.
Logs
The Datadog sidecar collects logs through a shared volume. To forward logs from your main container to the sidecar, configure your application to write all logs to a location such as shared-volume/logs/*.log using the steps below. You must follow the setup in the GCP UI to add the environment variable DD_SERVERLESS_LOG_PATH and a shared Volume Mount to both the main and sidecar container.
To set up logging in your application, see Go Log Collection. To set up trace log correlation, see Correlating Go Logs and Traces.
Tracing
In your main application, add the .NET tracing library. See Tracing .NET Applications for instructions.
Profiling
The profiler is shipped within Datadog tracing libraries. If you are already using APM to collect traces for your application, you can skip installing the library and proceed to enabling the profiler. See Enabling the .NET Profiler to add the environment variables.
Metrics
The tracing library also collects custom metrics. See the code examples.
Logs
The Datadog sidecar collects logs through a shared volume. To forward logs from your main container to the sidecar, configure your application to write all logs to a location such as shared-volume/logs/*.log using the steps below. You must follow the setup in the GCP UI to add the environment variable DD_SERVERLESS_LOG_PATH and a shared Volume Mount to both the main and sidecar container.
To set up logging in your application, see C# Log Collection. To set up trace log correlation, see Correlating .NET Logs and Traces.
Containers
If you are deploying a new Cloud Run function for the first time through the console, wait for Cloud Run to create the service and update the placeholder revision image. Then, follow the steps below to add the sidecar container, shared volume mount, startup check, and environment variables.
Sidecar container
In Cloud Run, select Edit & Deploy New Revision.
At the bottom of the page, select Add Container.
For Container image URL, select
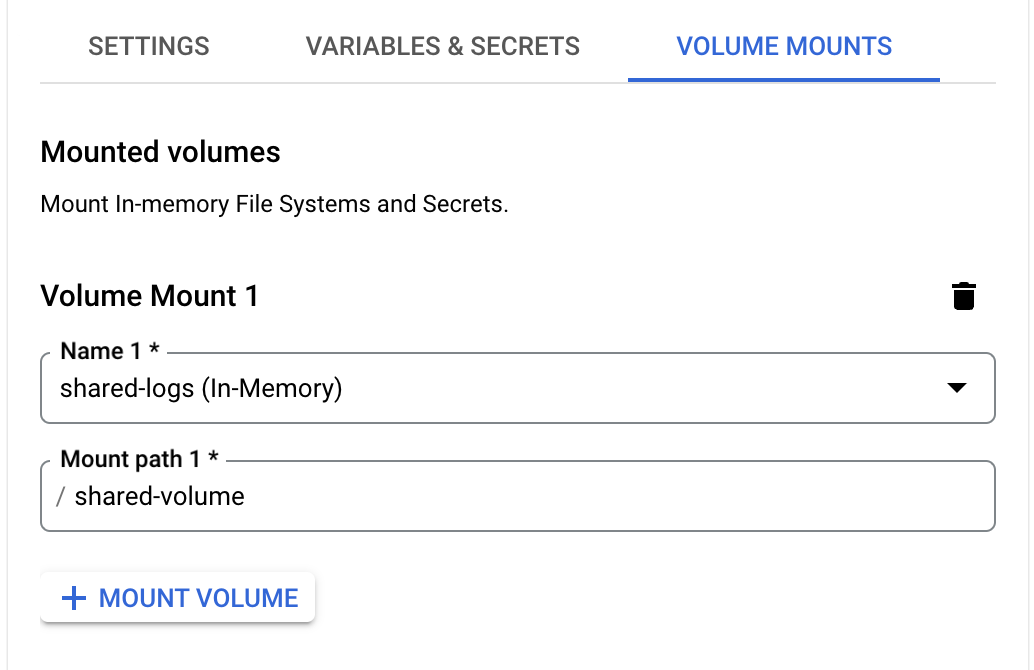
gcr.io/datadoghq/serverless-init:latest.Go to Volume Mounts and set up a volume mount for logs. Ensure that the mount path matches your application’s write location. For example:
Go to Settings and add a startup check.
- Select health check type: Startup check
- Select probe type: TCP
- Port: Enter a port number. Make note of this, as it is used in the next step.
Go to Variables & Secrets and add the following Required environment variables as name-value pairs:
DD_SERVICE: A name for your service. For example,gcr-sidecar-test.DD_ENV: A name for your environment. For example,dev.DD_SERVERLESS_LOG_PATH: Your log path. For example,/shared-volume/logs/*.log.DD_API_KEY: Your Datadog API key.DD_HEALTH_PORT: The port you selected for the startup check in the previous step.FUNCTION_TARGET: The entry point of your function. For example,gcfv2.HelloworldApplication.
For a list of all environment variables, including additional tags, see Environment variables.
Main container
- Go to Volume Mounts and add the same shared volume as you did for the sidecar container. Note: Save your changes by selecting Done. Do not deploy changes until the final step.
- Go to Variables & Secrets and add the same
DD_SERVICEenvironment variable that you set for the sidecar container. - Go to Settings. In the Container start up order drop-down menu, select your sidecar.
- Deploy your main application.
Environment variables
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
DD_API_KEY | Datadog API key - Required |
DD_SITE | Datadog site - Required |
FUNCTION_TARGET | The entry point of your function - Required |
DD_SERVICE | See Unified Service Tagging - Required |
DD_LOGS_INJECTION | When true, enrich all logs with trace data for supported loggers in Java, Node, .NET, and PHP. See additional docs for Python, Go, and Ruby. |
DD_VERSION | See Unified Service Tagging. |
DD_ENV | See Unified Service Tagging. |
DD_SOURCE | See Unified Service Tagging. |
DD_TAGS | See Unified Service Tagging. |
Do not use the DD_LOGS_ENABLED environment variable. This variable is only used for the serverless-init install method.
FUNCTION_TARGET can also be found on the source tab inside Google console: Function entry point.
Example application
The following example contains a single app with tracing, metrics, and logs set up.
// This line must come before importing the logger.
const tracer = require('dd-trace').init({
logInjection: true
});
const functions = require('@google-cloud/functions-framework');
const { createLogger, format, transports } = require('winston');
const fs = require('fs');
// Create a directory
const directoryPath = '/shared-volume/logs';
fs.mkdir(directoryPath, { recursive: true }, (err) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
return;
}
console.log('Directory created successfully!');
});
// Create a file inside the directory
const filePath = directoryPath + '/index.log';
console.log('Directory created successfully!' + filePath);
const logger = createLogger({
level: 'info',
exitOnError: false,
format: format.json(),
transports: [
new transports.File({ filename: filePath }),
],
});
function handler(req, res) {
logger.log('info', 'Hello simple log!');
tracer.dogstatsd.increment('ninja.run.func.sent', 1, { environment: 'test', runtime: 'nodejs' });
return res.send('Welcome to Datadog 💜!');
}
const handlerWithTrace = tracer.wrap('example-span', handler)
functions.http('httpexample', handlerWithTrace)
module.exports = handlerWithTrace
module.exports = logger;
package.json
{
"name": "updater",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "test nodejs run function",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"@google-cloud/functions-framework": "^3.4.2",
"dd-trace": "^5.19.0",
"winston": "^3.13.1",
"express": "^4.17.1"
}
}
import functions_framework
import ddtrace
import logging
from datadog import initialize, statsd
import os
ddtrace.patch(logging=True)
file_path = "/shared-volume/logs/app.log" # This is the path to the shared volume
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(file_path), exist_ok=True)
FORMAT = ('%(asctime)s %(levelname)s [%(name)s] [%(filename)s:%(lineno)d] '
'[dd.service=%(dd.service)s dd.env=%(dd.env)s dd.version=%(dd.version)s dd.trace_id=%(dd.trace_id)s dd.span_id=%(dd.span_id)s] '
'- %(message)s')
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG, filename=file_path, format=FORMAT, force=True)
ddlogs = []
initialize(**{'statsd_port': 8125})
@ddtrace.tracer.wrap()
@functions_framework.http
def hello_http(request):
log = request.args.get("log")
statsd.increment("ninja.run.func.sent", tags=["runtime:python"])
if log != None:
with ddtrace.tracer.trace('sending-test-logs') as span:
span.set_tag('logs', 'TEST')
logging.debug(log)
ddlogs.append(log)
return "Welcome to Datadog!💜"
requirements.txt
Flask
functions-framework
ddtrace
datadog
HelloworldApplication.java
package gcfv2;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import com.google.cloud.functions.HttpFunction;
import com.google.cloud.functions.HttpRequest;
import com.google.cloud.functions.HttpResponse;
import com.timgroup.statsd.NonBlockingStatsDClientBuilder;
import com.timgroup.statsd.StatsDClient;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger;
public class HelloworldApplication implements HttpFunction {
private static final StatsDClient Statsd = new NonBlockingStatsDClientBuilder().hostname("localhost").build();
protected static final Logger logger4 = LogManager.getLogger();
public static void createLogFile() {
File directory = new File("shared-volume/logs");
if (!directory.exists()) {
directory.mkdirs(); // Create directory if it doesn't exist
}
else {
try {
File logFile = new File("shared-volume/logs/app.log");
if (!logFile.exists()){
logFile.createNewFile();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void service(final HttpRequest request, final HttpResponse response) throws Exception {
createLogFile();
Statsd.incrementCounter("ninja.run.func.sent");
final BufferedWriter writer = response.getWriter();
logger4.info("Hello GCP!");
writer.write("Hello Datadog!!");
}
}
Pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>functions</groupId>
<artifactId>functions-hello-world</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<artifactId>libraries-bom</artifactId>
<groupId>com.google.cloud</groupId>
<scope>import</scope>
<type>pom</type>
<version>26.32.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Required for Function primitives -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.cloud.functions</groupId>
<artifactId>functions-framework-api</artifactId>
<version>1.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.cloud.functions.invoker</groupId>
<artifactId>java-function-invoker</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.datadoghq</groupId>
<artifactId>java-dogstatsd-client</artifactId>
<version>4.4.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<!--
Google Cloud Functions Framework Maven plugin
This plugin allows you to run Cloud Functions Java code
locally. Use the following terminal command to run a
given function locally:
mvn function:run -Drun.functionTarget=your.package.yourFunction
-->
<groupId>com.google.cloud.functions</groupId>
<artifactId>function-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.11.0</version>
<configuration>
<functionTarget>functions.HelloWorld</functionTarget>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.4</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Dockerfile
# Download Datadog Java Agent
FROM maven:3.8.3-openjdk-17 AS build
# Set working directory
WORKDIR /
# Download the required Maven dependency
RUN mvn dependency:get -Dartifact=com.google.cloud.functions.invoker:java-function-invoker:1.4.0 \
&& mvn dependency:copy -Dartifact=com.google.cloud.functions.invoker:java-function-invoker:1.4.0 -DoutputDirectory=/
FROM openjdk:17-jdk
# Set the working directory in the container
WORKDIR /
ADD 'https://dtdg.co/latest-java-tracer' dd-java-agent.jar
COPY --from=build java-function-invoker-1.4.0.jar java-function-invoker.jar
# Copy the JAR file into the container
COPY target/functions-hello-world-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar helloworld.jar
ENV JAVA_OPTS=-javaagent:dd-java-agent.jar
# Expose the port (Cloud Run automatically assigns the actual port via $PORT)
ENV PORT=8080
EXPOSE 8080 8125/udp
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-javaagent:/dd-java-agent.jar", "-jar", "/java-function-invoker.jar","--classpath", "/helloworld.jar","--target", "functions.HelloWorld"]
package helloworld
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
dd_logrus "gopkg.in/DataDog/dd-trace-go.v1/contrib/sirupsen/logrus"
"html/template"
"net/http"
"os"
"path/filepath"
"github.com/DataDog/datadog-go/v5/statsd"
"github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/functions-framework-go/functions"
"gopkg.in/DataDog/dd-trace-go.v1/ddtrace"
"gopkg.in/DataDog/dd-trace-go.v1/ddtrace/tracer"
)
const logDir = "/shared-volume/logs"
var ddlogs []string
var logFile *os.File
var logCounter int
var dogstatsdClient *statsd.Client
const homeTemplate = `
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Datadog Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to Datadog!💜</h1>
<form action="" method="get">
<input type="text" name="log" placeholder="Enter Log">
<button>Add Log</button>
</form>
<h3>Logs Sent to Datadog:</h3>
<ul>
{{range .}}
<li>{{.}}</li>
{{end}}
</ul>
</body>
`
func init() {
logrus.SetFormatter(&logrus.JSONFormatter{})
logrus.AddHook(&dd_logrus.DDContextLogHook{})
err := os.MkdirAll(logDir, 0755)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
logFilePath := filepath.Join(logDir, "maincontainer.log")
logrus.Println("Saving logs in ", logFilePath)
logFileLocal, err := os.OpenFile(logFilePath, os.O_WRONLY|os.O_APPEND|os.O_CREATE, 0644)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
logrus.SetOutput(logFileLocal)
logFile = logFileLocal
logrus.Print("Main container started...")
dogstatsdClient, err = statsd.New("127.0.0.1:8125")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
tracer.Start()
functions.HTTP("HelloHTTP", helloHTTP)
}
// helloHTTP is an HTTP Cloud Function with a request parameter.
func helloHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
span := tracer.StartSpan("maincontainer", tracer.ResourceName("/helloHTTP"))
logrus.Printf("Yay!! Main container works %v", span)
err := dogstatsdClient.Incr("ninja.run.func.sent", []string{"runtime:go"}, 1)
if err != nil {
logrus.Error("Error incrementing counter:", err)
}
defer span.Finish()
sent_log := r.URL.Query().Get("log")
if sent_log != "" {
logCounter++
writeLogsToFile(fmt.Sprintf("received request %d", logCounter), span.Context())
writeLogsToFile(sent_log, span.Context())
ddlogs = append(ddlogs, sent_log)
}
tmpl, err := template.New("home").Parse(homeTemplate)
if err != nil {
logrus.Error("Error parsing template:", err)
}
tmpl.Execute(w, ddlogs)
}
func writeLogsToFile(log_msg string, context ddtrace.SpanContext) {
span := tracer.StartSpan(
"writeLogToFile",
tracer.ResourceName("/writeLogsToFile"),
tracer.ChildOf(context))
defer span.Finish()
_, err := logFile.WriteString(log_msg + "\n")
if err != nil {
logrus.Println("Error writing to log file:", err)
}
}
go.mod
module example.com/gcf
require (
github.com/DataDog/datadog-go/v5 v5.5.0
github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/functions-framework-go v1.9.0
github.com/sirupsen/logrus v1.9.3
gopkg.in/DataDog/dd-trace-go.v1 v1.68.0
)
using Google.Cloud.Functions.Framework;
using StatsdClient;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using System.IO;
using System.Text.Json;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Datadog.Trace;
using Serilog;
using Serilog.Formatting.Compact;
using Serilog.Sinks.File;
namespace HelloHttp;
public class Function : IHttpFunction
{
public DogStatsdService _dsd;
public Function() {
var dogstatsdConfig = new StatsdConfig
{
StatsdServerName = "127.0.0.1",
StatsdPort = 8125,
};
_dsd = new DogStatsdService();
_dsd.Configure(dogstatsdConfig);
string directoryPath = "/shared-volume/logs";
string filePath = Path.Combine(directoryPath, "app.log");
// Create the directory if it doesn't exist
if (!Directory.Exists(directoryPath))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(directoryPath);
}
// Create a file if it doesn't exist
if (!File.Exists(filePath))
{
File.WriteAllText(filePath, "Hello, this is the content of the file.");
}
Log.Logger = new LoggerConfiguration()
.WriteTo.File(new RenderedCompactJsonFormatter(), "/shared-volume/logs/app.log")
.CreateLogger();
}
public async Task HandleAsync(HttpContext context)
{
using (var scope = Tracer.Instance.StartActive("test-function-dotnet"))
{
_dsd.Increment("ninja.run.func.sent", tags: new[] {"runtime:dotnet"});
Log.Information("Hello Datadog Cloud Run Functions! 💜");
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello Datadog Cloud Run Functions! 💜");
}
}
}
HelloHttp.csproj
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<OutputType>Exe</OutputType>
<TargetFramework>net8.0</TargetFramework>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Google.Cloud.Functions.Hosting" Version="2.0.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Datadog.Trace.Bundle" Version="2.56.0" />
<PackageReference Include="StatsdClient" Version="2.0.68" />
<PackageReference Include="DogStatsD-CSharp-Client" Version="8.0.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Serilog" Version="4.1.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Serilog.Formatting.Compact" Version="3.0.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Serilog.Sinks.File" Version="6.0.0" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>