- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- Tracing
- Profileur
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Développeurs
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Checks custom
- Intégrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Checks de service
- IDE Plugins
- Communauté
- Guides
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Application mobile
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Alertes
- Infrastructure
- Métriques
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Conteneurs
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Product Analytics
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Exécuteur de tests intelligent
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- Administration
Enable Data Jobs Monitoring for Databricks
Cette page n'est pas encore disponible en français, sa traduction est en cours.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Data Jobs Monitoring gives visibility into the performance and reliability of your Apache Spark and Databricks jobs.
Setup
Databricks Networking Restrictions can block some Datadog functions. Add the following Datadog IP ranges to your allow-list: webhook IPs, API IPs.
Follow these steps to enable Data Jobs Monitoring for Databricks.
- Configure the Datadog-Databricks integration for a Databricks workspace.
- Install the Datadog Agent on your Databricks cluster(s) in the workspace.
Configure the Datadog-Databricks integration
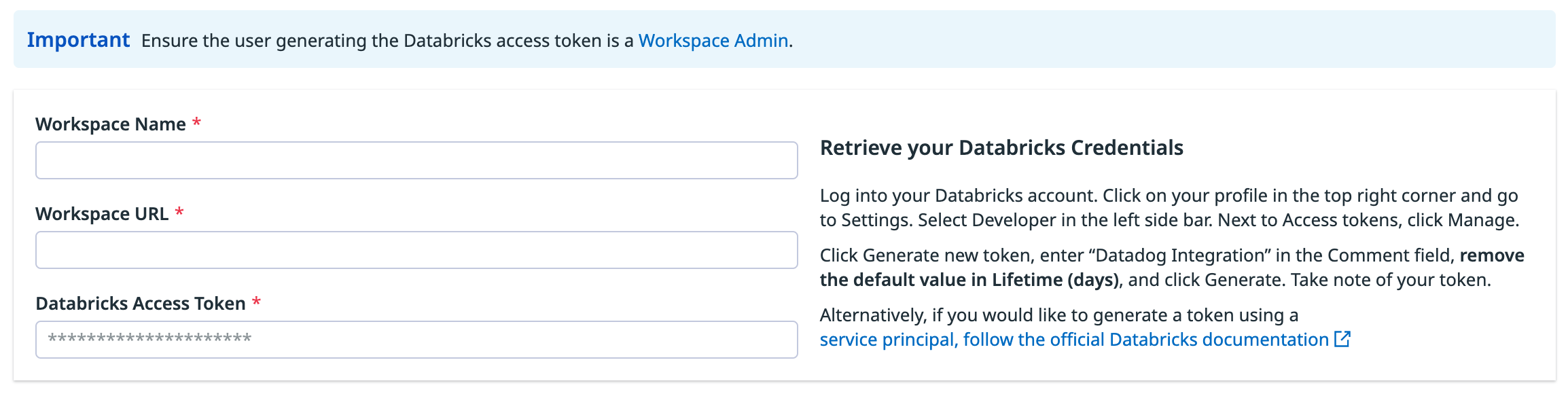
In your Databricks workspace, click on your profile in the top right corner and go to Settings. Select Developer in the left side bar. Next to Access tokens, click Manage.
Click Generate new token, enter “Datadog Integration” in the Comment field, remove the default value in Lifetime (days), and click Generate. Take note of your token.
Important:
- Make sure you delete the default value in Lifetime (days) so that the token doesn’t expire and the integration doesn’t break.
- Ensure the account generating the token has CAN VIEW access for the Databricks jobs and clusters you want to monitor.
As an alternative, follow the official Databricks documentation to generate access token for a service principal.
In Datadog, open the Databricks integration tile.
On the Configure tab, click Add Databricks Workspace.
Enter a workspace name, your Databricks workspace URL, and the Databricks token you generated.
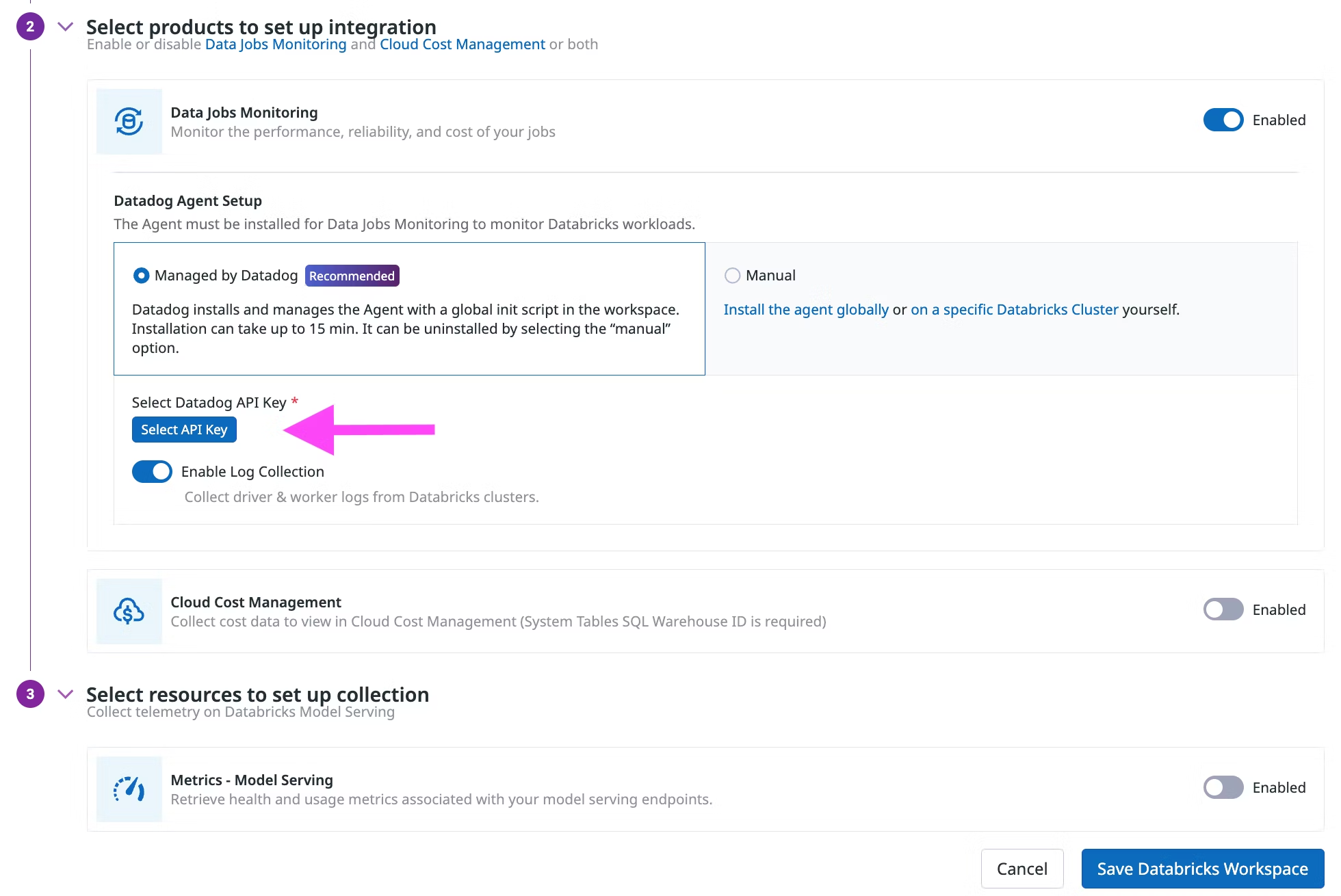
In the Select products to set up integration section, make sure the Data Jobs Monitoring product is Enabled.
In the Datadog Agent Setup section, chooose either
- Managed by Datadog (recommended): Datadog installs and manages the Agent with a global init script in the workspace.
- Manually: Follow the instructions below to install and manage the init script for installing the Agent globally or on specific Databricks clusters.
Install the Datadog Agent
The Datadog Agent must be installed on Databricks clusters to monitor Databricks jobs that run on all-purpose or job clusters.
Datadog can install and manage a global init script in the Databricks workspace. The Datadog Agent is installed on all clusters in the workspace, when they start.
This setup does not work on Databricks clusters in Standard (formerly Shared) access mode, because global init scripts cannot be installed on those clusters. If you are using clusters with the Standard (formerly Shared) access mode, you must follow the Manually install on a specific cluster instructions for installation on those specific clusters.
When integrating a workspace with Datadog
In the Select products to set up integration section, make sure the Data Jobs Monitoring product is Enabled.
In the Datadog Agent Setup section, select the Managed by Datadog toggle button.
Click Select API Key to either select an existing Datadog API key or create a new Datadog API key.
(Optional) Disable Enable Log Collection if you do not want to collect driver and worker logs for correlating with jobs.
Click Save Databricks Workspace.
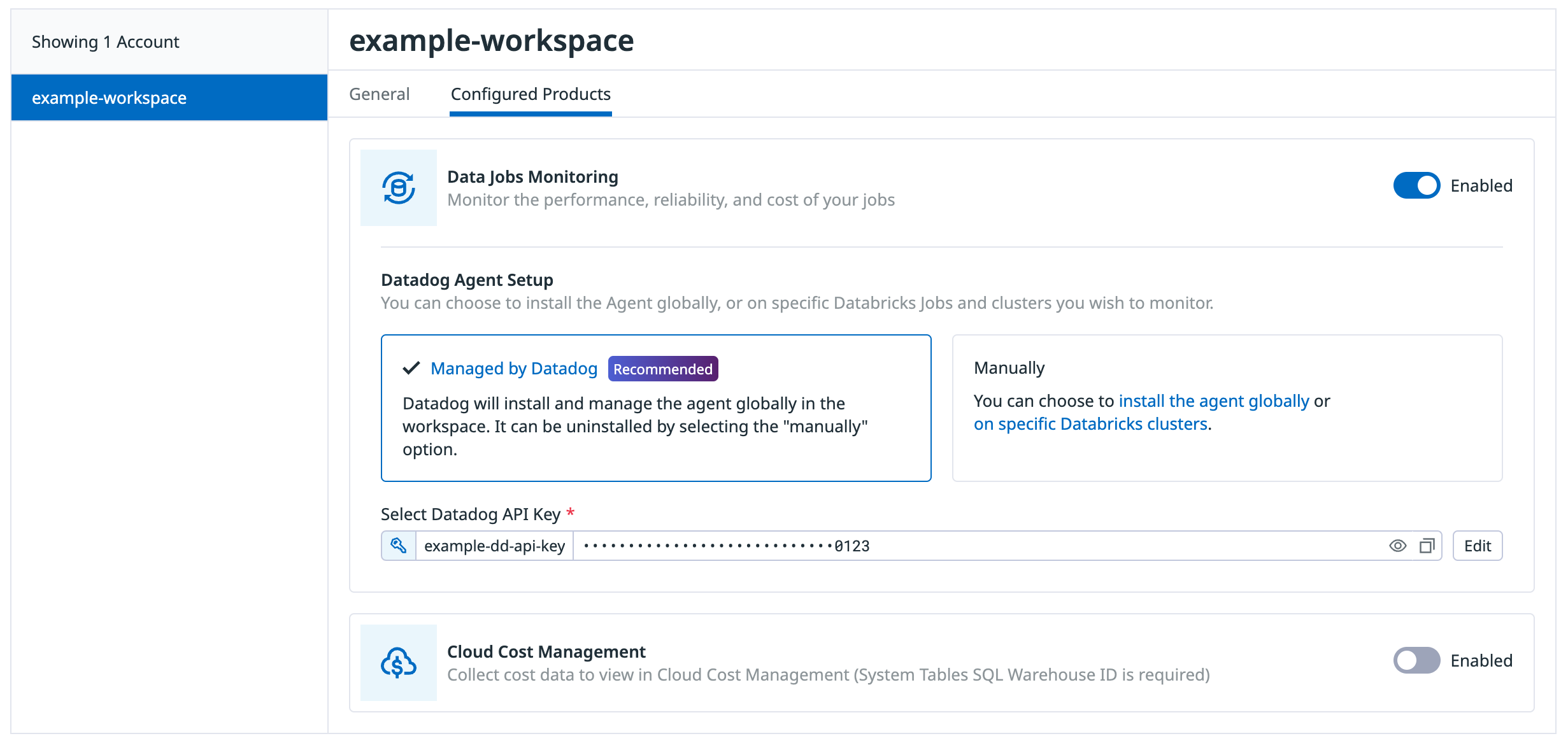
When adding the init script to a Databricks workspace already integrated with Datadog
On the Configure tab, click the workspace in the list of workspaces
Click the Configured Products tab
Make sure the Data Jobs Monitoring product is Enabled.
In the Datadog Agent Setup section, select the Managed by Datadog toggle button.
Click Select API Key to either select an existing Datadog API key or create a new Datadog API key.
(Optional) Disable Enable Log Collection if you do not want to collect driver and worker logs for correlating with jobs.
Click Save Databricks Workspace at the bottom of the browser window.
This setup does not work on Databricks clusters in Standard (formerly Shared) access mode, because global init scripts cannot be installed on those clusters. If you are using clusters with the Standard (formerly Shared) access mode, you must follow the Manually install on a specific cluster instructions for installation on those specific clusters.
In Databricks, click your display name (email address) in the upper right corner of the page.
Select Settings and click the Compute tab.
In the All purpose clusters section, next to Global init scripts, click Manage.
Click Add. Name your script. Then, in the Script field, copy and paste the following script, remembering to replace the placeholders with your parameter values.
#!/bin/bash # Required parameters export DD_API_KEY=<YOUR API KEY> export DD_SITE=<YOUR DATADOG SITE> export DATABRICKS_WORKSPACE="<YOUR WORKSPACE NAME>" # Download and run the latest init script curl -L https://install.datadoghq.com/scripts/install-databricks.sh > djm-install-script bash djm-install-script || trueThe script above sets the required parameters, and downloads and runs the latest init script for Data Jobs Monitoring in Databricks. If you want to pin your script to a specific version, you can replace the filename in the URL with
install-databricks-0.10.0.shto use version0.10.0, for example. The source code used to generate this script, and the changes between script versions, can be found on the Datadog Agent repository.To enable the script for all new and restarted clusters, toggle Enabled.
Click Add.
Set the required init script parameters
Provide the values for the init script parameters at the beginning of the global init script.
export DD_API_KEY=<YOUR API KEY>
export DD_SITE=<YOUR DATADOG SITE>
export DATABRICKS_WORKSPACE="<YOUR WORKSPACE NAME>"
Optionally, you can also set other init script parameters and Datadog environment variables here, such as DD_ENV and DD_SERVICE. The script can be configured using the following parameters:
| Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| DD_API_KEY | Your Datadog API key. | |
| DD_SITE | Your Datadog site. | |
| DATABRICKS_WORKSPACE | Name of your Databricks Workspace. It should match the name provided in the Datadog-Databricks integration step. Enclose the name in double quotes if it contains whitespace. | |
| DRIVER_LOGS_ENABLED | Collect spark driver logs in Datadog. | false |
| WORKER_LOGS_ENABLED | Collect spark workers logs in Datadog. | false |
| DD_DJM_ADD_LOGS_TO_FAILURE_REPORT | Include init script logs for debugging when reporting a failure back to Datadog. | false |
In Databricks, create a init script file in Workspace with the following content. Be sure to make note of the file path.
#!/bin/bash # Download and run the latest init script curl -L https://install.datadoghq.com/scripts/install-databricks.sh > djm-install-script bash djm-install-script || trueThe script above downloads and runs the latest init script for Data Jobs Monitoring in Databricks. If you want to pin your script to a specific version, you can replace the filename in the URL with
install-databricks-0.10.0.shto use version0.10.0, for example. The source code used to generate this script, and the changes between script versions, can be found on the Datadog Agent repository.On the cluster configuration page, click the Advanced options toggle.
At the bottom of the page, go to the Init Scripts tab.
- Under the Destination drop-down, select
Workspace. - Under Init script path, enter the path to your init script.
- Click Add.
- Under the Destination drop-down, select
Set the required init script parameters
In Databricks, on the cluster configuration page, click the Advanced options toggle.
At the bottom of the page, go to the Spark tab.
In the Environment variables textbox, provide the values for the init script parameters.
DD_API_KEY=<YOUR API KEY> DD_SITE=<YOUR DATADOG SITE> DATABRICKS_WORKSPACE="<YOUR WORKSPACE NAME>"Optionally, you can also set other init script parameters and Datadog environment variables here, such as
DD_ENVandDD_SERVICE. The script can be configured using the following parameters:
| Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| DD_API_KEY | Your Datadog API key. | |
| DD_SITE | Your Datadog site. | |
| DATABRICKS_WORKSPACE | Name of your Databricks Workspace. It should match the name provided in the Datadog-Databricks integration step. Enclose the name in double quotes if it contains whitespace. | |
| DRIVER_LOGS_ENABLED | Collect spark driver logs in Datadog. | false |
| WORKER_LOGS_ENABLED | Collect spark workers logs in Datadog. | false |
| DD_DJM_ADD_LOGS_TO_FAILURE_REPORT | Include init script logs for debugging when reporting a failure back to Datadog. | false |
- Click Confirm.
Restart already-running clusters
The init script installs the Agent when clusters start.
Already-running all-purpose clusters or long-lived job clusters must be manually restarted for the init script to install the Datadog Agent.
For scheduled jobs that run on job clusters, the init script installs the Datadog Agent automatically on the next run.
Validation
In Datadog, view the Data Jobs Monitoring page to see a list of all your Databricks jobs.
Troubleshooting
If you don’t see any data in DJM after installing the product, follow those steps.
The init script installs the Datadog Agent. To make sure it is properly installed, ssh into the cluster and run the Agent status command:
sudo datadog-agent status
If the Agent is not installed, view the installation logs located in /tmp/datadog-djm-init.log.
If you need further assistance from Datadog support, add the following environment variable to the init script. This ensures that logs are sent to Datadog when a failure occurs.
export DD_DJM_ADD_LOGS_TO_FAILURE_REPORT=true
Advanced Configuration
Tag spans at runtime
You can set tags on Spark spans at runtime. These tags are applied only to spans that start after the tag is added.
// Add tag for all next Spark computations
sparkContext.setLocalProperty("spark.datadog.tags.key", "value")
spark.read.parquet(...)
To remove a runtime tag:
// Remove tag for all next Spark computations
sparkContext.setLocalProperty("spark.datadog.tags.key", null)
Aggregate cluster metrics from one-time job runs
This configuration is applicable if you want cluster resource utilization data about your jobs and create a new job and cluster for each run via the one-time run API endpoint (common when using orchestration tools outside of Databricks such as Airflow or Azure Data Factory).
If you are submitting Databricks Jobs through the one-time run API endpoint, each job run has a unique job ID. This can make it difficult to group and analyze cluster metrics for jobs that use ephemeral clusters. To aggregate cluster utilization from the same job and assess performance across multiple runs, you must set the DD_JOB_NAME variable inside the spark_env_vars of every new_cluster to the same value as your request payload’s run_name.
Here’s an example of a one-time job run request body:
{
"run_name": "Example Job",
"idempotency_token": "8f018174-4792-40d5-bcbc-3e6a527352c8",
"tasks": [
{
"task_key": "Example Task",
"description": "Description of task",
"depends_on": [],
"notebook_task": {
"notebook_path": "/Path/to/example/task/notebook",
"source": "WORKSPACE"
},
"new_cluster": {
"num_workers": 1,
"spark_version": "13.3.x-scala2.12",
"node_type_id": "i3.xlarge",
"spark_env_vars": {
"DD_JOB_NAME": "Example Job"
}
}
}
]
}Set up Data Jobs Monitoring with Databricks Networking Restrictions
With Databricks Networking Restrictions, Datadog may not have access to your Databricks APIs, which is required to collect traces for Databricks job executions along with tags and other metadata.
If you are controlling Databricks API access with IP access lists, allow-listing Datadog’s specific webhook IP addresses allows Datadog to connect to the Databricks APIs in your workspace. See Databricks’s documentation for configuring IP access lists for workspaces to give Datadog API access.
To add workspaces using the Datadog UI, you must also allow-list Datadog’s API IP addresses.
If you are using Databricks Private Connectivity, reach out to the Datadog support team to discuss potential options.
Further Reading
Documentation, liens et articles supplémentaires utiles: