- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- Tracing
- Profileur
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Développeurs
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Checks custom
- Intégrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Checks de service
- IDE Plugins
- Communauté
- Guides
- API
- Application mobile
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Alertes
- Infrastructure
- Métriques
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Conteneurs
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Product Analytics
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Exécuteur de tests intelligent
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- Administration
Postgres Custom Metric Collection
Cette page n'est pas encore disponible en français, sa traduction est en cours.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
To collect custom metrics with the Postgres integration, use the custom_queries option in the conf.d/postgres.d/conf.yaml file at the root of your Agent’s configuration directory. See the sample postgres.d/conf.yaml for more details.
Note: When generating custom metrics that require querying additional tables, you may need to grant the SELECT permission on those tables to the Postgres user. Example: grant SELECT on <TABLE_NAME> to <USER>;
Configuration
custom_queries has the following options:
| Option | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| metric_prefix | Yes | Each metric starts with the chosen prefix. |
| query | Yes | This is the SQL to execute. It can be a simple statement or a multi-line script. All of the rows of the results are evaluated. Use the pipe if you require a multi-line script. |
| columns | Yes | This is a list representing each column ordered sequentially from left to right. There are 2 required pieces of data: - name: This is the suffix to append to the metric_prefix to form the full metric name. If the type is specified as tag, the column is instead applied as a tag to every metric collected by this query.- type: This is the submission method (gauge, count, rate, etc.). This can also be set to tag to tag each metric in the row with the name and value (<name>:<row_value>) of the item in this column. |
| tags | No | A list of static tags to apply to each metric. |
Notes
At least one of the items in defined
columnsshould be a metric type (gauge,count,rate, etc.).The number of items defined in
columnsmust equal the number of columns returned in the query.The order in which the items in
columnsare defined must be same order returned in the query.custom_queries: - query: Select F3, F2, F1 from Table; columns: - {name: f3_metric_alias, type: gauge} - {name: f2_tagkey , type: tag } - {name: f1_metric_alias, type: count} [...]
Example
Database and table
Below is the company table from testdb database. The table contains 3 employee records:
testdb=# SELECT * FROM company;
id| name | age| address |salary | entry_date | last_raise_time
-------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Paul | 32 | California | 20000 | 1457570000 | 1457570300
2 | Allen | 25 | Texas | 30000 | 1457570060 | 1457570300
3 | Teddy | 23 | Norway | 45000 | 1457570120 | 1457570300
From a SQL query to the YAML configuration
The goal is to capture the age and salary of Paul as metric values with his name and address as tags.
SQL query:
SELECT age,salary,name,address FROM company WHERE name = 'Paul'
Corresponding custom_queries YAML configuration:
custom_queries:
- metric_prefix: postgresql
query: SELECT age,salary,name,address FROM company WHERE name = 'Paul'
columns:
- name: employee_age
type: gauge
- name: employee_salary
type: gauge
- name: name
type: tag
- name: localisation
type: tag
tags:
- query:custom
After updating the Postgres YAML file, restart the Datadog Agent.
Validation
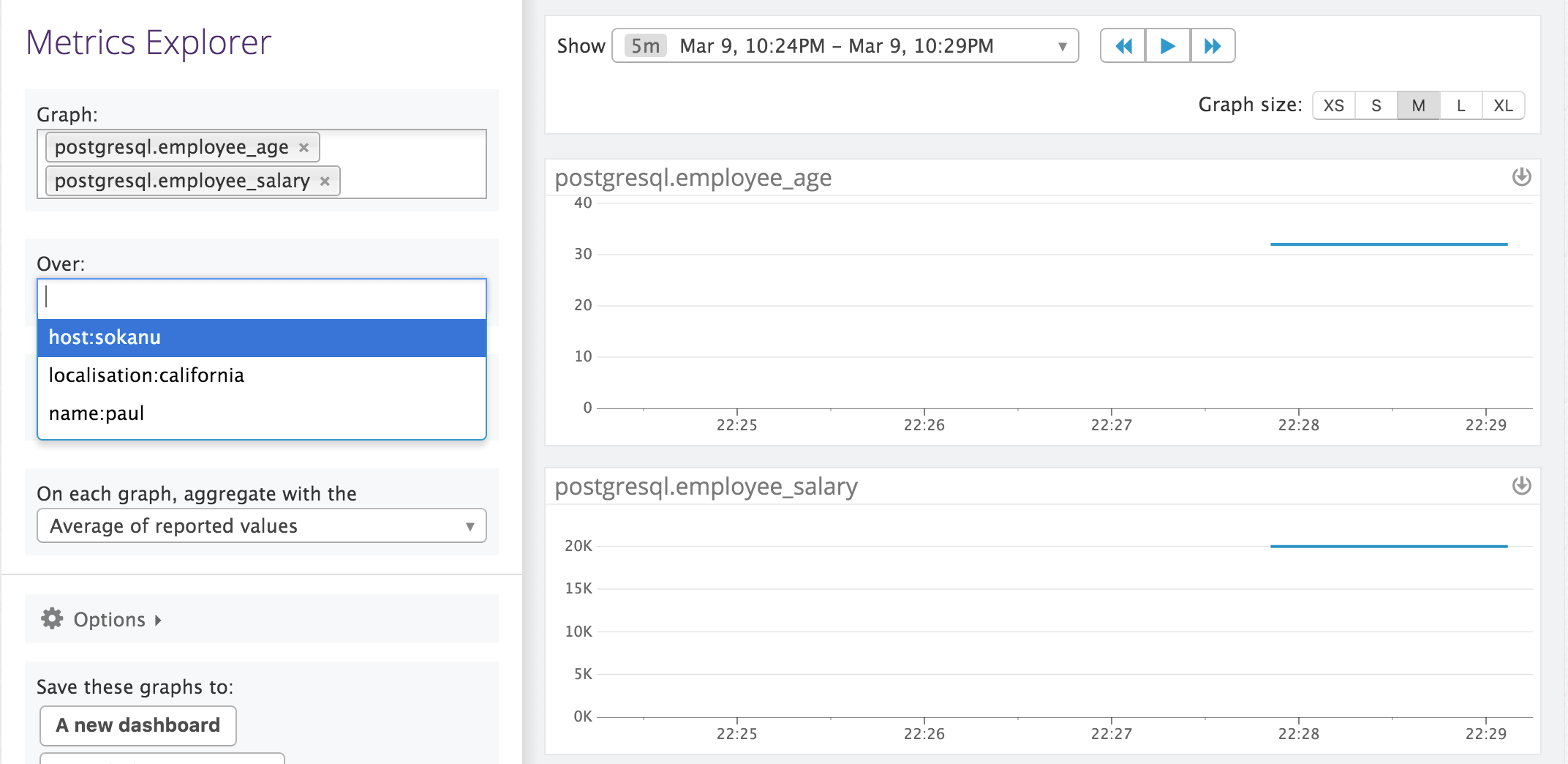
To verify the result, search for the metrics using the Metrics Explorer:
Debugging
Run the Agent’s status subcommand and look for postgres under the Checks section:
postgres
--------
- instance #0 [ERROR]: 'Missing metric_prefix parameter in custom_queries'
- Collected 0 metrics, 0 events & 0 service checks
Additionally, the Agent’s logs may provide useful information.
Further Reading
Documentation, liens et articles supplémentaires utiles: