- 重要な情報
- はじめに
- Datadog
- Datadog サイト
- DevSecOps
- AWS Lambda のサーバーレス
- エージェント
- インテグレーション
- コンテナ
- ダッシュボード
- アラート設定
- ログ管理
- トレーシング
- プロファイラー
- タグ
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic モニタリング
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- 用語集
- Standard Attributes
- ガイド
- インテグレーション
- エージェント
- OpenTelemetry
- 開発者
- 認可
- DogStatsD
- カスタムチェック
- インテグレーション
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- サービスのチェック
- IDE インテグレーション
- コミュニティ
- ガイド
- API
- モバイルアプリケーション
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- アプリ内
- Service Management
- インフラストラクチャー
- アプリケーションパフォーマンス
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- データベース モニタリング
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility (CI/CDの可視化)
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- セキュリティ
- セキュリティの概要
- Cloud SIEM
- クラウド セキュリティ マネジメント
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- ログ管理
- Observability Pipelines(観測データの制御)
- ログ管理
- 管理
Code Security
このページは日本語には対応しておりません。随時翻訳に取り組んでいます。翻訳に関してご質問やご意見ございましたら、お気軽にご連絡ください。
Overview
Datadog Code Security identifies code-level vulnerabilities in your services and provides actionable insights and recommended fixes.
For a list of supported services, see the Library Compatibility Requirements.
Code Security uses an Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) approach to find vulnerabilities within your application code. IAST uses instrumentation embedded in your code like application performance monitoring (APM).
Code Security also monitors your code’s interactions with other components of your stack, such as libraries and infrastructure.
IAST enables Datadog to identify vulnerabilities using legitimate application traffic instead of relying on external tests that could require extra configuration or periodic scheduling.
Code Security’s runtime application monitoring provides an up-to-date view of your attack surface that enables you to quickly identify potential issues.
Code-level vulnerabilities list
The Code Security detection rules support the following languages.
| Severity | Detection Rule | Java | .NET | Node.js | Python |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Critical | NoSQL Injection | FALSE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| Critical | SQL Injection | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Critical | Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Critical | Code Injection | FALSE | FALSE | TRUE | FALSE |
| Critical | Command Injection | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| High | LDAP Injection | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| High | Hardcoded Secrets | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| High | Hardcoded Passwords | FALSE | FALSE | TRUE | FALSE |
| High | Path Traversal | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| High | Trust Boundary Violation | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Untrusted Deserialization | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Unvalidated Redirect | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| High | XPath Injection | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Header Injection | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| High | Directory Listing Leak | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Default HTML Escape Invalid | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Verb Tampering | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Medium | No SameSite Cookie | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Medium | Insecure Cookie | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Medium | No HttpOnly Cookie | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Medium | Weak Hashing | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Medium | Weak Cipher | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Medium | Stacktrace Leak | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Medium | Reflection Injection | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Medium | Insecure Authentication Protocol | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Medium | Hardcoded Key | FALSE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Medium | Insecure JSP Layout | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Low | HSTS Header Missing | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| Low | X-Content-Type-Options Header Missing | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| Low | Weak Randomness | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Low | Admin Console Active | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Low | Session Timeout | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Low | Session Rewriting | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
Explore and manage code vulnerabilities
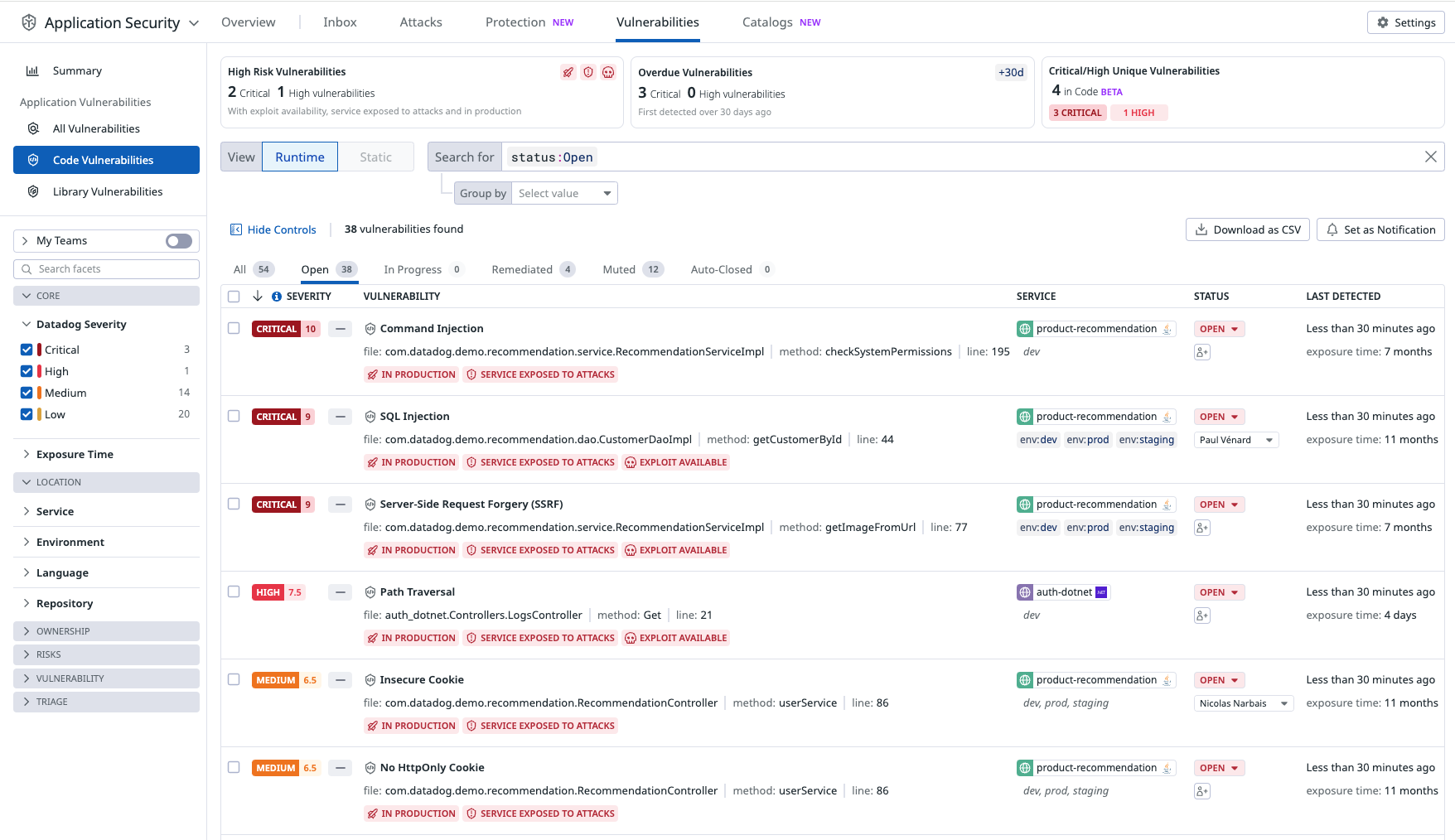
The Vulnerability Explorer uses real-time threat data to help you understand vulnerabilities endangering your system. Vulnerabilities are ordered by severity.
To triage vulnerabilities, each vulnerability contains a brief description of the issue, including:
- Impacted services.
- Vulnerability type.
- First detection.
- The exact file and line number where the vulnerability was found.
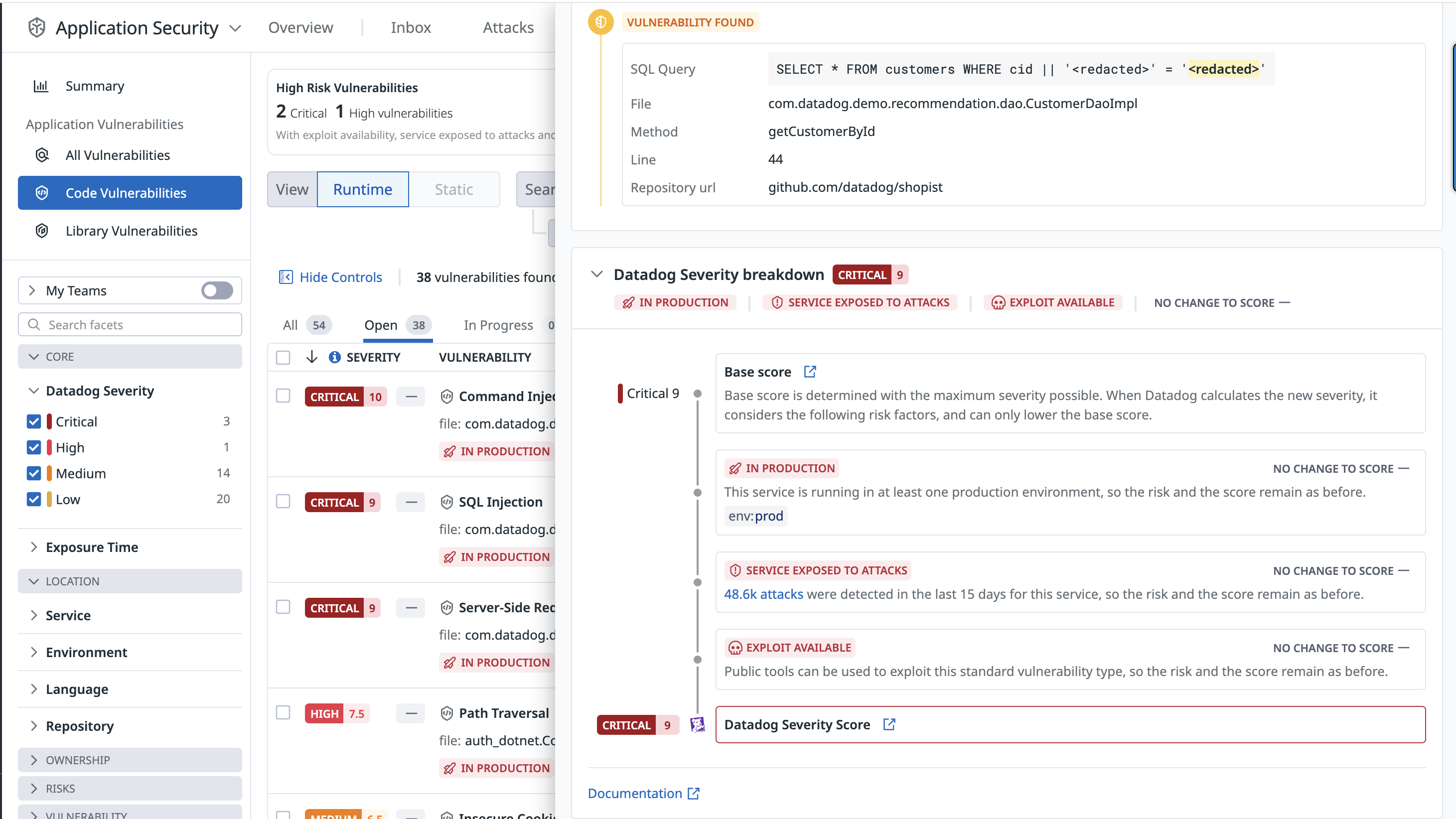
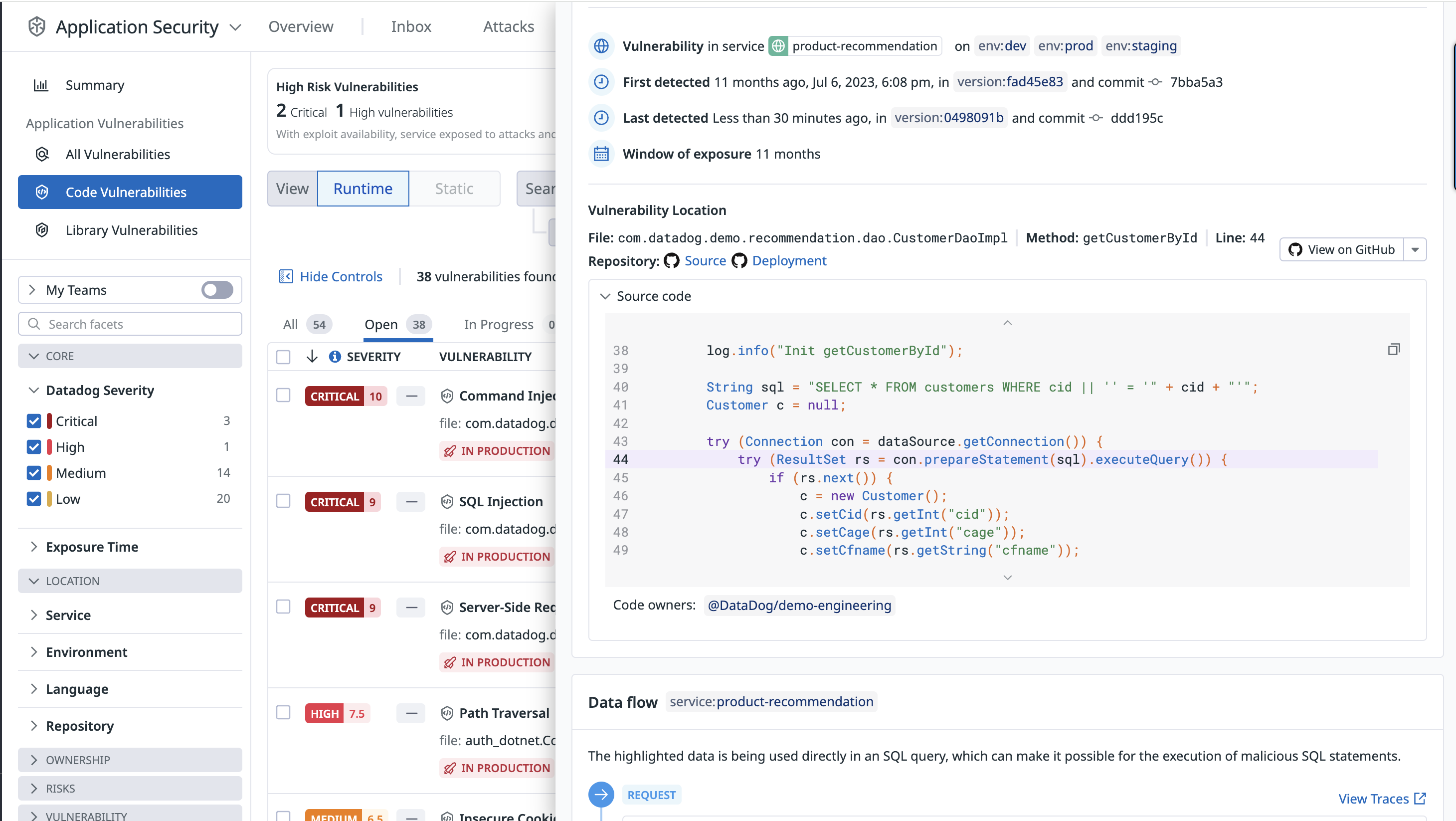
Each vulnerability detail includes a risk score (see screenshot below) and a severity rating: critical, high, medium, or low.
The risk score is tailored to the specific runtime context, including factors such as where the vulnerability is deployed and whether the service is targeted by active attacks.
Remediation
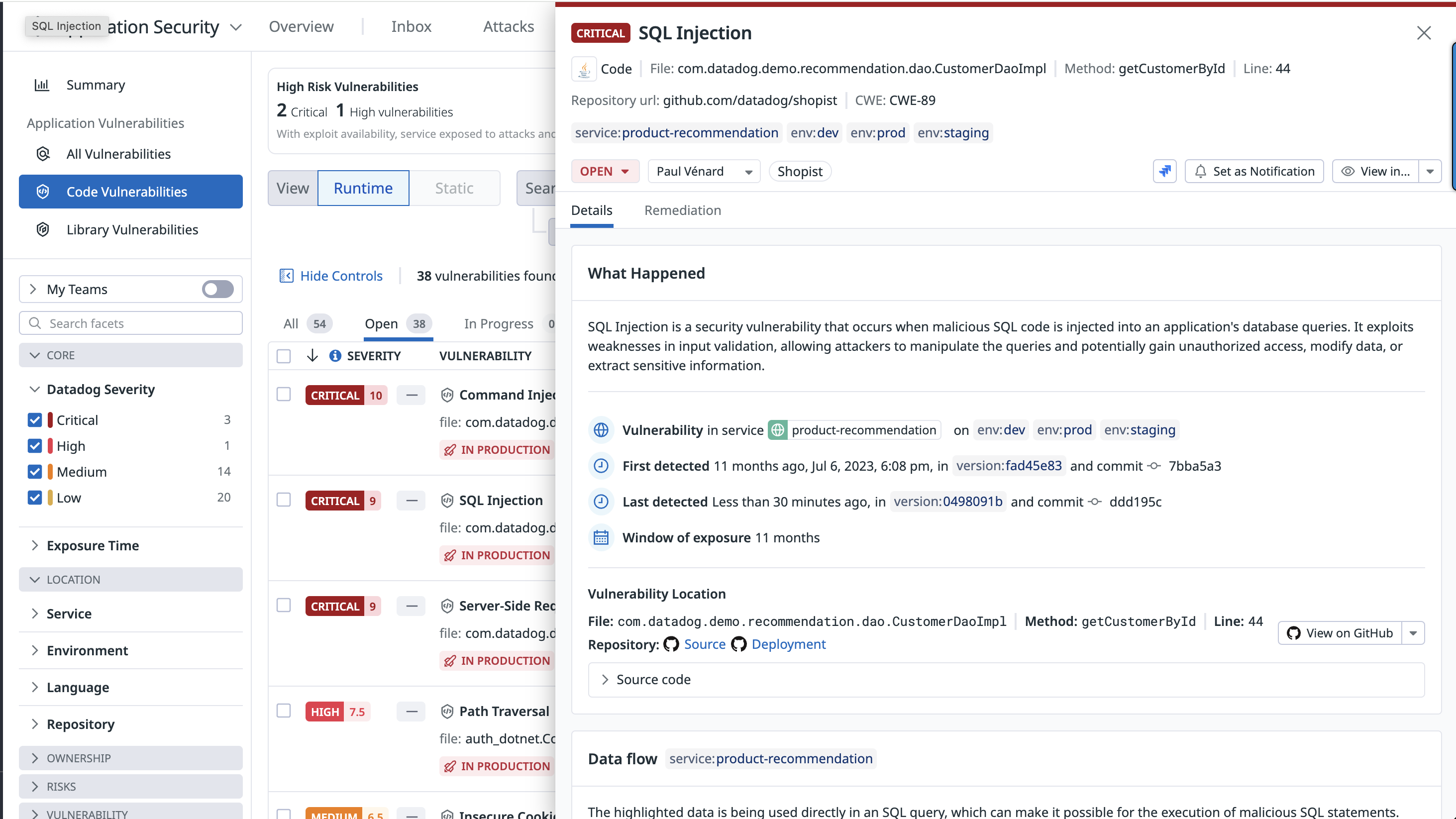
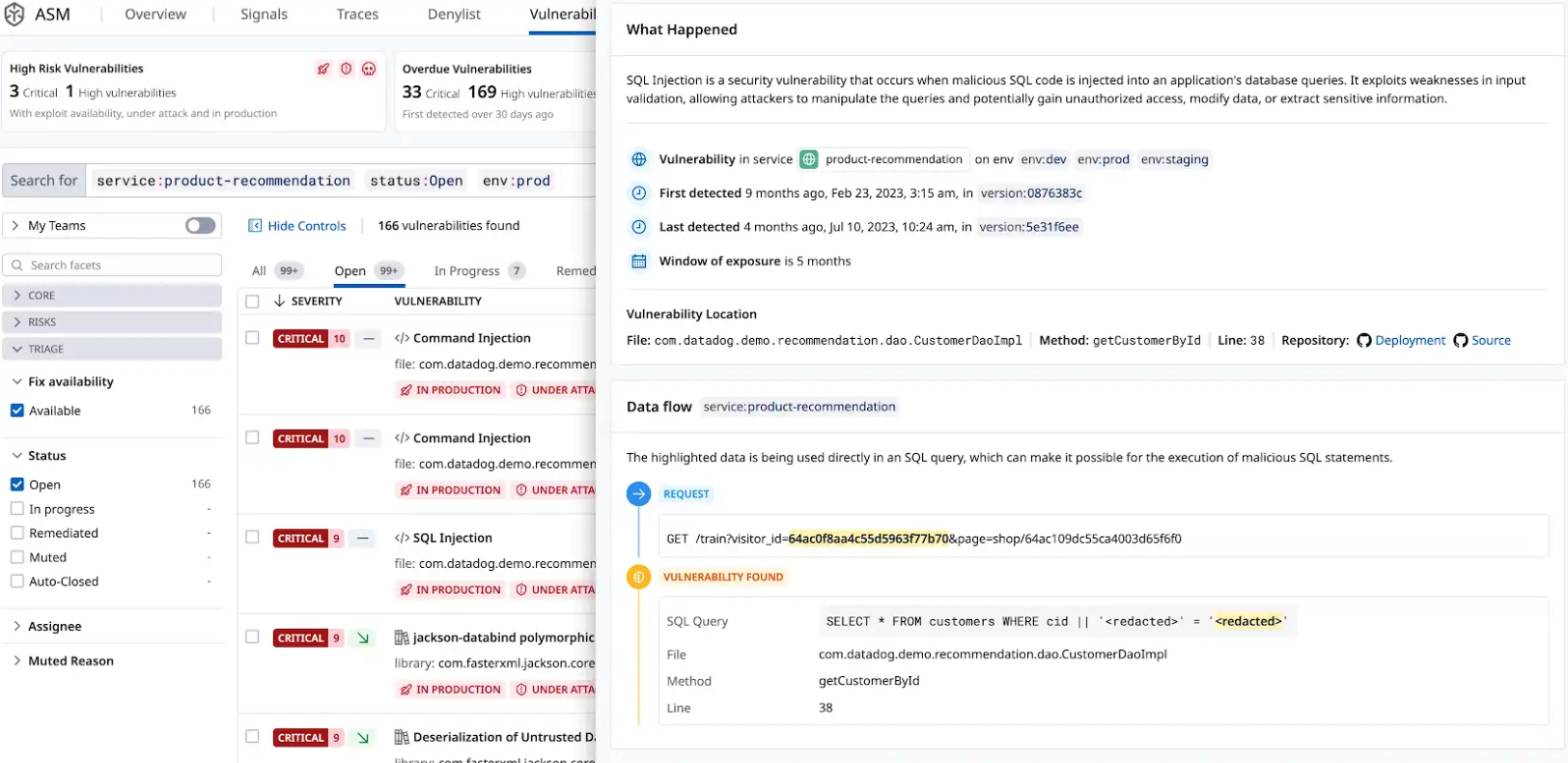
Datadog Code Security automatically provides the information teams need to identify where a vulnerability is in an application, from the affected filename down to the exact method and line number.
When the GitHub integration is enabled, Code Security shows the first impacted version of a service, the commit that introduced the vulnerability, and a snippet of the vulnerable code. This information gives teams insight into where and when a vulnerability occurred and helps to prioritize their work.
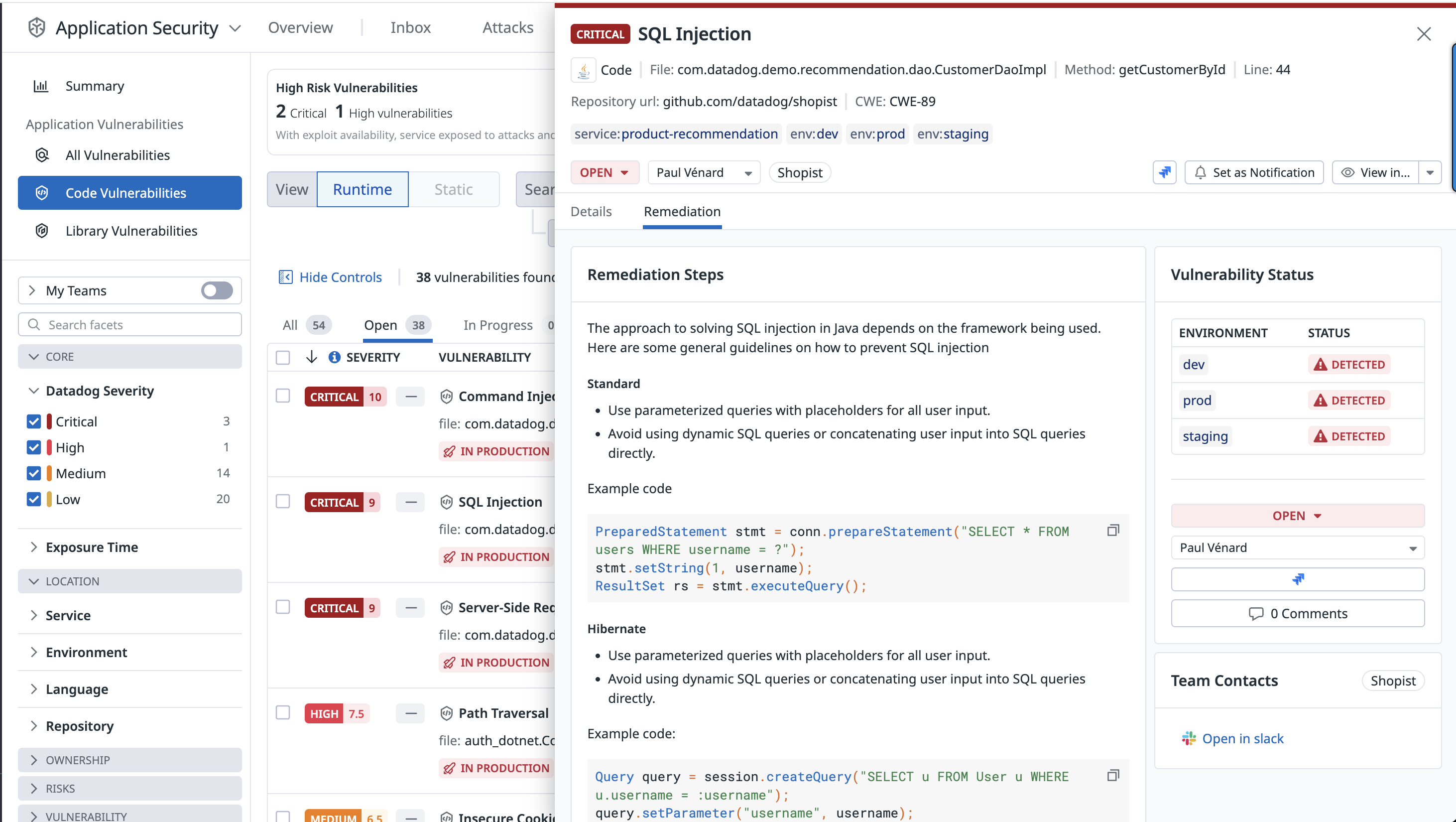
Detailed remediation steps are provided for each detected vulnerability.
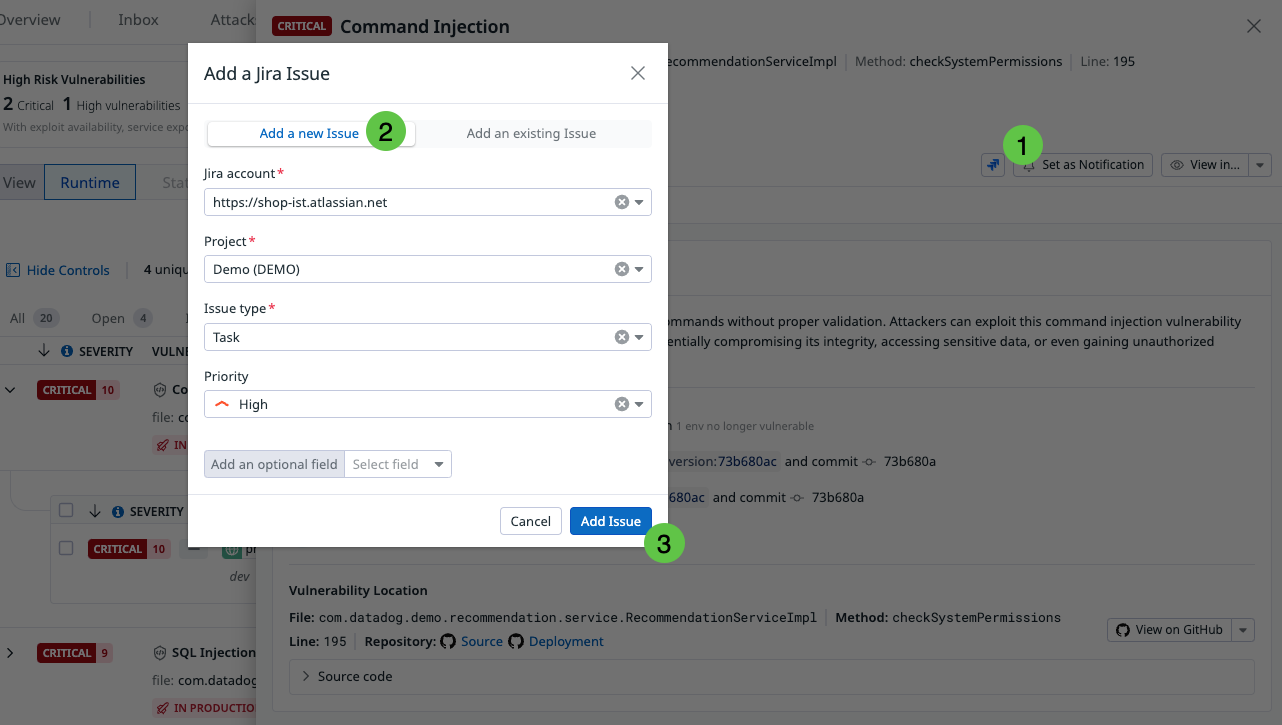
Recommendations enable you to change the status of a vulnerability, assign it to a team member for review, and create a Jira issue for tracking.
Note: To create Jira issues for vulnerabilities, you must configure the Jira integration, and have the manage_integrations permission. For detailed instructions, see the Jira integration documentation, as well as the Role Based Access Control documentation.
Enabling Code Security
To enable Code Security, you can use Single Step Instrumentation or configure the Datadog Tracing Library. Detailed instructions for both methods can be found in the Security > Application Security > Settings section.
If you need additional help, contact Datadog support.
Further Reading
お役に立つドキュメント、リンクや記事: