- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Integrations
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- APM Tracing
- Profiler
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic Monitoring
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Test Impact Analysis
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Datadog Mobile App
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Infrastructure
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Product Analytics
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Optimization
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Docker Prometheus and OpenMetrics metrics collection
Collect your exposed Prometheus and OpenMetrics metrics from your application running inside your containers by using the Datadog Agent, and the Datadog-OpenMetrics or Datadog-Prometheus integrations.
Overview
Starting with version 6.5.0, the Agent includes OpenMetrics and Prometheus checks capable of scraping Prometheus endpoints. Datadog recommends using the OpenMetrics check since it is more efficient and fully supports Prometheus text format. For more advanced usage of the OpenMetricsCheck interface, including writing a custom check, see the Developer Tools section. Use the Prometheus check only when the metrics endpoint does not support a text format.
This page explains the basic usage of these checks, enabling you to import all your Prometheus exposed metrics within Datadog.
The CLI commands on this page are for the Docker runtime. Replace docker with nerdctl for the containerd runtime, or podman for the Podman runtime.
Setup
Installation
Launch the Docker Agent next to your other containers by replacing <DATADOG_API_KEY> with the API key for your organization in the command below:
docker run -d --cgroupns host \
--pid host \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \
-v /proc/:/host/proc/:ro \
-v /sys/fs/cgroup/:/host/sys/fs/cgroup:ro \
-e DD_API_KEY="<DATADOG_API_KEY>" \
-e DD_SITE="<YOUR_DATADOG_SITE>" \
gcr.io/datadoghq/agent:latest
docker run -d --name dd-agent -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \
-v /proc/:/host/proc/:ro \
-v /cgroup/:/host/sys/fs/cgroup:ro \
-e DD_API_KEY="<DATADOG_API_KEY>" \
-e DD_SITE="<YOUR_DATADOG_SITE>" \
gcr.io/datadoghq/agent:latest
docker run -d -e DD_API_KEY="<DATADOG_API_KEY>" \
-e DD_SITE="<YOUR_DATADOG_SITE>" \
gcr.io/datadoghq/agent:latest
Note: Your Datadog site is .
Configuration
The Agent detects if it’s running on Docker and automatically searches all container labels for Datadog-OpenMetrics labels. Autodiscovery expects labels to look like these examples, depending on the file type:
LABEL "com.datadoghq.ad.check_names"='["openmetrics"]'
LABEL "com.datadoghq.ad.init_configs"='[{}]'
LABEL "com.datadoghq.ad.instances"='[{"openmetrics_endpoint":"http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT>","namespace":"<NAMESPACE>","metrics":[{"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>": "<NEW_METRIC_NAME>"}]}]'
Multiple endpoints example
LABEL "com.datadoghq.ad.check_names"='["openmetrics","openmetrics"]'
LABEL "com.datadoghq.ad.init_configs"='[{},{}]'
LABEL "com.datadoghq.ad.instances"='[{"openmetrics_endpoint":"http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT>","namespace":"<NAMESPACE>","metrics":[{"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>": "<NEW_METRIC_NAME>"}]}, {"openmetrics_endpoint":"http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT>","namespace":"<NAMESPACE>","metrics":[{"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>": "<NEW_METRIC_NAME>"}]}]'
labels:
com.datadoghq.ad.check_names: '["openmetrics"]'
com.datadoghq.ad.init_configs: '[{}]'
com.datadoghq.ad.instances: |
[
{
"openmetrics_endpoint": "http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT>",
"namespace": "<NAMESPACE>",
"metrics": [
{"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>": "<NEW_METRIC_NAME>"}
]
}
]
Multiple endpoints example:
labels:
com.datadoghq.ad.check_names: '["openmetrics", "openmetrics"]'
com.datadoghq.ad.init_configs: '[{},{}]'
com.datadoghq.ad.instances: |
[
{
"openmetrics_endpoint": "http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT>",
"namespace": "<NAMESPACE>",
"metrics": [
{"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>": "<NEW_METRIC_NAME>"}
]
},
{
"openmetrics_endpoint": "http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT>",
"namespace": "<NAMESPACE>",
"metrics": [
{"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>": "<NEW_METRIC_NAME>"}
]
}
]
# single metric
-l com.datadoghq.ad.check_names='["openmetrics"]' -l com.datadoghq.ad.init_configs='[{}]' -l com.datadoghq.ad.instances="[{\"openmetrics_endpoint\":\"http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT>\",\"namespace\":\"<NAMESPACE>\",\"metrics\":[{\"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>\": \"<NEW_METRIC_NAME>\"}]}]"
Examples of metrics formatting in com.datadoghq.ad.instances
# multiple metrics
-l com.datadoghq.ad.instances="[{\"openmetrics_endpoint\":\"http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT>\",\"namespace\":\"<NAMESPACE>\",\"metrics\":[{\"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>\": \"<NEW_METRIC_NAME>\"}, {\"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>\": \"<NEW_METRIC_NAME>\"}]}]"
# all metrics of a base type
-l com.datadoghq.ad.instances="[{\"openmetrics_endpoint\":\"http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT>\",\"namespace\":\"<NAMESPACE>\",\"metrics\":[\"<METRIC_BASE_TO_FETCH>.*\"]}]"
# all metrics
-l com.datadoghq.ad.instances="[{\"openmetrics_endpoint\":\"http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT>\",\"namespace\":\"<NAMESPACE>\",\"metrics\":[\".*\"]}]"
Multiple endpoints example:
-l com.datadoghq.ad.check_names='["openmetrics", "openmetrics"]' -l com.datadoghq.ad.init_configs='[{},{}]' -l com.datadoghq.ad.instances='["{\"openmetrics_endpoint\":\"http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT> \",\"namespace\":\"<NAMESPACE>\",\"metrics\":[{\"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>\": \"<NEW_METRIC_NAME>\"}]}", "{\"openmetrics_endpoint\":\"http://%%host%%:<PROMETHEUS_PORT>/<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT> \",\"namespace\":\"<NAMESPACE>\",\"metrics\":[{\"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>\": \"<NEW_METRIC_NAME>\"}]}"]'
With the following configuration placeholder values:
| Placeholder | Description |
|---|---|
<PROMETHEUS_PORT> | Port to connect to in order to access the Prometheus endpoint. Can alternatively use the Autodiscovery Template Variable %%port%%. |
<PROMETHEUS_ENDPOINT> | URL path for the metrics served by the container, in Prometheus format. |
<NAMESPACE> | Set namespace to be prefixed to every metric when viewed in Datadog. |
<METRIC_TO_FETCH> | Prometheus metrics key to be fetched from the Prometheus endpoint. |
<NEW_METRIC_NAME> | Transforms the <METRIC_TO_FETCH> metric key to <NEW_METRIC_NAME> in Datadog. |
The metrics configuration is a list of metrics to retrieve as custom metrics. Include each metric to fetch and the desired metric name in Datadog as key value pairs, for example, {"<METRIC_TO_FETCH>":"<NEW_METRIC_NAME>"}. You can alternatively provide a list of metric names strings, interpreted as regular expressions, to bring the desired metrics with their current names. Note: Regular expressions can potentially send a lot of custom metrics.
For a full list of available parameters for instances, including namespace and metrics, see the sample configuration openmetrics.d/conf.yaml.
Getting started
Simple metric collection
To get started with collecting metrics exposed by Prometheus running within a container, follow these steps:
Launch the Datadog Agent:
docker run -d --cgroupns host \ --pid host \ -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \ -v /proc/:/host/proc/:ro \ -v /sys/fs/cgroup/:/host/sys/fs/cgroup:ro \ -e DD_API_KEY="<DATADOG_API_KEY>" \ gcr.io/datadoghq/agent:latestdocker run -d -e DD_API_KEY="<DATADOG_API_KEY>" \ gcr.io/datadoghq/agent:latest \ -v \\.\pipe\docker_engine:\\.\pipe\docker_engineLaunch a Prometheus container exposing example metrics for the Agent to collect, with the Autodiscovery Labels for the OpenMetrics Check.
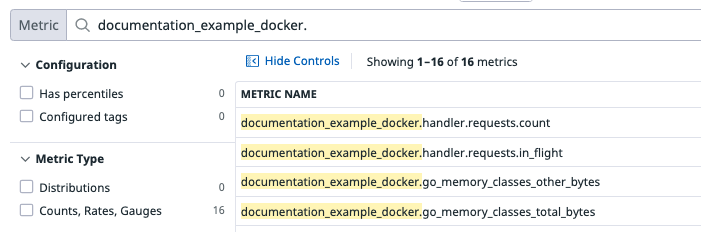
The following labels will have the Agent collect the metrics
promhttp_metric_handler_requests,promhttp_metric_handler_requests_in_flight, and all exposed metrics starting withgo_memory.labels: com.datadoghq.ad.check_names: '["openmetrics"]' com.datadoghq.ad.init_configs: '[{}]' com.datadoghq.ad.instances: | [ { "openmetrics_endpoint": "http://%%host%%:%%port%%/metrics", "namespace": "documentation_example_docker", "metrics": [ {"promhttp_metric_handler_requests": "handler.requests"}, {"promhttp_metric_handler_requests_in_flight": "handler.requests.in_flight"}, "go_memory.*" ] } ]To launch an example Prometheus container with these labels you can run:
docker run -d -l com.datadoghq.ad.check_names='["openmetrics"]' -l com.datadoghq.ad.init_configs='[{}]' -l com.datadoghq.ad.instances='[{"openmetrics_endpoint":"http://%%host%%:%%port%%/metrics","namespace":"documentation_example_docker","metrics":[{"promhttp_metric_handler_requests":"handler.requests"},{"promhttp_metric_handler_requests_in_flight":"handler.requests.in_flight"},"go_memory.*"]}]' prom/prometheusGo into your Metric summary page to see the collected metrics:
From custom to official integration
By default, all metrics retrieved by the generic Prometheus check are considered custom metrics. If you are monitoring off-the-shelf software and think it deserves an official integration, don’t hesitate to contribute!
Official integrations have their own dedicated directories. There’s a default instance mechanism in the generic check to hardcode the default configuration and metrics metadata. For example, reference the kube-proxy integration.
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: