- Esenciales
- Empezando
- Datadog
- Sitio web de Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless para Lambda AWS
- Agent
- Integraciones
- Contenedores
- Dashboards
- Monitores
- Logs
- Rastreo de APM
- Generador de perfiles
- Etiquetas (tags)
- API
- Catálogo de servicios
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Monitorización Synthetic
- Gestión de incidencias
- Monitorización de bases de datos
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Análisis de código
- Centro de aprendizaje
- Compatibilidad
- Glosario
- Atributos estándar
- Guías
- Agent
- Uso básico del Agent
- Arquitectura
- IoT
- Plataformas compatibles
- Recopilación de logs
- Configuración
- Configuración remota
- Automatización de flotas
- Actualizar el Agent
- Solucionar problemas
- Detección de nombres de host en contenedores
- Modo de depuración
- Flare del Agent
- Estado del check del Agent
- Problemas de NTP
- Problemas de permisos
- Problemas de integraciones
- Problemas del sitio
- Problemas de Autodiscovery
- Problemas de contenedores de Windows
- Configuración del tiempo de ejecución del Agent
- Consumo elevado de memoria o CPU
- Guías
- Seguridad de datos
- Integraciones
- OpenTelemetry
- Desarrolladores
- Autorización
- DogStatsD
- Checks personalizados
- Integraciones
- Crear una integración basada en el Agent
- Crear una integración API
- Crear un pipeline de logs
- Referencia de activos de integración
- Crear una oferta de mercado
- Crear un cuadro
- Crear un dashboard de integración
- Crear un monitor recomendado
- Crear una regla de detección Cloud SIEM
- OAuth para integraciones
- Instalar la herramienta de desarrollo de integraciones del Agente
- Checks de servicio
- Complementos de IDE
- Comunidad
- Guías
- API
- Aplicación móvil de Datadog
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- En la aplicación
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- Editor DDSQL
- Hojas
- Monitores y alertas
- Infraestructura
- Métricas
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Catálogo de servicios
- Catálogo de APIs
- Error Tracking
- Gestión de servicios
- Objetivos de nivel de servicio (SLOs)
- Gestión de incidentes
- De guardia
- Gestión de eventos
- Gestión de casos
- Workflow Automation
- App Builder
- Infraestructura
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Contenedores
- Serverless
- Monitorización de red
- Coste de la nube
- Rendimiento de las aplicaciones
- APM
- Términos y conceptos de APM
- Instrumentación de aplicación
- Recopilación de métricas de APM
- Configuración de pipelines de trazas
- Correlacionar trazas (traces) y otros datos de telemetría
- Trace Explorer
- Observabilidad del servicio
- Instrumentación dinámica
- Error Tracking
- Seguridad de los datos
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Gastos generales de integración del Agent
- Arquitecturas de configuración
- Configuración de Postgres
- Configuración de MySQL
- Configuración de SQL Server
- Configuración de Oracle
- Configuración de MongoDB
- Conexión de DBM y trazas
- Datos recopilados
- Explorar hosts de bases de datos
- Explorar métricas de consultas
- Explorar ejemplos de consulta
- Solucionar problemas
- Guías
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Experiencia digital
- Real User Monitoring
- Monitorización del navegador
- Configuración
- Configuración avanzada
- Datos recopilados
- Monitorización del rendimiento de páginas
- Monitorización de signos vitales de rendimiento
- Monitorización del rendimiento de recursos
- Recopilación de errores del navegador
- Rastrear las acciones de los usuarios
- Señales de frustración
- Error Tracking
- Solucionar problemas
- Monitorización de móviles y TV
- Plataforma
- Session Replay
- Exploración de datos de RUM
- Feature Flag Tracking
- Error Tracking
- Guías
- Seguridad de los datos
- Monitorización del navegador
- Análisis de productos
- Pruebas y monitorización de Synthetics
- Continuous Testing
- Entrega de software
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Configuración
- Tests en contenedores
- Búsqueda y gestión
- Explorador
- Monitores
- Flujos de trabajo de desarrolladores
- Cobertura de código
- Instrumentar tests de navegador con RUM
- Instrumentar tests de Swift con RUM
- Detección temprana de defectos
- Reintentos automáticos de tests
- Correlacionar logs y tests
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- Métricas de DORA
- Seguridad
- Información general de seguridad
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Observabilidad de la IA
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Gestión de logs
- Administración
- Gestión de cuentas
- Seguridad de los datos
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Ayuda
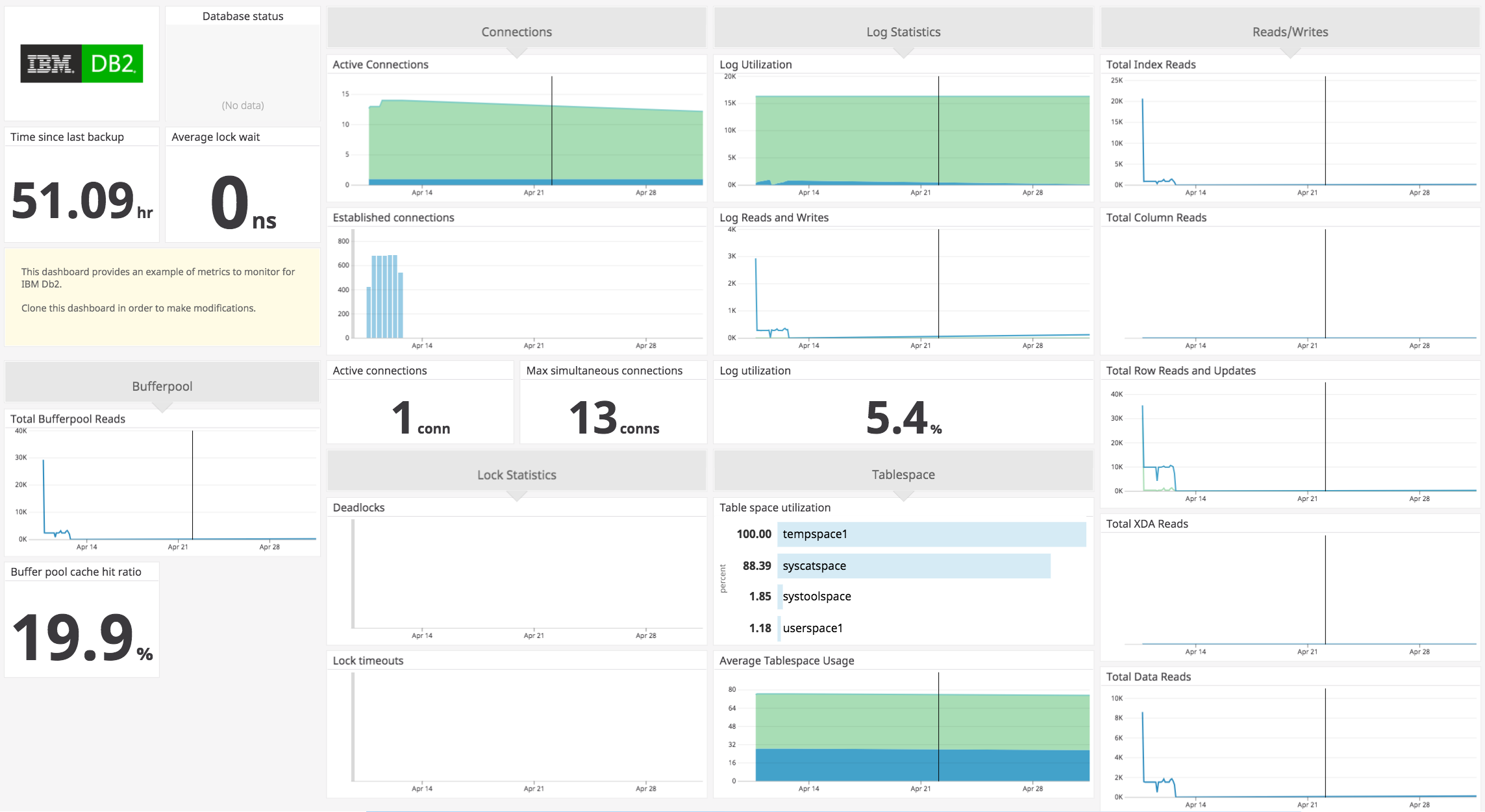
IBM Db2
Supported OS
Versión de la integración2.2.0
Información general
Este check monitoriza IBM Db2 a través del Datadog Agent.
Configuración
Instalación
El check de IBM Db2 está incluido en el paquete del Datadog Agent.
Dependencias
Se necesita la biblioteca de cliente ibm_db. Para instalarla, asegúrate de que dispones de un compilador operativo y ejecútalo:
Unix
sudo -Hu dd-agent /opt/datadog-agent/embedded/bin/pip install ibm_db==3.1.0
Nota: Si utilizas el Agent con Python 2, usa ibm_db==3.0.1 en lugar de ibm_db=3.1.0.
Windows
En el Agent v6.11 y anteriores:
"C:\Program Files\Datadog\Datadog Agent\embedded\python.exe" -m pip install ibm_db==3.0.1
Para las versiones del Agent entre la 6.12 y la 7.0:
"C:\Program Files\Datadog\Datadog Agent\embedded<PYTHON_MAJOR_VERSION>\python.exe" -m pip install ibm_db==3.0.1
Para las versiones del Agent posteriores a la 7.0:
"C:\Program Files\Datadog\Datadog Agent\embedded3\python.exe" -m pip install ibm_db==3.2.2
En Linux, puede ser necesaria la funcionalidad XML. Si encuentras errores durante
el proceso de compilación, instala libxslt-dev (o libxslt-devel para RPM).
Habilitar la monitorización
La integración de IBM Db2 extrae los datos mediante las siguientes funciones de tabla:
MON_GET_TABLESPACEMON_GET_TRANSACTION_LOGMON_GET_BUFFERPOOLMON_GET_DATABASEMON_GET_INSTANCE
Para obtener más información sobre estas funciones de tabla, consulta la documentación oficial de IBM.
Para monitorizar una instancia de Db2, crea un usuario de Db2 con el permiso EXECUTE en las cinco funciones de tabla anteriores, o concede al usuario de Db2 uno de los siguientes roles:
- Autoridad
DATAACCESS - Autoridad
DBADM - Autoridad
SQLADM
Para monitorizar el estado de una instancia, sus bases de datos asociadas y los objetos de base de datos, habilita los interruptores de monitorización del sistema de base de datos para cada uno de los objetos que quieras monitorizar:
- Sentencia
- Bloqueo
- Tablas
- Grupo de buffers
Cambia al usuario maestro de la instancia y ejecuta estos comandos en la línea db2:
update dbm cfg using HEALTH_MON on
update dbm cfg using DFT_MON_STMT on
update dbm cfg using DFT_MON_LOCK on
update dbm cfg using DFT_MON_TABLE on
update dbm cfg using DFT_MON_BUFPOOL on
Luego, ejecuta get dbm cfg y deberías ver lo siguiente:
Default database monitor switches
Buffer pool (DFT_MON_BUFPOOL) = ON
Lock (DFT_MON_LOCK) = ON
Sort (DFT_MON_SORT) = OFF
Statement (DFT_MON_STMT) = ON
Table (DFT_MON_TABLE) = ON
Timestamp (DFT_MON_TIMESTAMP) = ON
Unit of work (DFT_MON_UOW) = OFF
Monitor health of instance and databases (HEALTH_MON) = ON
Configuración
Host
Para configurar este check para un Agent que se ejecuta en un host, haz lo siguiente:
Recopilación de métricas
Edita el archivo
ibm_db2.d/conf.yaml, que se encuentra en la carpetaconf.d/en la raíz del directorio de configuración del Agent, para empezar a recopilar los datos de rendimiento deibm_db2. Consulta el archivo de ejemplo ibm_db2.d/conf.yaml para conocer todas las opciones de configuración disponibles.
Recopilación de logs
Disponible para las versiones del Agent a partir de la 6.0
La recopilación de logs se encuentra deshabilitada de manera predeterminada en el Datadog Agent; habilítala en el archivo
datadog.yaml:logs_enabled: trueAñade este bloque de configuración a tu archivo
ibm_db2.d/conf.yamlpara empezar a recopilar logs de IBM Db2:logs: - type: file path: /home/db2inst1/sqllib/db2dump/db2diag.log source: ibm_db2 service: db2sysc log_processing_rules: - type: multi_line name: new_log_start_with_date pattern: \d{4}\-(0?[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01])\-(0?[1-9]|1[012])
Contenedores
En el caso de los entornos en contenedores, consulta las Plantillas de integración de Autodiscovery para obtener orientación sobre la aplicación de los parámetros que se indican abajo.
Recopilación de métricas
| Parámetro | Valor |
|---|---|
<INTEGRATION_NAME> | ibm_db2 |
<INIT_CONFIG> | en blanco o {} |
<INSTANCE_CONFIG> | {"db": "<DB_NAME>", "username":"<USERNAME>", "password":"<PASSWORD>", "host":"%%host%%", "port":"%%port%%"} |
Recopilación de logs
Disponible para las versiones del Agent a partir de la 6.0
La recopilación de logs se encuentra deshabilitada de manera predeterminada en el Datadog Agent. Para habilitarla, consulta Recopilación de logs de Kubernetes.
| Parámetro | Valor |
|---|---|
<LOG_CONFIG> | `{“source”: “ibm_db2”, “service”: “<SERVICE_NAME>”, “log_processing_rules”: {“type”:“multi_line”,“name”:“new_log_start_with_date”, “pattern”:"\d{4}-(0?[1-9] |
Validación
Ejecuta el subcomando de estado del Agent y busca ibm_db2 en la sección Checks.
Datos recopilados
Métricas
| ibm_db2.application.active (gauge) | The number of applications that are currently connected to the database. Shown as connection |
| ibm_db2.application.executing (gauge) | The number of applications for which the database manager is currently processing a request. Shown as connection |
| ibm_db2.backup.latest (gauge) | The time elapsed since the latest database backup was completed. Shown as second |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.column.hit_percent (gauge) | The percentage of time that the database manager did not need to load a page from disk to service a column-organized table data page request. Shown as percent |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.column.reads.logical (count) | The number of column-organized table data pages read from the logical table space containers for temporary, regular, and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.column.reads.physical (count) | The number of column-organized table data pages read from the physical table space containers for temporary, regular, and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.column.reads.total (count) | The total number of column-organized table data pages read from the table space containers for temporary, regular, and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.data.hit_percent (gauge) | The percentage of time that the database manager did not need to load a page from disk to service a data page request. Shown as percent |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.data.reads.logical (count) | The number of data pages read from the logical table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.data.reads.physical (count) | The number of data pages read from the physical table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.data.reads.total (count) | The total number of data pages read from the table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.group.column.hit_percent (gauge) | The percentage of time that the group database manager did not need to load a page from disk to service a column-organized table data page request. Shown as percent |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.group.data.hit_percent (gauge) | The percentage of time that the group database manager did not need to load a page from disk to service a data page request. Shown as percent |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.group.hit_percent (gauge) | The percentage of time that the group database manager did not need to load a page from disk to service a page request. Shown as percent |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.group.index.hit_percent (gauge) | The percentage of time that the group database manager did not need to load a page from disk to service an index page request. Shown as percent |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.group.xda.hit_percent (gauge) | The percentage of time that the group database manager did not need to load a page from disk to service an index page request. Shown as percent |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.hit_percent (gauge) | The percentage of time that the database manager did not need to load a page from disk to service a page request. Shown as percent |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.index.hit_percent (gauge) | The percentage of time that the database manager did not need to load a page from disk to service an index page request. Shown as percent |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.index.reads.logical (count) | The number of index pages read from the logical table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.index.reads.physical (count) | The number of index pages read from the physical table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.index.reads.total (count) | The total number of index pages read from the table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.reads.logical (count) | The number of pages read from the logical table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.reads.physical (count) | The number of pages read from the physical table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.reads.total (count) | The total number of pages read from the table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.xda.hit_percent (gauge) | The percentage of time that the database manager did not need to load a page from disk to service an index page request. Shown as percent |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.xda.reads.logical (count) | The number of data pages for XML storage objects (XDAs) read from the logical table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.xda.reads.physical (count) | The number of data pages for XML storage objects (XDAs) read from the physical table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.bufferpool.xda.reads.total (count) | The total number of data pages for XML storage objects (XDAs) read from the table space containers for temporary, regular and large table spaces. Shown as get |
| ibm_db2.connection.active (gauge) | The current number of connections. Shown as connection |
| ibm_db2.connection.max (gauge) | The highest number of simultaneous connections to the database since the database was activated. Shown as connection |
| ibm_db2.connection.total (count) | The total number of connections to the database since the first connect, activate, or last reset (coordinator agents). Shown as connection |
| ibm_db2.lock.active (gauge) | The number of locks currently held. Shown as lock |
| ibm_db2.lock.dead (count) | The total number of deadlocks that have occurred. Shown as lock |
| ibm_db2.lock.pages (gauge) | The memory pages (4 KiB each) currently in use by the lock list. Shown as page |
| ibm_db2.lock.timeouts (count) | The number of times that a request to lock an object timed out instead of being granted. Shown as lock |
| ibm_db2.lock.wait (gauge) | The average wait time for a lock. Shown as millisecond |
| ibm_db2.lock.waiting (gauge) | The number of agents waiting on a lock. Shown as lock |
| ibm_db2.log.available (gauge) | The disk blocks (4 KiB each) of active log space in the database that is not being used by uncommitted transactions. Shown as block |
| ibm_db2.log.reads (count) | The number of log pages read from disk by the logger. Shown as read |
| ibm_db2.log.used (gauge) | The disk blocks (4 KiB each) of active log space currently used in the database. Shown as block |
| ibm_db2.log.utilized (gauge) | The utilization of active log space as a percentage. Shown as percent |
| ibm_db2.log.writes (count) | The number of log pages written to disk by the logger. Shown as write |
| ibm_db2.row.modified.total (count) | The total number of rows inserted, updated, or deleted. Shown as row |
| ibm_db2.row.reads.total (count) | The total number of rows that had to be read in order to return result sets. Shown as row |
| ibm_db2.row.returned.total (count) | The total number of rows that have been selected by and returned to applications. Shown as row |
| ibm_db2.tablespace.size (gauge) | The total size of the table space in bytes. Shown as byte |
| ibm_db2.tablespace.usable (gauge) | The total usable size of the table space in bytes. Shown as byte |
| ibm_db2.tablespace.used (gauge) | The total used size of the table space in bytes. Shown as byte |
| ibm_db2.tablespace.utilized (gauge) | The utilization of the table space as a percentage. Shown as percent |
Eventos
ibm_db2.tablespace_state_changese activa cada vez que cambia el estado de un espacio de tablas.
Checks de servicio
ibm_db2.can_connect
Returns CRITICAL if the Agent is unable to connect to the monitored IBM Db2 database, or OK otherwise.
Statuses: ok, critical
ibm_db2.status
Returns CRITICAL if the monitored IBM Db2 database is quiesced, WARNING for quiesce-pending or rollforwards, or OK otherwise.
Statuses: ok, warning, critical, unknown
Solucionar problemas
Error del controlador de la CLI SQL1531N
Es posible que te encuentres con un problema que produce un logs con errores como el siguiente:
2023-08-10 23:34:47 UTC | CORE | ERROR | (pkg/collector/python/datadog_agent.go:129 in LogMessage) | ibm_db2:c051131490335a94 | (ibm_db2.py:563) | Unable to connect to database `datadog` as user `db2inst1`: [IBM][CLI Driver] SQL1531N The connection failed because the name specified with the DSN connection string keyword could not be found in either the db2dsdriver.cfg configuration file or the db2cli.ini configuration file. Data source name specified in the connection string: "DATADOG". SQLCODE=-1531
En ese caso, lo más probable es que se deba a una de las siguientes situaciones:
- Falta un host y un puerto en la configuración (conf.yaml).
- El controlador de la CLI no es capaz de localizar la base de datos debido a la ausencia de
db2cli.iniydb2dsdriver.cfg.
El Agent necesita la información de los dos escenarios anteriores para determinar dónde conectarse correctamente a la base de datos. Para resolver este problema, puedes incluir un parámetro de host y puerto para cada instancia del check de ibm_db2 que tenga este problema. De manera alternativa, si quieres utilizar los DSN definidos en los archivos db2cli.ini o db2dsdriver.cfg, puedes copiar dichos archivos en el directorio clidriver que utiliza el Agent. En circunstancias normales, ese directorio se encuentra en /opt/datadog-agent/embedded/lib/python3.9/site-packages/clidriver/cfg para Linux.
Instalación de la biblioteca de cliente ibm_db sin conexión
Si trabajas en un entorno sin conexión o con una red restringida donde no es posible ejecutar pip install ibm_db==x.y.z con x.y.z como el número de versión, puedes instalar ibm_db mediante el siguiente método:
En una máquina con acceso a una red, descarga los archivos .tar de origen de la biblioteca
ibm_dby la ODBC y la CLI. La ODBC y la CLI deben descargarse por separado porque la bibliotecaibm_dblos necesita, pero no pueden descargarse a través delpip. El siguiente script instala el archivo de almacenamiento paraibm_db==x.y.zen una máquina Linux, dondex.y.zes el número de versión:curl -Lo ibm_db.tar.gz https://github.com/ibmdb/python-ibmdb/archive/refs/tags/vx.y.z.tar.gz curl -Lo linuxx64_odbc_cli.tar.gz https://public.dhe.ibm.com/ibmdl/export/pub/software/data/db2/drivers/odbc_cli/linuxx64_odbc_cli.tar.gzMueve los dos archivos al host restringido y, luego, extrae el archivo.
tar -xvf ibm_db.tar.gz tar -xvf linuxx64_odbc_cli.tar.gzDefine la variable de entorno
IBM_DB_HOMEcomo la localización de donde extrajiste/clidriverdelinuxx64_odbc_cli.tar.gz. Esto evitará que la bibliotecaibm_dbinstale una nueva versión de la ODBC y la CLI, ya que eso generaría un error.export IBM_DB_HOME=/path/to/clidriverCon el
pipintegrado en el Agent, instala la bibliotecaibm_dbde manera local. Los archivos de esta biblioteca se encuentran dentro delpython-ibmdb-x.y.zextraído deibm_db.tar.gz./opt/datadog-agent/embedded/bin/pip install --no-index --no-deps --no-build-isolation /path/to/python-ibmdb-x.y.z/IBM_DB/ibm_db/
Si obtienes el siguiente error:
error: subprocess-exited-with-error
× Preparing metadata (pyproject.toml) did not run successfully.
| exit code: 1
-> [8 lines of output]
Detected 64-bit Python
Detected platform = linux, uname = x86_64
Downloading https://public.dhe.ibm.com/ibmdl/export/pub/software/data/db2/drivers/odbc_cli/linuxx64_odbc_cli.tar.gz
Downloading DSDriver from url = https://public.dhe.ibm.com/ibmdl/export/pub/software/data/db2/drivers/odbc_cli/linuxx64_odbc_cli.tar.gz
Pre-requisite check [which gcc] : Failed
No Gcc installation detected.
Please install gcc and continue with the installation of the ibm_db.
[end of output]
Es posible que debas instalar gcc.
¿Necesitas ayuda? Ponte en contacto con el equipo de asistencia de Datadog.
Referencias adicionales
Más enlaces, artículos y documentación útiles:
