- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Integrations
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- APM Tracing
- Profiler
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic Monitoring
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Test Impact Analysis
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- API
- Datadog Mobile App
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Infrastructure
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Product Analytics
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Optimization
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
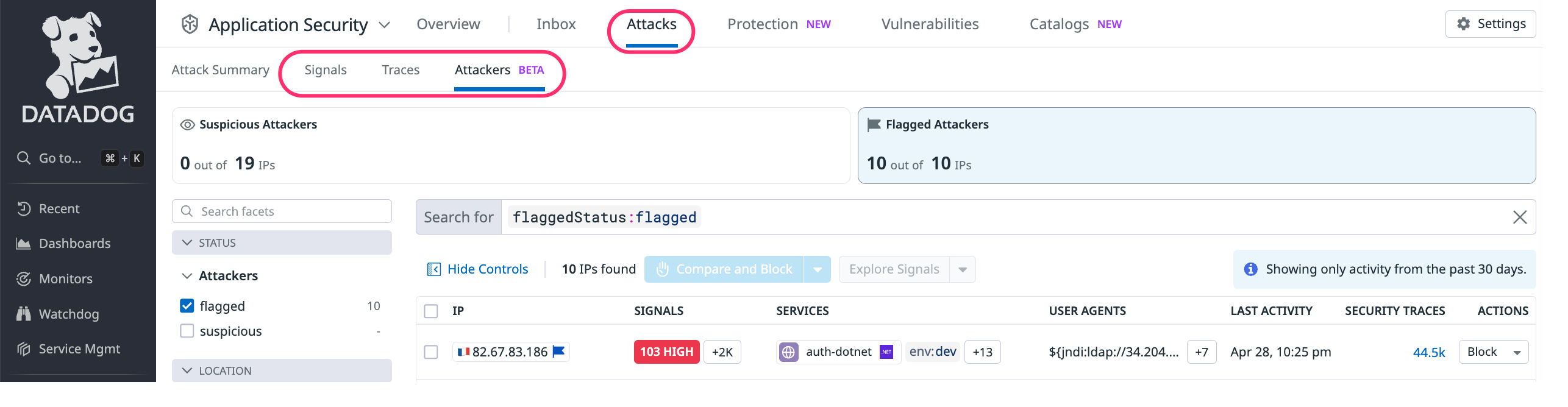
Attacker Explorer
This topic describes how to use Attacker Explorer to investigate and block Flagged Attackers.
Overview
Datadog Application Security Management (ASM) identifies attackers as suspicious and flagged. With Attacker Explorer, you can investigate and take action against the attackers.
Definitions
Suspicious Attackers: IP addresses that have sent attack traffic in the last 24 hours up to a maximum threshold.
Flagged Attackers: IP addresses that have sent attack traffic, exceeding the threshold of Suspicious Attackers, in the last 24 hours. Flagged Attackers should be reviewed and blocked.
Flagged Attackers and Suspicious Attackers are mutually exclusive. An IP cannot be in both states at the same time.
How Attacker Explorer differs from Signal and Trace explorers
To understand the difference between the different explorers, review these approaches:
- Protect: Automated blocking using ASM Protection configuration. Customers should block attack tools as their first automated blocking action. Blocking attack tools reduces common vulnerability discovery for OWASP threats such as SQLi, command injection, and SSRF.
- Reactive: Blocking using Signals or Attackers explorer in response to observed threats.
Each explorer focuses on a specific use case:
- Signal Explorer: List of actionable alerts such as Credential Stuffing Attack or Command Injection. Signals have workflow capabilities, a description, severity, and correlated Traces. Interactions include user assignment workflows, automated protection, analytics, search, and pivoting to Trace Explorer.
- Trace Explorer: List of evidence for business logic events, such as logins, or attack payloads. Interactions include analytics and search.
- Attacker Explorer: List of Flagged and Suspicious Attackers. Interactions include:
- Bulk actions for attacker analytics and blocking
- Drill-down into the history of any attacker
- Search
- Pivoting to other explorers
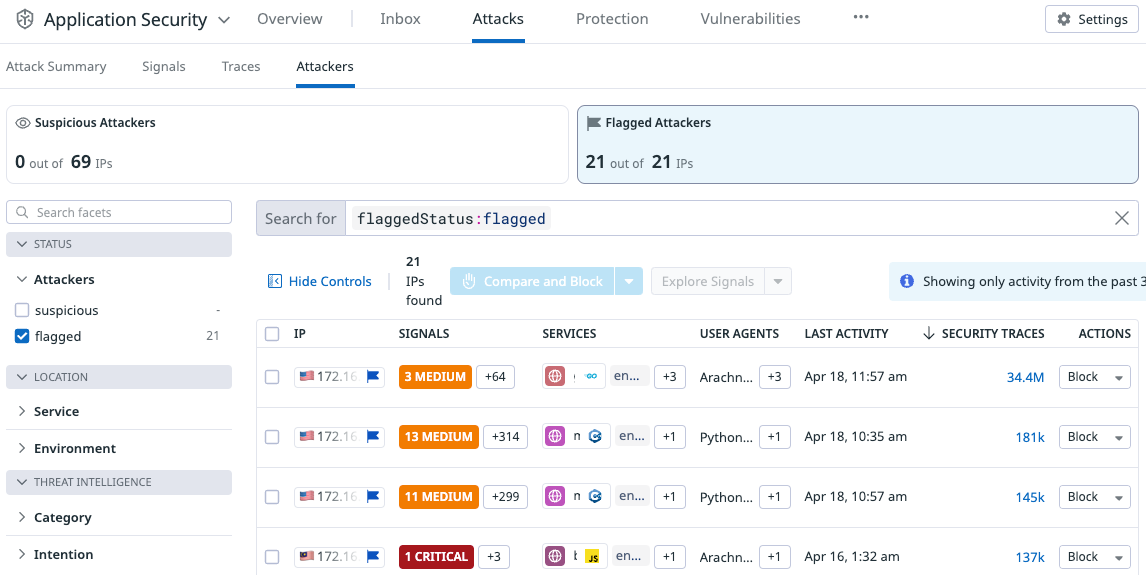
Explore and filter attackers
To start reviewing attackers, go to Attacker Explorer.
There are two sections to the Attacker Explorer:
- Facets and search. These enable you to filter traffic by service or attacker attributes.
- The list of attackers with security metrics.
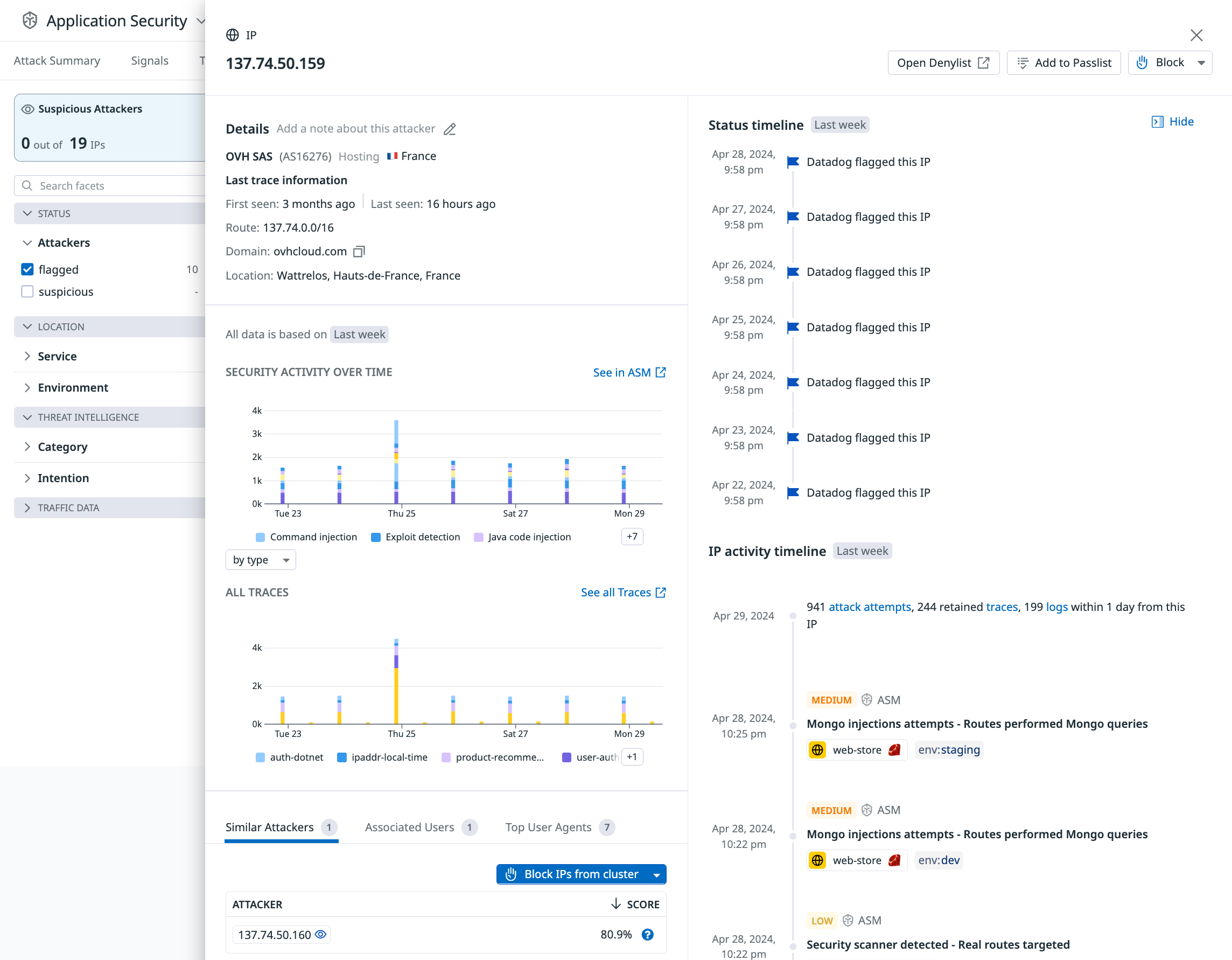
Investigate an IP
Click on any row to view the history and attributes of the IP.
IPs can be blocked or added to the Passlist from the IP drawer.
Best practices for blocking with Attacker Explorer
- Account takeover attacks: Use short durations for blocking IP addresses.
- Add authorized scanners to monitored passlists to observe activity but prevent blocking.
- Block mobile ISPs with caution. These networks might have large numbers of users and mobile devices behind single IP addresses.
Block individual IPs
To block an individual IP temporarily or permanently, do the following:
- Click
Blockon the row. - Choose a blocking duration.
Block IPs in bulk
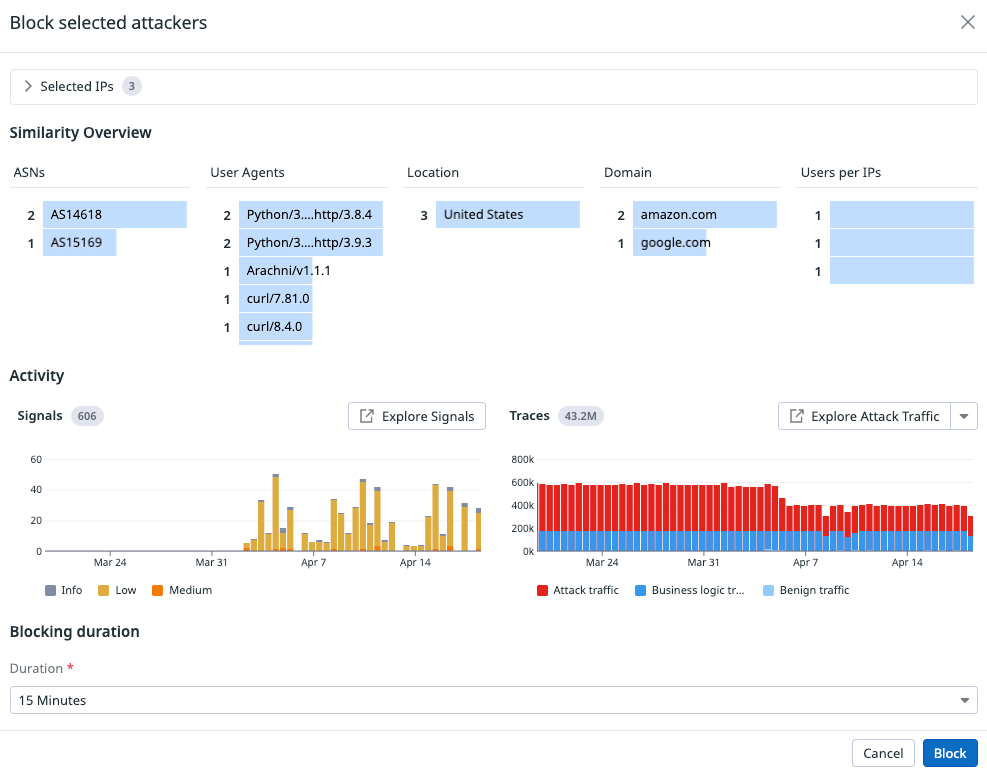
You can select multiple IPs and block them temporarily or permanently using the Attacker Explorer’s Compare and Block option.
Compare and Block provides metrics about the IPs to help you block with safety and confidence. For example, Similarity Overview and Activity, described later in this topic.
To compare and block IPs in bulk, do the following:
Filter the list of Attackers with a search or facets.
Select multiple IPs.
Select the Compare and Block option.
In the following example, the selected IPs are from the same location and appear to be related. The Compare and Block option opens the Block selected attackers view, showing metrics and attributes for the selected IP addresses.
To block attackers, click Block.
Block selected attackers metrics
When you select the Compare and Block option, the Block selected attackers view opens, showing metrics and attributes for the selected IP addresses.
Metrics for Similarity Overview and Activity are scoped to the last 30 days.
The Block selected attackers view metrics are explained in the following sections.
Selected IPs
Contains the IPs selected from the explorer. Deselecting an IP removes it from the metrics sections and Block action.
Similarity overview
Each column exists to help block with confidence and safety. The provided attributes are also used by ASM’s Attacker Similarity feature.
- ASNs
- Autonomous System Numbers. Attacks with large numbers of IP addresses might originate from the same ASN, especially when attacks originate from data centers and cloud IPs.
- User Agents
- Attackers, commercial scanners, and your own software might use predictable user agents that can help qualify what should be included or excluded from blocking.
- Location
- Companies might have policies or serviceable markets that determine what countries they allow traffic from.
- Domain
- The owner of the ASN. This is helpful when an organization owns multiple ASNs.
- Users per IPs
- The number of users who have authenticated from the IP. IPs with large numbers of logins might indicate a load balancer or many users from the same location, like a company site.
Activity
The time scope for activity is 30 days.
Signals
The signals associated with the IP addresses over the selected time.
Traces
The traces associated with the IP addresses over the selected time.
Benign traffic is sampled APM traffic which are traces without business logic or attack traffic detections.
Attack traffic is all ASM traces, inclusive of business logic.
Block
This adds the IP addresses to the Denylist for the specified duration.