- 重要な情報
- はじめに
- Datadog
- Datadog サイト
- DevSecOps
- AWS Lambda のサーバーレス
- エージェント
- インテグレーション
- コンテナ
- ダッシュボード
- アラート設定
- ログ管理
- トレーシング
- プロファイラー
- タグ
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic モニタリング
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- 用語集
- Standard Attributes
- ガイド
- インテグレーション
- エージェント
- OpenTelemetry
- 開発者
- 認可
- DogStatsD
- カスタムチェック
- インテグレーション
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- サービスのチェック
- IDE インテグレーション
- コミュニティ
- ガイド
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- モバイルアプリケーション
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- アプリ内
- Service Management
- インフラストラクチャー
- アプリケーションパフォーマンス
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- データベース モニタリング
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility (CI/CDの可視化)
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- セキュリティ
- セキュリティの概要
- Cloud SIEM
- クラウド セキュリティ マネジメント
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- ログ管理
- Observability Pipelines(観測データの制御)
- ログ管理
- 管理
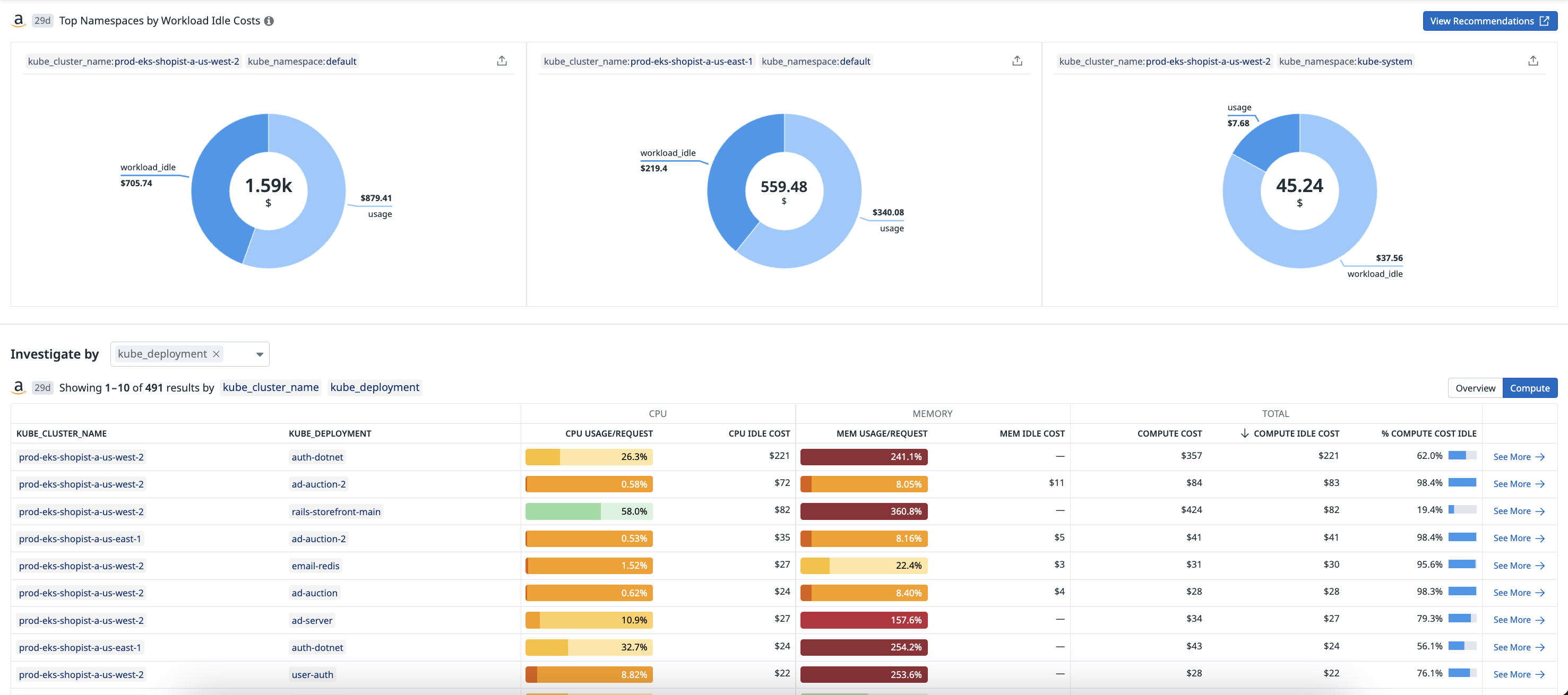
コンテナのコストの割り当て
選択した Datadog サイト (US1) では Cloud Cost Management はサポートされていません。
概要
Datadog Cloud Cost Management (CCM) automatically allocates the costs of your cloud clusters to individual services and workloads running in those clusters. Use cost metrics enriched with tags from pods, nodes, containers, and tasks to visualize container workload cost in the context of your entire cloud bill.
- Clouds
- CCM allocates costs of your AWS, Azure, or Google host instances. A host is a computer (such as an EC2 instance in AWS, a virtual machine in Azure, or a Compute Engine instance in Google Cloud) that is listed in your cloud provider’s cost and usage report and may be running Kubernetes pods.
- Resources
- CCM allocates costs for Kubernetes clusters and includes cost analysis for many associated resources such as Kubernetes persistent volumes used by your pods.
CCM displays costs for resources including CPU, memory, and more depending on the cloud and orchestrator you are using on the Containers page.
前提条件
CCM allocates costs of AWS ECS clusters as well as all Kubernetes clusters, including those managed through Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS).
The following table presents the list of collected features and the minimal Agent and Cluster Agent versions for each.
| 機能 | 最低限必要な Agent のバージョン | 最低限必要な Cluster Agent のバージョン |
|---|---|---|
| コンテナコスト割当 | 7.27.0 | 1.11.0 |
| AWS Persistent Volume Allocation | 7.46.0 | 1.11.0 |
- Configure the AWS Cloud Cost Management integration on the Cloud Costs Setup page.
- For Kubernetes support, install the Datadog Agent in a Kubernetes environment and ensure that you enable the Orchestrator Explorer in your Agent configuration.
- For AWS ECS support, set up Datadog Container Monitoring in ECS tasks.
- Optionally, enable AWS Split Cost Allocation for usage-based ECS allocation.
CCM allocates costs of all Kubernetes clusters, including those managed through Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
The following table presents the list of collected features and the minimal Agent and Cluster Agent versions for each.
| 機能 | 最低限必要な Agent のバージョン | 最低限必要な Cluster Agent のバージョン |
|---|---|---|
| コンテナコスト割当 | 7.27.0 | 1.11.0 |
- Configure the Azure Cost Management integration on the Cloud Costs Setup page.
- Install the Datadog Agent in a Kubernetes environment and ensure that you enable the Orchestrator Explorer in your Agent configuration.
CCM allocates costs of all Kubernetes clusters, including those managed through Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
The following table presents the list of collected features and the minimal Agent and Cluster Agent versions for each.
| 機能 | 最低限必要な Agent のバージョン | 最低限必要な Cluster Agent のバージョン |
|---|---|---|
| コンテナコスト割当 | 7.27.0 | 1.11.0 |
- Configure the Google Cloud Cost Management integration on the Cloud Costs Setup page.
- Install the Datadog Agent in a Kubernetes environment and ensure that you enable the Orchestrator Explorer in your Agent configuration.
コストの割り当て
Cost allocation divides host compute and other resource costs from your cloud provider into individual tasks or pods associated with them. These divided costs are then enriched with tags from related resources so you can break down costs by any associated dimensions.
Use the allocated_resource tag to visualize the spend resource associated with your costs at various levels, including the Kubernetes node, container orchestration host, storage volume, or entire cluster level.
These divided costs are enriched with tags from nodes, pods, tasks, and volumes. You can use these tags to break down costs by any associated dimensions.
Compute
For Kubernetes compute allocation, a Kubernetes node is joined with its associated host instance costs. The node’s cluster name and all node tags are added to the entire compute cost for the node. This allows you to associate cluster-level dimensions with the cost of the instance, without considering the pods scheduled to the node.
次に、Datadog はその日に該当ノード上で動作していたすべてのポッドを調査します。ノードのコストは、ポッドが使用したリソースとその実行時間に基づいて割り当てられます。この算出されたコストは、ポッドのすべてのタグを含めて詳細化されます。
Note: Only tags from pods and nodes are added to cost metrics. To include labels, enable labels as tags for nodes and pods.
All other costs are given the same value and tags as the source metric aws.cost.amortized.
Persistent volume storage
For Kubernetes Persistent Volume storage allocation, Persistent Volumes (PV), Persistent Volume Claims (PVC), nodes, and pods are joined with their associated EBS volume costs. All associated PV, PVC, node, and pod tags are added to the EBS volume cost line items.
Next, Datadog looks at all of the pods that claimed the volume on that day. The cost of the volume is allocated to a pod based on the resources it used and the length of time it ran. These resources include the provisioned capacity for storage, IOPS, and throughput. This allocated cost is enriched with all of the pod’s tags.
AWS ECS on EC2
ECS の割り当てにおいて、Datadog は ECS に使用された各 EC2 インスタンスでどのタスクが実行されたかを判定します。AWS Split Cost Allocation を有効にすると、メトリクスは予約ではなく使用量に基づいて ECS コストを割り当てるため、より細かい詳細が得られます。
タスクが使用したリソースに基づいて、Datadog はインスタンスのコンピュートコストの適切な部分をそのタスクに割り当てます。算出されたコストは、タスクのすべてのタグおよびタスク内で動作しているコンテナの全てのタグ (コンテナ名を除く) によって詳細化されます。
AWS ECS on Fargate
ECS tasks that run on Fargate are already fully allocated in the CUR. CCM enriches that data by adding out-of-the-box tags and container tags to the AWS Fargate cost.
Compute
For Kubernetes compute allocation, a Kubernetes node is joined with its associated host instance costs. The node’s cluster name and all node tags are added to the entire compute cost for the node. This allows you to associate cluster-level dimensions with the cost of the instance, without considering the pods scheduled to the node.
次に、Datadog はその日に該当ノード上で動作していたすべてのポッドを調査します。ノードのコストは、ポッドが使用したリソースとその実行時間に基づいて割り当てられます。この算出されたコストは、ポッドのすべてのタグを含めて詳細化されます。
Note: Only tags from pods and nodes are added to cost metrics. To include labels, enable labels as tags for nodes and pods.
All other costs are given the same value and tags as the source metric azure.cost.amortized.
Compute
For Kubernetes compute allocation, a Kubernetes node is joined with its associated host instance costs. The node’s cluster name and all node tags are added to the entire compute cost for the node. This allows you to associate cluster-level dimensions with the cost of the instance, without considering the pods scheduled to the node.
次に、Datadog はその日に該当ノード上で動作していたすべてのポッドを調査します。ノードのコストは、ポッドが使用したリソースとその実行時間に基づいて割り当てられます。この算出されたコストは、ポッドのすべてのタグを含めて詳細化されます。
Note: Only tags from pods and nodes are added to cost metrics. To include labels, enable labels as tags for nodes and pods.
All other costs are given the same value and tags as the source metric gcp.cost.amortized.
Agentless Kubernetes costs
To view the costs of GKE clusters without enabling Datadog Infrastructure Monitoring, use GKE cost allocation. Enable GKE cost allocation on unmonitored GKE clusters to access this feature set.
Limitations and differences from the Datadog Agent
- There is no support for tracking workload idle costs.
- The cost of individual pods are not tracked, only the aggregated cost of a workload and the namespace. There is no
pod_nametag. - GKE enriches data using pod labels only and ignores any Datadog tags you add.
- The full list of limitations can be found in the official GKE documentation.
To enable GKE cost allocation, see the official GKE documentation.
支出の把握
Use the allocated_spend_type tag to visualize the spend category associated with your costs at various levels, including the Kubernetes node, container orchestration host, storage volume, or entire cluster level.
Compute
The cost of a host instance is split into two components: 60% for the CPU and 40% for the memory. Each component is allocated to individual workloads based on their resource reservations and usage.
Costs are allocated into the following spend types:
| Spend type | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 使用方法 | Cost of resources (such as memory and CPU) used by workloads, based on the average usage on that day. |
| Workload idle | Cost of resources (such as memory and CPU) that are reserved and allocated but not used by workloads. This is the difference between the total resources requested and the average usage. |
| Cluster idle | Cost of resources (such as memory and CPU) that are not reserved by workloads in a cluster. This is the difference between the total cost of the resources and what is allocated to workloads. |
Persistent volume
The cost of an AWS EBS volume has three components: IOPS, throughput, and storage. Each is allocated according to a pod’s usage when the volume is mounted.
| Spend type | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 使用方法 | Cost of provisioned IOPS, throughput, or storage used by workloads. Storage cost is based on the maximum amount of volume storage used that day, while IOPS and throughput costs are based on the average amount of volume storage used that day. |
| Workload idle | Cost of provisioned IOPS, throughput, or storage that are reserved and allocated but not used by workloads. Storage cost is based on the maximum amount of volume storage used that day, while IOPS and throughput costs are based on the average amount of volume storage used that day. This is the difference between the total resources requested and the average usage. Note: This tag is only available if you have enabled Resource Collection in your AWS Integration. To prevent being charged for Cloud Security Posture Management, ensure that during the Resource Collection setup, the Cloud Security Posture Management box is unchecked. |
| Cluster idle | Cost of provisioned IOPS, throughput, or storage that are not reserved by any pods that day. This is the difference between the total cost of the resources and what is allocated to workloads. |
Note: Persistent volume allocation is only supported in Kubernetes clusters, and is only available for pods that are part of a Kubernetes StatefulSet.
Compute
The cost of a host instance is split into two components: 60% for the CPU and 40% for the memory. Each component is allocated to individual workloads based on their resource reservations and usage.
Costs are allocated into the following spend types:
| Spend type | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 使用方法 | Cost of resources (such as memory and CPU) used by workloads, based on the average usage on that day. |
| Workload idle | Cost of resources (such as memory and CPU) that are reserved and allocated but not used by workloads. This is the difference between the total resources requested and the average usage. |
| Cluster idle | Cost of resources (such as memory and CPU) that are not reserved by workloads in a cluster. This is the difference between the total cost of the resources and what is allocated to workloads. |
Compute
The cost of a host instance is split into two components: 60% for the CPU and 40% for the memory. Each component is allocated to individual workloads based on their resource reservations and usage.
Costs are allocated into the following spend types:
| Spend type | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 使用方法 | Cost of resources (such as memory and CPU) used by workloads, based on the average usage on that day. |
| Workload idle | Cost of resources (such as memory and CPU) that are reserved and allocated but not used by workloads. This is the difference between the total resources requested and the average usage. |
| Cluster idle | Cost of resources (such as memory and CPU) that are not reserved by workloads in a cluster. This is the difference between the total cost of the resources and what is allocated to workloads. |
| Not monitored | Cost of resources where the spend type is unknown. To resolve this, install the Datadog Agent on these clusters or nodes. |
Understanding resources
Depending on the cloud provider, certain resources may or may not be available for cost allocation.
| Resource | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | |||
| メモリ | |||
| |||
| |||
| ECS costs | N/A | N/A | |
| Networking costs | Limited* | Limited* | |
| GPU | Limited* | ||
| Limited* | Limited* |
Limited* resources have been identified as part of your Kubernetes spend, but are not fully allocated to specific workloads or pods. These resources are host-level costs, not pod or namespace-level costs, and are identified with allocated_spend_type:<resource>_not_supported.
コストメトリクス
When the prerequisites are met, the following cost metrics automatically appear.
| Cost Metric | 説明 |
|---|---|
aws.cost.amortized.shared.resources.allocated | EC2 costs allocated by the CPU & memory used by a pod or ECS task, using a 60:40 split for CPU & memory respectively. Also includes allocated EBS costs. Based on aws.cost.amortized |
aws.cost.net.amortized.shared.resources.allocated | Net EC2 costs allocated by CPU & memory used by a pod or ECS task, using a 60:40 split for CPU & memory respectively. Also includes allocated AWS EBS costs. Based on aws.cost.net.amortized, if available |
| Cost Metric | 説明 |
|---|---|
azure.cost.amortized.shared.resources.allocated | Azure VM costs allocated by the CPU & memory used by a pod or container task, using a 60:40 split for CPU & memory respectively. Also includes allocated Azure costs. Based on azure.cost.amortized |
| Cost Metric | 説明 |
|---|---|
gcp.cost.amortized.shared.resources.allocated | Google Compute Engine costs allocated by the CPU & memory used by a pod, using 60:40 split for CPU & memory respectively. This allocation method is used when the bill does not already provide a specific split between CPU and memory usage. Based on gcp.cost.amortized |
These cost metrics include all of your cloud costs. This allows you to continue visualizing all of your cloud costs at one time.
For example, say you have the tag team on a storage bucket, a cloud provider managed database, and Kubernetes pods. You can use these metrics to group costs by team, which includes the costs for all three.
Applying tags
Datadog consolidates and applies the following tags from various sources to cost metrics.
Kubernetes
In addition to Kubernetes pod and Kubernetes node tags, the following non-exhaustive list of out-of-the-box tags are applied to cost metrics:
| すぐに使えるタグ | 説明 |
|---|---|
orchestrator:kubernetes | The orchestration platform associated with the item is Kubernetes. |
kube_cluster_name | Kubernetes クラスターの名前。 |
kube_namespace | The namespace where workloads are running. |
kube_deployment | The name of the Kubernetes Deployment. |
kube_stateful_set | The name of the Kubernetes StatefulSet. |
pod_name | The name of any individual pod. |
Conflicts are resolved by favoring higher-specificity tags such as pod tags over lower-specificity tags such as host tags. For example, a Kubernetes pod tagged service:datadog-agent running on a node tagged service:aws-node results in a final tag service:datadog-agent.
Persistent volume
In addition to Kubernetes pod and Kubernetes node tags, the following out-of-the-box tags are applied to cost metrics.
| すぐに使えるタグ | 説明 |
|---|---|
persistent_volume_reclaim_policy | The Kubernetes Reclaim Policy on the Persistent Volume. |
storage_class_name | The Kubernetes Storage Class used to instantiate the Persistent Volume. |
volume_mode | The Volume Mode of the Persistent Volume. |
ebs_volume_type | The type of the AWS EBS volume. Can be gp3, gp2, or others. |
Amazon ECS
In addition to ECS task tags, the following out-of-the-box tags are applied to cost metrics.
Note: Most tags from ECS containers are applied (excluding container_name).
| すぐに使えるタグ | 説明 |
|---|---|
orchestrator:ecs | The orchestration platform associated with the item is AWS ECS. |
ecs_cluster_name | ECS クラスターの名前。 |
is_aws_ecs | ECS の実行に関連するすべてのコスト。 |
is_aws_ecs_on_ec2 | EC2 上の ECS の実行に関連するすべての EC2 コンピュートコスト。 |
is_aws_ecs_on_fargate | Fargate 上の ECS の実行に関連するすべてのコスト。 |
Kubernetes
In addition to Kubernetes pod and Kubernetes node tags, the following non-exhaustive list of out-of-the-box tags are applied to cost metrics:
| すぐに使えるタグ | 説明 |
|---|---|
orchestrator:kubernetes | The orchestration platform associated with the item is Kubernetes. |
kube_cluster_name | Kubernetes クラスターの名前。 |
kube_namespace | The namespace where workloads are running. |
kube_deployment | The name of the Kubernetes Deployment. |
kube_stateful_set | The name of the Kubernetes StatefulSet. |
pod_name | The name of any individual pod. |
allocated_resource:data_transfer | The tracking and allocation of costs associated with data transfer activities used by Azure services or workloads. |
allocated_resource:local_storage | The tracking and allocation of costs at a host level associated with local storage resources used by Azure services or workloads. |
Kubernetes
In addition to Kubernetes pod and Kubernetes node tags, the following non-exhaustive list of out-of-the-box tags are applied to cost metrics:
| すぐに使えるタグ | 説明 |
|---|---|
orchestrator:kubernetes | The orchestration platform associated with the item is Kubernetes. |
kube_cluster_name | Kubernetes クラスターの名前。 |
kube_namespace | The namespace where workloads are running. |
kube_deployment | The name of the Kubernetes Deployment. |
kube_stateful_set | The name of the Kubernetes StatefulSet. |
pod_name | The name of any individual pod. |
allocated_spend_type:not_monitored | The tracking and allocation of Agentless Kubernetes costs associated with resources used by Google Cloud services or workloads, and the Datadog Agent is not monitoring those resources. |
allocated_resource:data_transfer | The tracking and allocation of costs associated with data transfer activities used by Google Cloud services or workloads. |
allocated_resource:gpu | The tracking and allocation of costs at a host level associated with GPU resources used by Google Cloud services or workloads. |
allocated_resource:local_storage | The tracking and allocation of costs at a host level associated with local storage resources used by Google Cloud services or workloads. |
参考資料
お役に立つドキュメント、リンクや記事: