- Esenciales
- Empezando
- Datadog
- Sitio web de Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless para Lambda AWS
- Agent
- Integraciones
- Contenedores
- Dashboards
- Monitores
- Logs
- Rastreo de APM
- Generador de perfiles
- Etiquetas (tags)
- API
- Catálogo de servicios
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Monitorización Synthetic
- Gestión de incidencias
- Monitorización de bases de datos
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Análisis de código
- Centro de aprendizaje
- Compatibilidad
- Glosario
- Atributos estándar
- Guías
- Agent
- Uso básico del Agent
- Arquitectura
- IoT
- Plataformas compatibles
- Recopilación de logs
- Configuración
- Configuración remota
- Automatización de flotas
- Actualizar el Agent
- Solucionar problemas
- Detección de nombres de host en contenedores
- Modo de depuración
- Flare del Agent
- Estado del check del Agent
- Problemas de NTP
- Problemas de permisos
- Problemas de integraciones
- Problemas del sitio
- Problemas de Autodiscovery
- Problemas de contenedores de Windows
- Configuración del tiempo de ejecución del Agent
- Consumo elevado de memoria o CPU
- Guías
- Seguridad de datos
- Integraciones
- OpenTelemetry
- Desarrolladores
- Autorización
- DogStatsD
- Checks personalizados
- Integraciones
- Crear una integración basada en el Agent
- Crear una integración API
- Crear un pipeline de logs
- Referencia de activos de integración
- Crear una oferta de mercado
- Crear un cuadro
- Crear un dashboard de integración
- Crear un monitor recomendado
- Crear una regla de detección Cloud SIEM
- OAuth para integraciones
- Instalar la herramienta de desarrollo de integraciones del Agente
- Checks de servicio
- Complementos de IDE
- Comunidad
- Guías
- API
- Aplicación móvil de Datadog
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- En la aplicación
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- Editor DDSQL
- Hojas
- Monitores y alertas
- Infraestructura
- Métricas
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Catálogo de servicios
- Catálogo de APIs
- Error Tracking
- Gestión de servicios
- Objetivos de nivel de servicio (SLOs)
- Gestión de incidentes
- De guardia
- Gestión de eventos
- Gestión de casos
- Workflow Automation
- App Builder
- Infraestructura
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Contenedores
- Serverless
- Monitorización de red
- Coste de la nube
- Rendimiento de las aplicaciones
- APM
- Términos y conceptos de APM
- Instrumentación de aplicación
- Recopilación de métricas de APM
- Configuración de pipelines de trazas
- Correlacionar trazas (traces) y otros datos de telemetría
- Trace Explorer
- Observabilidad del servicio
- Instrumentación dinámica
- Error Tracking
- Seguridad de los datos
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Gastos generales de integración del Agent
- Arquitecturas de configuración
- Configuración de Postgres
- Configuración de MySQL
- Configuración de SQL Server
- Configuración de Oracle
- Configuración de MongoDB
- Conexión de DBM y trazas
- Datos recopilados
- Explorar hosts de bases de datos
- Explorar métricas de consultas
- Explorar ejemplos de consulta
- Solucionar problemas
- Guías
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Experiencia digital
- Real User Monitoring
- Monitorización del navegador
- Configuración
- Configuración avanzada
- Datos recopilados
- Monitorización del rendimiento de páginas
- Monitorización de signos vitales de rendimiento
- Monitorización del rendimiento de recursos
- Recopilación de errores del navegador
- Rastrear las acciones de los usuarios
- Señales de frustración
- Error Tracking
- Solucionar problemas
- Monitorización de móviles y TV
- Plataforma
- Session Replay
- Exploración de datos de RUM
- Feature Flag Tracking
- Error Tracking
- Guías
- Seguridad de los datos
- Monitorización del navegador
- Análisis de productos
- Pruebas y monitorización de Synthetics
- Continuous Testing
- Entrega de software
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Configuración
- Tests en contenedores
- Búsqueda y gestión
- Explorador
- Monitores
- Flujos de trabajo de desarrolladores
- Cobertura de código
- Instrumentar tests de navegador con RUM
- Instrumentar tests de Swift con RUM
- Detección temprana de defectos
- Reintentos automáticos de tests
- Correlacionar logs y tests
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- Métricas de DORA
- Seguridad
- Información general de seguridad
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Observabilidad de la IA
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Gestión de logs
- Administración
- Gestión de cuentas
- Seguridad de los datos
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Ayuda
Amazon Elastic Load Balancing
This page is not yet available in Spanish. We are working on its translation.
If you have any questions or feedback about our current translation project, feel free to reach out to us!
If you have any questions or feedback about our current translation project, feel free to reach out to us!
Overview
Amazon Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple Amazon EC2 instances in the cloud.
Datadog collects metrics and metadata from all three flavors of Elastic Load Balancers that AWS offers: Application (ALB), Classic (ELB), and Network Load Balancers (NLB).
Enable this integration to see in Datadog all your Elastic Load Balancing metrics.
Note: This integration requires the permissions ’ec2:describe**’ and ’elasticloadbalancing:describe*’ to be fully enabled.
Setup
Installation
If you haven’t already, set up the Amazon Web Services integration first.
Metric collection
- In the AWS integration page, ensure that
ApplicationELB,ELB, andNetworkELBare enabled under theMetric Collectiontab. - Install the Datadog - Amazon ELB integration.
Log collection
Enable Amazon ELB or ALB logging
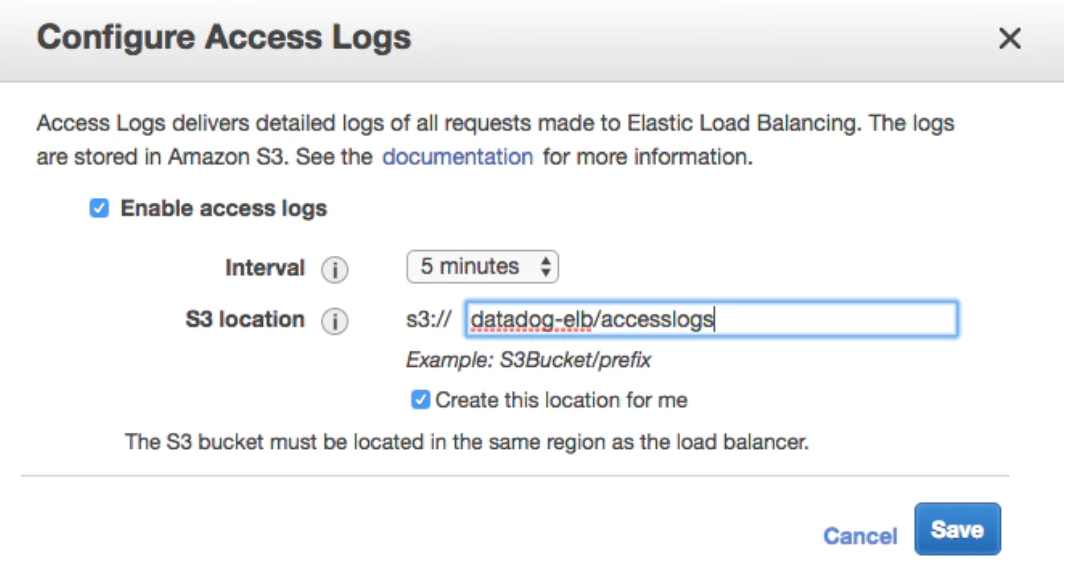
Enable the logging on your ELB or your ALB first to collect your logs. ALB and ELB logs can be written in an Amazon S3 bucket and consumed by a Lambda function. For more information, see Enable access logs for your Classic Load Balancer.
Set the interval to 5 minutes and define your S3 bucket and prefix. To avoid having an ambiguously defined S3 event notification configuration, be sure to use a unique location that does not overlap with any other load balancer’s log location. When multiple load balancers are logging to the same bucket, be sure to use a unique prefix, such as my-bucket-for-elb-logs/my-elb-name, to have their logs stored in separate locations.
Send logs to Datadog
- If you haven’t already, set up the Datadog Forwarder Lambda function in your AWS account.
- Once set up, go to the Datadog Forwarder Lambda function. Set up your triggers automatically or manually on the S3 bucket that contains your ELB logs. For the manual setup, use the event type
All object create events. - Use the Log Explorer to explore your logs.
For more information on collecting AWS Services logs, see Send AWS Services Logs with the Datadog Lambda Function.
Data Collected
Metrics
| aws.elb.active_connection_count (count) | The total number of concurrent TCP connections active from clients to the load balancer and from the load balancer to targets. Shown as connection |
| aws.elb.backend_connection_errors (rate) | Number of connections that were not successfully established between the load balancer and the registered instances. Shown as error |
| aws.elb.client_tlsnegotiation_error_count (count) | Number of TLS negotiation errors. Shown as error |
| aws.elb.consumed_lbcapacity_units (gauge) | Number of ELB capacity units consumed. Shown as unit |
| aws.elb.consumed_lcus (gauge) | The number of load balancer capacity units (LCU) used by your load balancer. Shown as unit |
| aws.elb.estimated_albactive_connection_count (count) | The estimated total number of concurrent TCP connections active from clients to the load balancer and from the load balancer to targets. Shown as connection |
| aws.elb.estimated_albconsumed_lcus (gauge) | The estimated total number of load balancer capacity units (LCU) used by an Application Load Balancer. Shown as unit |
| aws.elb.estimated_albnew_connection_count (count) | The estimated total number of new TCP connections established from clients to the load balancer and from the load balancer to targets Shown as connection |
| aws.elb.estimated_processed_bytes (count) | The estimated total number of bytes processed by an Application Load Balancer. Shown as byte |
| aws.elb.healthy_host_count (gauge) | Average number of healthy instances in each Availability Zone. Shown as host |
| aws.elb.healthy_host_count.maximum (gauge) | Maximum number of healthy instances in each Availability Zone. Shown as host |
| aws.elb.healthy_host_count.minimum (gauge) | Minimum number of healthy instances in each Availability Zone. Shown as host |
| aws.elb.healthy_host_count_deduped (gauge) | The number of healthy instances per Availability Zone, regardless of if the Cross-Zone Load Balancing option is enabled or not. Shown as host |
| aws.elb.httpcode_backend_2xx (rate) | Number of HTTP 2XX response codes generated by registered instances. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_backend_3xx (rate) | Number of HTTP 3XX response codes generated by registered instances. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_backend_4xx (rate) | Number of HTTP 4XX response codes generated by registered instances. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_backend_5xx (rate) | Number of HTTP 5XX response codes generated by registered instances. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_elb_4xx (rate) | Number of HTTP 4XX client error codes generated by the load balancer. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_elb_5_0_0 (count) | The number of HTTP 500 error codes that originate from the load balancer. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_elb_5_0_2 (count) | The number of HTTP 502 error codes that originate from the load balancer. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_elb_5_0_3 (count) | The number of HTTP 503 error codes that originate from the load balancer. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_elb_5_0_4 (count) | The number of HTTP 504 error codes that originate from the load balancer. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_elb_5xx (rate) | Number of HTTP 5XX client error codes generated by the load balancer. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_redirect (count) | The number of redirect actions that were successful. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_target_2xx (count) | Number of HTTP 2XX response codes generated by the targets. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_target_3xx (count) | Number of HTTP 3XX response codes generated by the targets. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_target_4xx (count) | Number of HTTP 4XX response codes generated by the targets. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.httpcode_target_5xx (count) | Number of HTTP 5XX response codes generated by the targets. Shown as response |
| aws.elb.ipv_6processed_bytes (count) | The total number of bytes processed by the load balancer over IPv6. Shown as byte |
| aws.elb.ipv_6request_count (count) | The number of IPv6 requests received by the load balancer. Shown as request |
| aws.elb.latency (gauge) | Average time elapsed after the request leaves the load balancer until a response is received. (ELB v1) Shown as second |
| aws.elb.latency.maximum (gauge) | Maximum time elapsed after the request leaves the load balancer until a response is received. (ELB v1) Shown as second |
| aws.elb.latency.minimum (gauge) | Minimum time elapsed after the request leaves the load balancer until a response is received. (ELB v1) Shown as second |
| aws.elb.latency.p95 (gauge) | 95th percentile of the time elapsed after the request leaves the load balancer until a response is received. (ELB v1) Shown as second |
| aws.elb.latency.p99 (gauge) | 99th percentile of the time elapsed after the request leaves the load balancer until a response is received. (ELB v1) Shown as second |
| aws.elb.new_connection_count (count) | The total number of new TCP connections established from clients to the load balancer and from the load balancer to targets. Shown as connection |
| aws.elb.processed_bytes (count) | The total number of bytes processed by the load balancer over IPv4 and IPv6. Shown as byte |
| aws.elb.request_count (rate) | Total number of completed requests that were received and routed to the registered instances. Shown as request |
| aws.elb.request_count_per_target (count) | The average number of requests received by each target in a target group. Shown as request |
| aws.elb.rule_evaluations (count) | The number of rules processed by the load balancer given a request rate averaged over an hour. |
| aws.elb.spillover_count (rate) | Total number of requests that were rejected because the queue was full. Shown as request |
| aws.elb.spillover_count.maximum (rate) | Maximum number of requests that were rejected because the queue was full per load balancer node. Shown as request |
| aws.elb.surge_queue_length (gauge) | Maximum number of requests that are pending submission to a registered instance. Shown as request |
| aws.elb.target_connection_error_count (count) | Number of connections that were not successfully established between the load balancer and the registered instances. Shown as error |
| aws.elb.target_response_time.average (gauge) | Average time elapsed after the request leaves the load balancer until a response is received. Identical to aws.applicationelb.target_response_time.average.Shown as second |
| aws.elb.target_response_time.maximum (gauge) | Maximum time elapsed after the request leaves the load balancer until a response is received. Identical to aws.applicationelb.target_response_time.maximum.Shown as second |
| aws.elb.target_response_time.p95 (gauge) | 95th percentile of the time elapsed after the request leaves the load balancer until a response is received. Identical to aws.applicationelb.target_response_time.p95.Shown as second |
| aws.elb.target_response_time.p99 (gauge) | 99th percentile of the time elapsed after the request leaves the load balancer until a response is received. Identical to aws.applicationelb.target_response_time.p99.Shown as second |
| aws.elb.un_healthy_host_count (gauge) | Average number of unhealthy instances in each Availability Zone. Shown as host |
| aws.elb.un_healthy_host_count.maximum (gauge) | Maximum number of unhealthy instances in each Availability Zone. Shown as host |
| aws.elb.un_healthy_host_count.minimum (gauge) | Minimum number of unhealthy instances in each Availability Zone. Shown as host |
| aws.elb.un_healthy_host_count_deduped (gauge) | The number of unhealthy instances per Availability Zone, regardless of if the Cross-Zone Load Balancing option is enabled or not. Shown as host |
Events
The Amazon Elastic Load Balancing integration does not include any events.
Service Checks
The Amazon Elastic Load Balancing integration does not include any service checks.
Troubleshooting
Need help? Contact Datadog support.