- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Integrations
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- APM Tracing
- Profiler
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic Monitoring
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Test Impact Analysis
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- API
- Datadog Mobile App
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Infrastructure
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Product Analytics
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Optimization
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Connection Issues with the SQL Server Integration
Common SQL Server connection issues
You can configure the Datadog Agent to collect metrics from SQL Server by following the instructions in the SQL Server integration tile in your account. This integration offers several basic SQL Server metrics, which you can expand to your own liking.
But there is a common connection error that users run into while they’re setting up this integration, one that can be especially frustrating to troubleshoot since there are many variables that can cause it. In full, the error looks like this:
'Unable to connect to SQL Server for instance 127.0.0.1,1433 - None. \n Traceback (most recent call last):\n File "C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Datadog\\Datadog Agent\\files\\..\\checks.d\\sqlserver.py", line 219, in get_cursor\n File "adodbapi\\adodbapi.pyc", line 116, in connect\nOperationalError: (com_error(-2147352567, \'Exception occurred.\', (0, u\'Microsoft OLE DB Provider for SQL Server\', u\'[DBNETLIB][ConnectionOpen (Connect()).]SQL Server does not exist or access denied.\', None, 0, -2147467259), None), \'Error opening connection to "Provider=SQLOLEDB;Data Source=127.0.0.1,1433;Initial Catalog=master;User ID=datadog;Password=******;"\')\n'
This error indicates that the Agent was unable to connect to your SQL Server to complete its data collection. This could be caused by any of the following:
- A typo in your SQL Server
conf.yamlhost, port, username, or password (it’s all worth triple-checking) - Your password contains a semicolon (
;)-use curly brackets around the password to resolve (password: "{<PASSWORD>}") - Your SQL Server’s TCP/IP connection has not been enabled
- Your SQL Server’s IPv4 address is incorrect or does not match what you’ve provided in your SQL Server
conf.yaml. - Your SQL Server’s TCP/IP port is incorrect or does not match what you’ve provided in your SQL Server
conf.yaml. - The authentication mode of your SQL Server is not set to the appropriate option between “SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode” vs. “Windows Authentication mode”
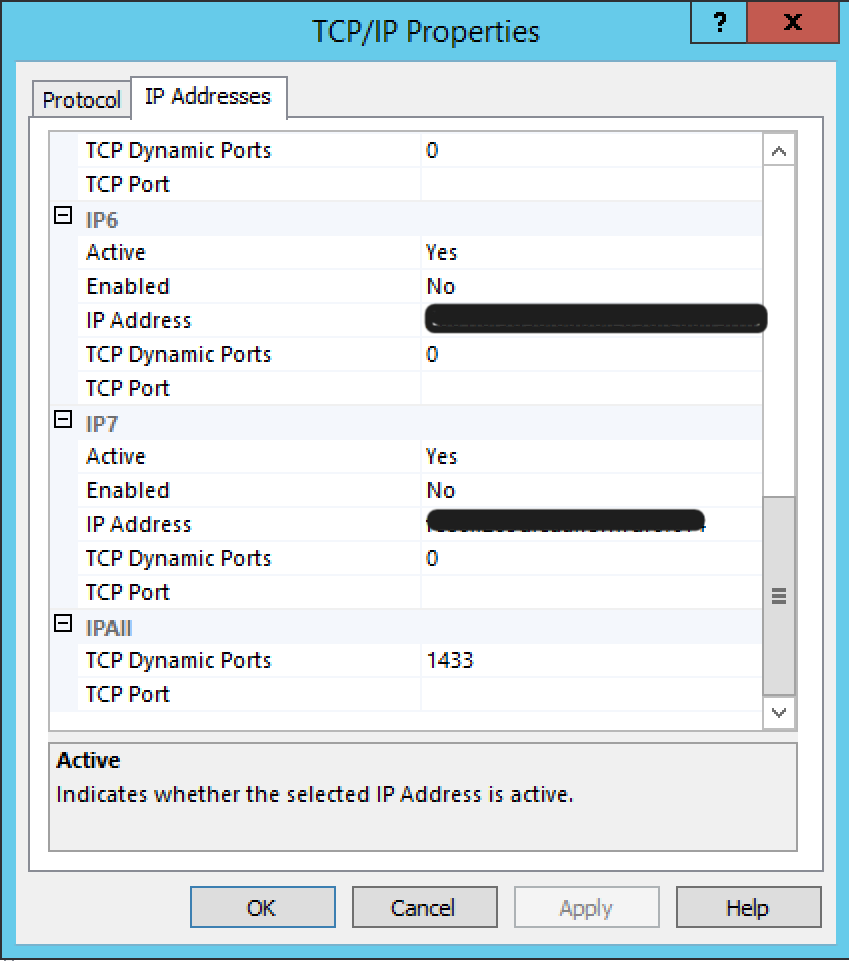
If you are unsure of how to set up a server to listen on the correct TCP/IP address/port, Microsoft’s Configure a Server to Listen on a Specific TCP Port should give you some direction (IPv4 and IPALL are the specifically relevant parts; there, you may set your port either as a “Dynamic” or as a “Static” port, but whichever you aren’t using should be left blank). If the Agent is installed on the same host as your SQL Server, it may be appropriate to set your host option to “127.0.0.1”, even if the host is not a localhost from your perspective as a user. The standard port for connections to SQL Server is 1433.
If you are unsure how to set your SQL Server’s authentication mode, see Microsoft’s Choose an Authentication Mode article.
Note: If you make any of the changes above to SQL Server, you must restart SQL Server before the changes take effect.
Here’s an example of some SQL Server IP/TCP settings that have worked on one of Datadog’s testing environments (Windows 2012 R2, SQL Server 2014 Express):
Empty connection string
Datadog’s SQL Server check relies on the adodbapi Python library, which has some limitations in the characters that it is able to use in making a connection string to a SQL Server. If your Agent experiences trouble connecting to your SQL Server, and if you find errors similar to the following in your Agent’s collector.logs, your sqlserver.yaml probably includes some character that causes issues with adodbapi.
OperationalError: (KeyError('Python string format error in connection string->',), 'Error opening connection to ""')
At the moment, the only character known to cause this specific connectivity issue is the % character. If you want to use the “%” character in your sqlserver.yaml, that is if your Datadog SQL Server user password includes a %), you need to escape that character by including a double %% in place of each single %.
Connecting to SQL Server on a Linux host
To connect SQL Server (either hosted on Linux or Windows) to a Linux host:
Install the Microsoft ODBC Driver for your Linux distribution. If you are unsure of the driver name to use, you can find it enclosed in brackets at the top of
/etc/odbcinst.ini.$ cat /etc/odbcinst.ini [ODBC Driver 13 for SQL Server] Description=Microsoft ODBC Driver 13 for SQL Server Driver=/opt/microsoft/msodbcsql/lib64/libmsodbcsql-13.1.so.7.0 UsageCount=1Copy the
odbc.iniandodbcinst.inifiles into the/opt/datadog-agent/embedded/etcfolder.If needed, install the pyodbc module. This can be done by running pip install pyodbc within your Agent’s python environment. For example:
$ sudo /opt/datadog-agent/embedded/bin/pip install pyodbcConfigure your SQL Server
conf.yamlto use the odbc connector and specify the proper driver as indicated in theodbcinst.inifile.init_config: instances: - host: <HOST>,<PORT> # enable the odbc connector connector: odbc # enable the ODBC driver driver: ODBC Driver 13 for SQL Server username: <USERNAME> password: <PASSWORD>